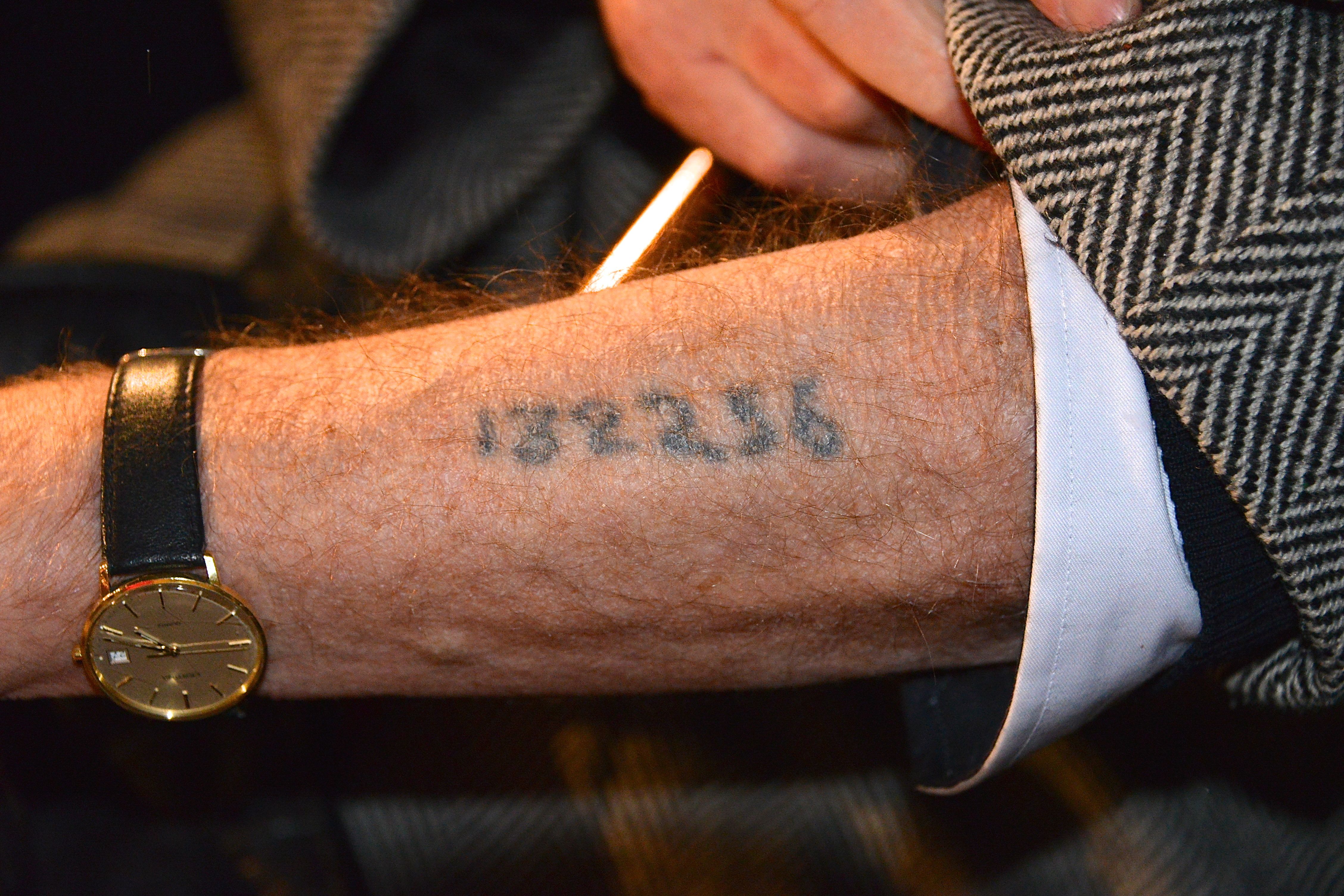|
Denise Holstein
Denise Holstein (6 February 1927 in Rouen) is an Auschwitz concentration camp survivor and Holocaust witness, who was liberated on 15 April 1945. As a Holocaust witness, Holstein tells her story in two books and in a documentary made by a student from the Lycée Corneille in Rouen. For almost fifty years, Holstein never spoke about her life before writing about it. As a Holocaust witness, Holstein visits school children, to describe and share her experiences. Life Holstein was born in Rouen into a wealthy and refined Jewish family. Her father, Bernard Holstein, who born in Kaunas in the Russian Empire (now Lithuania) on 20 August 1890 and was a dental surgeon. Bernard Holstein fought in two wars and was a reserve officer. Her mother, Juliette Holstein née Cohen was born on 16 October 1902 in Paris. She had a brother Jean who was born 26 July 1924. She studied at the Lycée Corneille and the Lycée Jeanne-d'Arc. Occupied France In 1939, as a reserve officer, Bernard Holstein was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rouen
Rouen (, ; or ) is a city on the River Seine in northern France. It is the prefecture of the Regions of France, region of Normandy (administrative region), Normandy and the Departments of France, department of Seine-Maritime. Formerly one of the largest and most prosperous cities of Middle Ages, medieval Europe, the population of the metropolitan area (french: functional area (France), aire d'attraction) is 702,945 (2018). People from Rouen are known as ''Rouennais''. Rouen was the seat of the Exchequer of Normandy during the Middle Ages. It was one of the capitals of the Anglo-Normans, Anglo-Norman dynasties, which ruled both England and large parts of modern France from the 11th to the 15th centuries. From the 13th century onwards, the city experienced a remarkable economic boom, thanks in particular to the development of textile factories and river trade. Claimed by both the French and the English during the Hundred Years' War, it was on its soil that Joan of Arc was tried ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Union Générale Des Israélites De France
The (General Union of French Jews; UGIF) was a body created by the antisemitic French politician Xavier Vallat under the Vichy regime after the Fall of France in World War II. UGIF was created by decree on 29 November 1941 following a German request, for the express purpose of enabling the discovery and classification of Jews in France and isolating them both morally and materially from the rest of the French population. It operated in two zones: the northern zone, chaired by , and the southern zone, under the chairmanship of . The mission of the UGIF was to represent Jews before the public authorities, particularly in matters of assistance, welfare and social reintegration. All other Jewish associations in France were dissolved and their assets donated to the UGIF, which all Jews living in France were required to join. The administrators of this body mostly belonged to the French-Jewish bourgeoisie, and were appointed by the Commissariat-General for Jewish Affairs (CGQ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nazi Hunter
A Nazi hunter is an individual who tracks down and gathers information on alleged former Nazis, or SS members, and Nazi collaborators who were involved in the Holocaust, typically for use at trial on charges of war crimes and crimes against humanity. Prominent Nazi hunters include Simon Wiesenthal, Tuviah Friedman, Serge Klarsfeld, Beate Klarsfeld, Ian Sayer, Yaron Svoray, Elliot Welles, and Efraim Zuroff. History With the onset of the Cold War following World War II, both the Western Allies and the USSR sought out former Nazi scientists and operatives for programs such as Operation Paperclip. Cooperative former Nazis, such as Wernher von Braun and Reinhard Gehlen, were occasionally given state protection in return for valuable information or services. At the time, Gehlen had been chief of the German Federal Intelligence Service or ''Bundesnachrichtendienst'' (federal intelligence agency), founder of the Gehlen Org, "a true life version of ODESSA" network, which helped exfiltr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Necker–Enfants Malades Hospital
