|
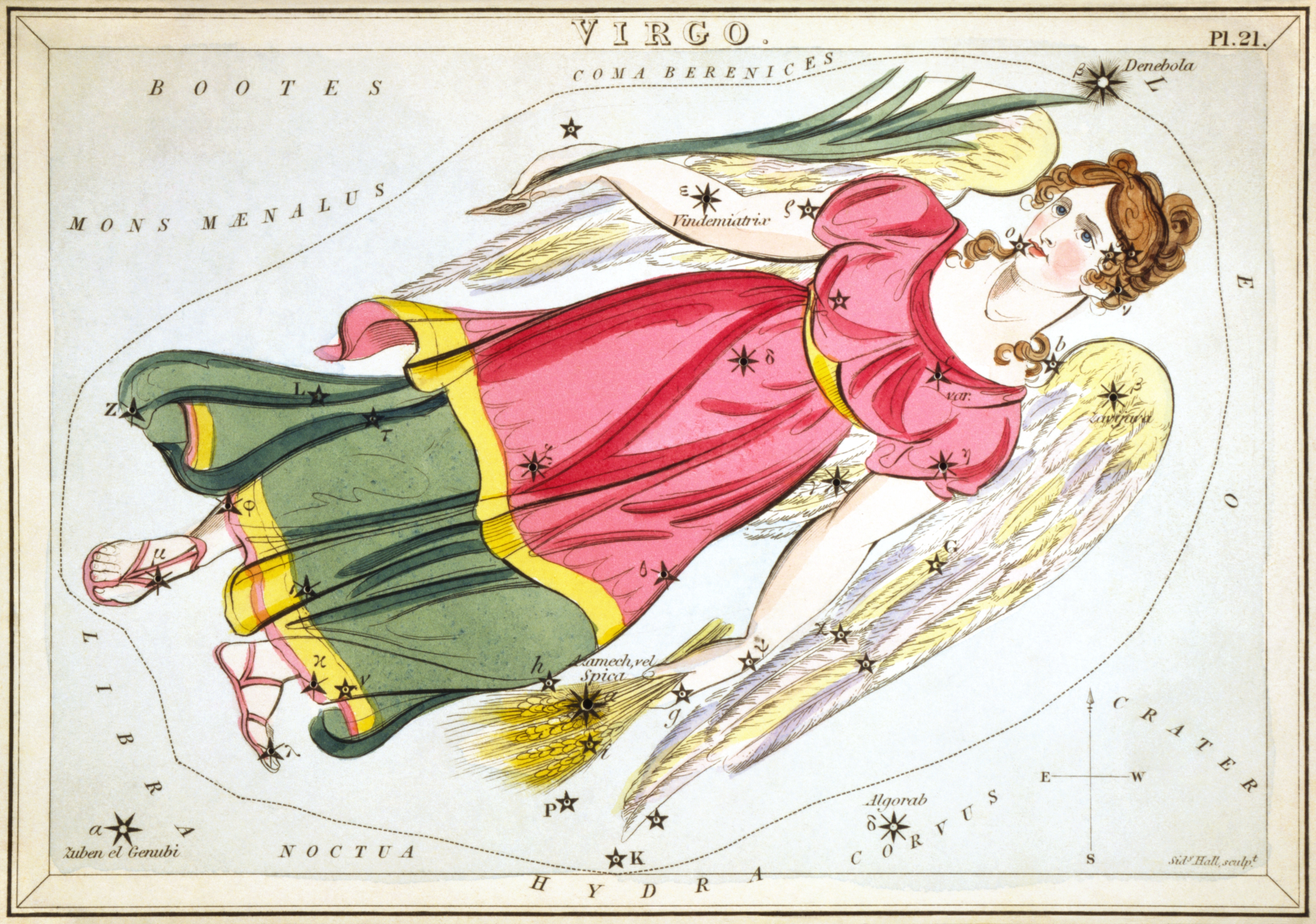
Delta Virginis
Delta Virginis (δ Virginis, abbreviated Del Vir, δ Vir), formally named Minelauva , is a star in the zodiac constellation of Virgo (constellation), Virgo. With an apparent visual magnitude of 3.4, this star is bright enough to be seen with the naked eye. Based upon stellar parallax, parallax measurements, it is located at a distance of about from the Sun. Nomenclature ''δ Virginis'' (Latinisation of names, Latinised to ''Delta Virginis'') is the star's Bayer designation. It bore the traditional, medieval names ''Auva'' and ''Minelauva'' from the Arabic من العواء ''min al-ʽawwāʼ'', meaning "in the lunar mansion of ''ʽawwaʼ''" (a name of unknown meaning). In 2016, the IAU organized a IAU Working Group on Star Names, Working Group on Star Names (WGSN) to catalog and standardize proper names for stars. The WGSN approved the name ''Minelauva'' for this star on 30 June 2017 and it is now so included in the List of IAU-approved Star Names. This star, along wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virgo (constellation)
Virgo is one of the constellations of the zodiac. Its name is Latin for maiden, and its old astronomical symbol is (♍︎). Lying between Leo (constellation), Leo to the west and Libra (constellation), Libra to the east, it is the second-largest constellation in the sky (after Hydra (constellation), Hydra) and the largest constellation in the zodiac. The ecliptic intersects the celestial equator within this constellation and Pisces (constellation), Pisces. Underlying these technical two definitions, the sun passes directly overhead of the equator, within this constellation, at the September equinox. Virgo can be easily found through its brightest star, Spica. Location Virgo is prominent in the spring sky in the Northern Hemisphere, visible all night in March and April. As the largest zodiac constellation, the Sun takes 44 days to pass through it, longer than any other. From 1990 and until 2062, this will take place from September 16 to October 30. It is located in the third ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latinisation Of Names
Latinisation (or Latinization) of names, also known as onomastic Latinisation, is the practice of rendering a ''non''-Latin name in a Latin style. It is commonly found with historical proper names, including personal names and toponyms, and in the standard binomial nomenclature of the life sciences. It goes further than romanisation, which is the transliteration of a word to the Latin alphabet from another script (e.g. Cyrillic). For authors writing in Latin, this change allows the name to function grammatically in a sentence through declension. In a scientific context, the main purpose of Latinisation may be to produce a name which is internationally consistent. Latinisation may be carried out by: * transforming the name into Latin sounds (e.g. for ), or * adding Latinate suffixes to the end of a name (e.g. for '' Meibom),'' or * translating a name with a specific meaning into Latin (e.g. for Italian ; both mean 'hunter'), or * choosing a new name based on some attribut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha Comae Berenices
Alpha Comae Berenices (α Comae Berenices, abbreviated Alpha Com, α Com) is a binary star in the constellation of Coma Berenices (Berenice's Hair), away. It consists of two main sequence stars, each a little hotter and more luminous than the Sun. Alpha Comae Berenices is said to represent the crown worn by Queen Berenice. The two components are designated Alpha Comae Berenices A (officially named Diadem , the traditional name for the system) and B. Nomenclature ''α Comae Berenices'' ( Latinised to ''Alpha Comae Berenices'') is the system's Bayer designation. The designations of the two components as ''Alpha Comae Berenices A'' and ''B'' derive from the convention used by the Washington Multiplicity Catalog (WMC) for multiple star systems, and adopted by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). The system bore the traditional names ''Diadem'' and ''Al Dafirah,'' the latter derived from the Arabic الضفيرة ''ađ̧-đ̧afīrah'' "the braid". In 2016, the I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asterism (astronomy)