The Necker–Enfants Malades Hospital ( ) is a French teaching hospital in the 15th arrondissement of Paris. It is a hospital of the Assistance Publique – Hôpitaux de Paris group and is affiliated to the Université Paris Cité. Necker–Enfants Malades Hospital was created in 1920 by the merger of Necker Hospital (), which was founded in 1778 by Suzanne Necker, with the physically contiguous Sick Children's Hospital (), the oldest children's hospital in the Western world, founded in 1801. History The ''Hôpital Necker'' was founded in 1778 by Madame Necker, born Suzanne Curchod, mother of Madame de Stael and wife of Jacques Necker, minister of Louis XVI. Jacques Necker was a leader in the movement to reform crowded hospitals by building smaller treatment centers closer to the patients' neighborhoods. Madame Necker subsequently remodeled an old monastery into the hospital, which prior to the French Revolution was known as the Hospice de Charité. It was a Catholic institu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quarantine
A quarantine is a restriction on the movement of people, animals and goods which is intended to prevent the spread of disease or pests. It is often used in connection to disease and illness, preventing the movement of those who may have been exposed to a communicable disease, yet do not have a confirmed medical diagnosis. It is distinct from medical isolation, in which those confirmed to be infected with a communicable disease are isolated from the healthy population. Quarantine considerations are often one aspect of border control. The concept of quarantine has been known since biblical times, and is known to have been practised through history in various places. Notable quarantines in modern history include the village of Eyam in 1665 during the bubonic plague outbreak in England; East Samoa during the 1918 flu pandemic; the Diphtheria outbreak during the 1925 serum run to Nome, the 1972 Yugoslav smallpox outbreak, the SARS pandemic, the Ebola pandemic and extensive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Typhus
Typhus, also known as typhus fever, is a group of infectious diseases that include epidemic typhus, scrub typhus, and murine typhus. Common symptoms include fever, headache, and a rash. Typically these begin one to two weeks after exposure. The diseases are caused by specific types of bacterial infection. Epidemic typhus is due to ''Rickettsia prowazekii'' spread by body lice, scrub typhus is due to ''Orientia tsutsugamushi'' spread by chiggers, and murine typhus is due to ''Rickettsia typhi'' spread by fleas. Vaccines have been developed, but none are commercially available. Prevention is achieved by reducing exposure to the organisms that spread the disease. Treatment is with the antibiotic doxycycline. Epidemic typhus generally occurs in outbreaks when poor sanitary conditions and crowding are present. While once common, it is now rare. Scrub typhus occurs in Southeast Asia, Japan, and northern Australia. Murine typhus occurs in tropical and subtropical areas of the worl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Josef Mengele
, allegiance = , branch = Schutzstaffel , serviceyears = 1938–1945 , rank = ''Schutzstaffel, SS''-''Hauptsturmführer'' (Captain) , servicenumber = , battles = , unit = , awards = , commands = , spouse = , children = Rolf Mengele , alma_mater = Josef Rudolf Mengele (; 16 March 19117 February 1979), also known as the Angel of Death (german: Todesengel), was a German (SS) officer and physician during World War II. He is mainly remembered for his actions at the Auschwitz II (Birkenau) concentration camp, where he performed Nazi human experimentation, deadly experiments on prisoners, was a member of the team of doctors who selected victims to be The Holocaust, killed in the gas chambers, and was one of the doctors who administered the gas. With Red Army troops sweeping through German-occupied Poland, Mengele was transferred from Auschwitz to the Gross-Rosen concentration camp on 17 January 1945, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Revier (Nazi Concentration Camps)
Revier was a term used in Nazi camps to designate the medical facility for inmates. It was abbreviated from the German word (infirmary). The Reviers were managed by Capos who most often did not have medical training. The conditions in reviers varied drastically, in most camps, a trip to the Revier was virtually a death sentence. Extermination camps In extermination camps (as well as in many labor camps, where extermination through labor was practiced) the name revier was immediately associated with death in many respects. Death was to be expected immediately upon entrance to a revier: An "insufficiently" sick person could be classified as malingerer, who was avoiding labor. The penalty was death. Even being admitted into the revier gave little hope: while the medical personnel (inmates) could be highly qualified doctors, they could not offer any help beyond very basic first aid. For example, the supply of medicine was very limited. In addition, rations for the sick were lower ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scarlet Fever
Scarlet fever, also known as Scarlatina, is an infectious disease caused by ''Streptococcus pyogenes'' a Group A streptococcus (GAS). The infection is a type of Group A streptococcal infection (Group A strep). It most commonly affects children between five and 15 years of age. The signs and symptoms include a sore throat, fever, headache, swollen lymph nodes, and a characteristic rash. The face is flushed and the rash is red and blanching. It typically feels like sandpaper and the tongue may be red and bumpy. The rash occurs as a result of capillary damage by exotoxins produced by ''S.pyogenes''. On darker pigmented skin the rash may be hard to discern. Scarlet fever affects a small number of people who have strep throat or streptococcal skin infections. The bacteria are usually spread by people coughing or sneezing. It can also be spread when a person touches an object that has the bacteria on it and then touches their mouth or nose. The diagnosis is typically confirmed by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Appellplatz
Appellplatz (often spelt ''appelplatz'') is a compound German word meaning "roll call" (''Appell'') and "area" or "place" (''Platz''). In English, the word is generally used to describe the location for the daily roll calls in Nazi concentration camps. Concentration camp usage Roll calls were a key component of the daily regimen in Nazi concentration camps, carried out to count the prisoners but also to inspect, humiliate, weaken and intimidate them. All prisoners were made to line up in rows and be counted very early in the morning and again at night. Even the bodies of those who had died since the previous roll call had to be brought to the Appellplatz to be counted. Roll calls were held year round no matter the weather, be it driving snow, pouring rain or extreme temperatures. Prisoners were made to stand at attention the entire time it took to count thousands of prisoners, which had to be done more than once if a mistake were made. Some prisoners died during or shortly af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Identification Of Inmates In German Concentration Camps
Identification of inmates in German concentration camps was performed mostly with identification numbers marked on clothing, or later, tattooed on the skin. More specialized identification in Nazi concentration camps was done with badges on clothing and armbands. Numbers A practice was established to tattoo the inmates with identification numbers. Prisoners sent straight to gas chambers didn't receive anything. Initially, in Auschwitz, the camp numbers were sewn on the clothes; with the increased death rate, it became difficult to identify corpses, since clothes were removed from corpses. Therefore, the medical personnel started to write the numbers on the corpses' chests with indelible ink. Difficulties increased in 1941 when Soviet prisoners of war came in masses, and the first few thousand tattoos were applied to them. This was done with a special stamp with the numbers to be tattooed composed of needles. The tattoo was applied to the upper left part of the breast. In March 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forced Labour
Forced labour, or unfree labour, is any work relation, especially in modern or early modern history, in which people are employed against their will with the threat of destitution, detention, violence including death, or other forms of extreme hardship to either themselves or members of their families. Unfree labour includes all forms of slavery, penal labour and the corresponding institutions, such as debt slavery, serfdom, corvée and labour camps. Definition Many forms of unfree labour are also covered by the term forced labour, which is defined by the International Labour Organization (ILO) as all involuntary work or service exacted under the menace of a penalty. However, under the ILO Forced Labour Convention of 1930, the term forced or compulsory labour does not include: *"any work or service exacted in virtue of compulsory military service laws for work of a purely military character;" *"any work or service which forms part of the normal civic obligations of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)