An asterism is an observed pattern or group of stars in the sky. Asterisms can be any identified pattern or group of stars, and therefore are a more general concept than the formally defined 88 constellations. Constellations are based on asterisms, but unlike asterisms, constellations outline and today completely divide the sky and all its celestial objects into regions around their central asterisms. For example, the asterism known as the Big Dipper comprises the seven brightest stars in the constellation Ursa Major. Another is the asterism of the Southern Cross, within the constellation of Crux. Asterisms range from simple shapes of just a few stars to more complex collections of many stars covering large portions of the sky. The stars themselves may be bright naked-eye objects or fainter, even telescopic, but they are generally all of a similar brightness to each other. The larger brighter asterisms are useful for people who are familiarizing themselves with the night sky. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supreme Palace Enclosure
Tai Wei Yuan, the Supreme Palace Enclosure (太微垣), is one of the San Yuan or Three enclosures Traditional Chinese astronomy has a system of dividing the celestial sphere into asterisms or constellations, known as "officials" ( Chinese ''xīng guān''). The Chinese asterisms are generally smaller than the constellations of Hellenistic .... Stars and constellations of this group are visible during spring in the Northern Hemisphere (autumn in the Southern). Asterisms The asterisms are : Map See also * Twenty-eight mansions Chinese constellations {{china-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Astronomy
Astronomy in China has a long history stretching from the Shang dynasty, being refined over a period of more than 3,000 years. The ancient Chinese people have identified stars from 1300 BCE, as Chinese star names later categorized in the twenty-eight mansions have been found on oracle bones unearthed at Anyang, dating back to the mid-Shang dynasty. The core of the "mansion" (宿 ''xiù'') system also took shape around this period, by the time of King Wu Ding (1250–1192 BCE). Detailed records of astronomical observations began during the Warring States period (fourth century BCE) and flourished from the Han period onward. Chinese astronomy was equatorial, centered on close observation of circumpolar stars, and was based on different principles from those in traditional Western astronomy, where heliacal risings and settings of zodiac constellations formed the basic ecliptic framework. Joseph Needham has described the ancient Chinese as the most persistent and accurate obser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epsilon Virginis
Epsilon Virginis (ε Virginis, abbreviated Epsilon Vir, ε Vir), formally named Vindemiatrix , is a star in the zodiac constellation of Virgo. The apparent visual magnitude of this star is +2.8, making it the third-brightest member of Virgo. Based upon parallax measurements made during the Hipparcos mission, Vindemiatrix lies at a distance of about from the Sun, give or take a half light-year. Stellar properties Vindemiatrix is a giant star with a stellar classification of G8 III. With 2.6 times the mass of the Sun, it has reached a stage in its evolution where the hydrogen fuel in its core is exhausted. As a result, it has expanded to over ten times the Sun's girth and is now radiating around 77 times as much luminosity as the Sun. This energy is being emitted from its outer atmosphere at an effective temperature of 5,086 K, which gives it the yellow-hued glow of a G-type star. Since 1943, the spectrum of this star has served as one of the stable anchor poin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eta Virginis
Eta Virginis (η Virginis, abbreviated Eta Vir, η Vir) is a triple star system in the zodiac constellation of Virgo. From parallax measurements taken during the Hipparcos mission it is about from the Sun. It has a combined apparent visual magnitude of 3.89, bright enough to be seen with the naked eye in dark skies. The system consists of a binary pair designated Eta Virginis A together with a third companion, Eta Virginis B. A's two components are themselves designated Eta Virginis Aa (officially named Zaniah , the traditional name of the system) and Ab. Nomenclature ''η Virginis'' ( Latinised to ''Eta Virginis'') is the system's Bayer designation. The designations of the two constituents as ''Eta Virginis A'' and those of ''A's''components - ''Eta Virginis Aa'' and ''Ab'' - derive from the convention used by the Washington Multiplicity Catalog (WMC) for multiple star systems, and adopted by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It bore the traditional name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamma Virginis
Gamma Virginis (γ Virginis, abbreviated Gamma Vir, γ Vir), officially named Porrima , is a binary star system in the constellation of Virgo. It consists of two almost identical main sequence stars at a distance of about 38 light-years. Name ''γ Virginis'' ( Latinised to ''Gamma Virginis'') is the star's Bayer designation. The traditional name ''Porrima'' derives from Ancient Rome: Porrima, also known as Antevorta, was one of the Camenae or goddesses of prophecy. In 2016, the International Astronomical Union organized a Working Group on Star Names (WGSN) to catalog and standardize proper names for stars. The WGSN's first bulletin of July 2016 included a table of the first two batches of names approved by the WGSN; which included ''Porrima'' for this star. In the catalogue of stars in the ''Calendarium of Al Achsasi Al Mouakket'', this star was designated ''Laouiyet al Aoua'', which was translated into Latin as ''Angulus Latratoris'', meaning 'the angle of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta Virginis
Beta Virginis, a name Latinised from β Virginis, is a star in the equatorial constellation of Virgo. It has the proper name Zavijava (), and, despite its designation ' beta', is the fifth-brightest star in Virgo with an apparent visual magnitude of 3.604. The distance to this star is 35.7 light-years based on parallax, and it is drifting further away with a radial velocity of +4.1 km/s. It is 0.69 of a degree north of the ecliptic, so it can be occulted by the Moon and (rarely) by planets. The next planetary occultation of Beta Virginis will take place on 11 August 2069, by Venus. Properties This is an F-type main-sequence star with a stellar classification of F9 V, which means it is generating energy through core hydrogen fusion. Sun-like oscillations have been detected in Beta Virginis, allowing its internal structure to be modeled in more detail. It is around 2.9 billion years old with a projected rotational velocity of 4.3 km/s and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IAU Working Group On Star Names
The International Astronomical Union (IAU) established a Working Group on Star Names (WGSN) in May 2016 to catalog and standardize proper names for stars for the international astronomical community. It operates under Division C – Education, Outreach and Heritage. The IAU states that it is keen to make a distinction between the terms ''name'' and ''designation''. To the IAU, ''name'' refers to the (usually colloquial) term used for a star in everyday conversation, while ''designation'' is solely alphanumerical, and used almost exclusively in official catalogues and for professional astronomy. (The WGSN notes that transliterated Bayer designations (e.g., Tau Ceti) are considered a special historical case and are treated as designations.) Terms of reference The terms of reference for the WGSN for the period 2016–2018 were approved by the IAU Executive Committee at its meeting on 6 May 2016. In summary, these are to: * establish IAU guidelines for the proposal and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lunar Mansion
Often called lunar mansion, a lunar station or lunar house is a segment of the ecliptic through which the Moon passes in its orbit around the Earth. The concept was used by several ancient cultures as part of their calendrical system. Stations in different cultures In general, though not always, the zodiac is divided into 27 or 28 segments relative to the vernal equinox point or the fixed stars – one for each day of the lunar month. (A sidereal month lasts about days.) The Moon's position is charted with respect to those fixed segments. Since the Moon's position at any given stage will vary according to Earth's position in its own orbit, lunar stations are an effective system for keeping track of the passage of seasons. Various cultures have used sets of lunar stations astrologically; for example, the Jyotisha astrological ''nakshatras'' of Hindu culture, the Arabic manzils (''manazil al-qamar''), the Twenty-Eight Mansions of Chinese astronomy, and the 36 ''d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |