|
Delal
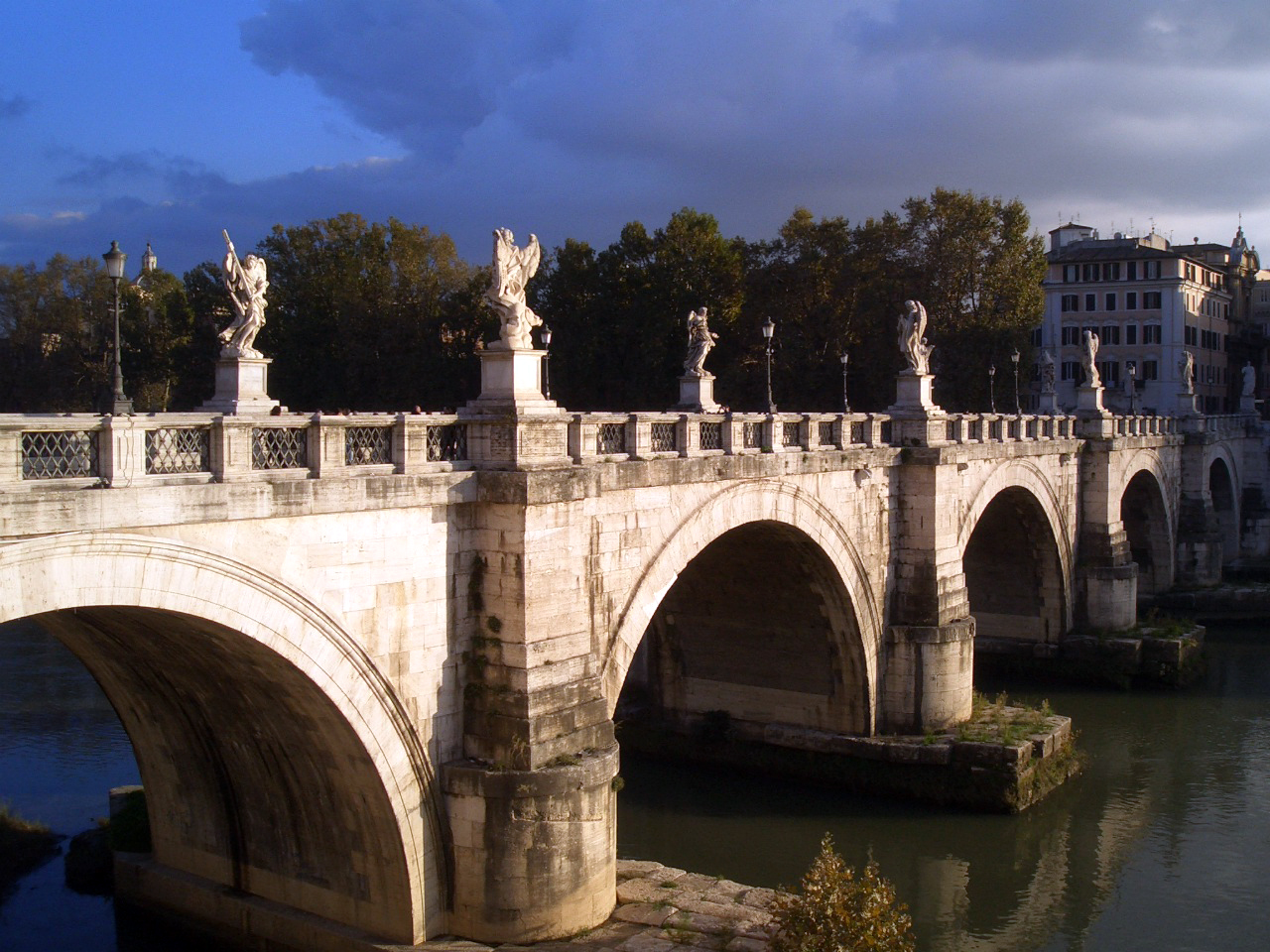
Delal, Zakho Bridge, Pira Delal or Pirdí Delal ("The Bridge Delal" in Kurdish), informally known also as ''Pira Berî,'' is an ancient stone bridge over the Khabur river in the town of Zakho, in the Kurdistan Region of Iraq. The bridge is about 115 metres long and 16 metres high. Etymology The term ''pir'' means "bridge" and ''delal'' means "dear or beautiful" in Kurdish, "Pira Delal" means "beautiful bridge" (though not in an aesthetic sense, but more of something that's unique). The name reflects the way the bridge is seen among the local people as well as tourists. The bridge was named Delal and the city of Zakho is called Zakhoka Delal (Delal's Zakho) in the honor of Delal, a heroine figure associated with a myth regarding the origins of the bridge (see below). History Pira Delal is believed to have been first built during the Roman era, while the present structure appears to be from the Abbasic era. Kurdish people all over Kurdistan visit Pira Delal as a monument of peace ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zakho
Zakho, also spelled Zaxo ( ku, زاخۆ, Zaxo, syr, ܙܵܟ݂ܘܿ, Zākhō, , ) is a city in the Kurdistan Region of Iraq, at the centre of the eponymous Zakho District of the Dohuk Governorate, located a few kilometers from the Iraq–Turkey border. The population of the town rose from about 30,000 in 1950 to 350,000 to 1992 due to Kurds fleeing other areas of the country. The original settlement may have been on a small island in the Little Khabur river, which flows through the modern city. The Khabur flows west from Zakho to form the border between Iraq and Turkey, continuing into the Tigris. The most important rivers in the area are the Zeriza, Seerkotik and the aforementioned Little Khabur. History Gertrude Bell, the renowned British archaeologist and Arabist who advised British governors in the region in the closing years of the British Mandate, was convinced that Zakho was the same place as the ancient town of Hasaniyeh. She also reported that one of the first Christia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khabur (Tigris)
The Khabur or Little Khabur ( ku, Xabûr, ''Ava Xabûr'' or ''Xabîr'', tr, Habur, ''Khabir'' or ''Habur Suyu'' (''Habur Water'')) is a river that rises in Turkey and flows through Iraq to join the Tigris at the tripoint of Turkey, Iraq and Syria. The river originates in the Uludere District in Turkey and emerges from a number of small rivers flowing off the Taurus Mountains, to the south-east of Hakkâri. From there, it generally flows south, crossing the Turkish-Iraqi border into Iraqi Kurdistan before turning west toward the Tigris. Zakho is an important town along the river, where the ancient Delal Bridge crosses the river. A few kilometres west of Zakho, the Little Khabur is joined by its main tributary the Hezil Suyu (or Nizil river or Hezil Çayı), which forms part of the border between Iraq and Turkey. From there onward the Little Khabur river forms the border for around 20 km to the Tigris and is also called (and often mistaken with) the Hezil Suyu. See also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Roman Bridges
This is a list of Roman bridges. The Romans were the world's first major bridge builders. The following list constitutes an attempt to list all known surviving remains of Roman bridges. A Roman bridge in the sense of this article includes any of these features: *Roman arches *Roman pillars *Roman foundations *Roman abutments *Roman roadway *Roman cutwaters Also listed are bridges which feature substantially Roman material (spolia), as long as the later bridge is erected on the site of a Roman precursor. Finally, incidences where only inscriptions lay testimony to a former Roman bridge are also included. In the following, bridges are classified either according to their material or their function. Most data not otherwise marked come from O’Connor's ''Roman Bridges'', which lists 330 stone bridges for traffic, 34 timber bridges and 54 aqueduct bridges. An even larger compilation of more than 900 Roman bridges (as of 2011) is offered by the Italian scholar Galliazzo, who is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bounty (reward)
A bounty is a payment or reward of money to locate, capture or kill an outlaw or a wanted person. Two modern examples of bounties are the ones placed for the capture of Saddam Hussein and his sons by the United States government and Microsoft's bounty for computer virus creators. Those who make a living by pursuing bounties are known as bounty hunters. Examples Historical examples Written promises of reward for the capture of or information regarding criminals go back to at least the first-century Roman Empire. Graffiti from Pompeii, a Roman city destroyed by a volcanic eruption in 79 AD, contained this message: A copper pot went missing from my shop. Anyone who returns it to me will be given 65 bronze coins ( ''sestertii''). Twenty more will be given for information leading to the capture of the thief. A bounty system was used in the American Civil War as an incentive to increase enlistments. Another bounty system was used in New South Wales to increase the number of immigran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bridges In Iraq
A bridge is a structure built to span a physical obstacle (such as a body of water, valley, road, or rail) without blocking the way underneath. It is constructed for the purpose of providing passage over the obstacle, which is usually something that is otherwise difficult or impossible to cross. There are many different designs of bridges, each serving a particular purpose and applicable to different situations. Designs of bridges vary depending on factors such as the function of the bridge, the nature of the terrain where the bridge is constructed and anchored, and the material used to make it, and the funds available to build it. The earliest bridges were likely made with fallen trees and stepping stones. The Neolithic people built boardwalk bridges across marshland. The Arkadiko Bridge (dating from the 13th century BC, in the Peloponnese) is one of the oldest arch bridges still in existence and use. Etymology The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' traces the origin of the wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
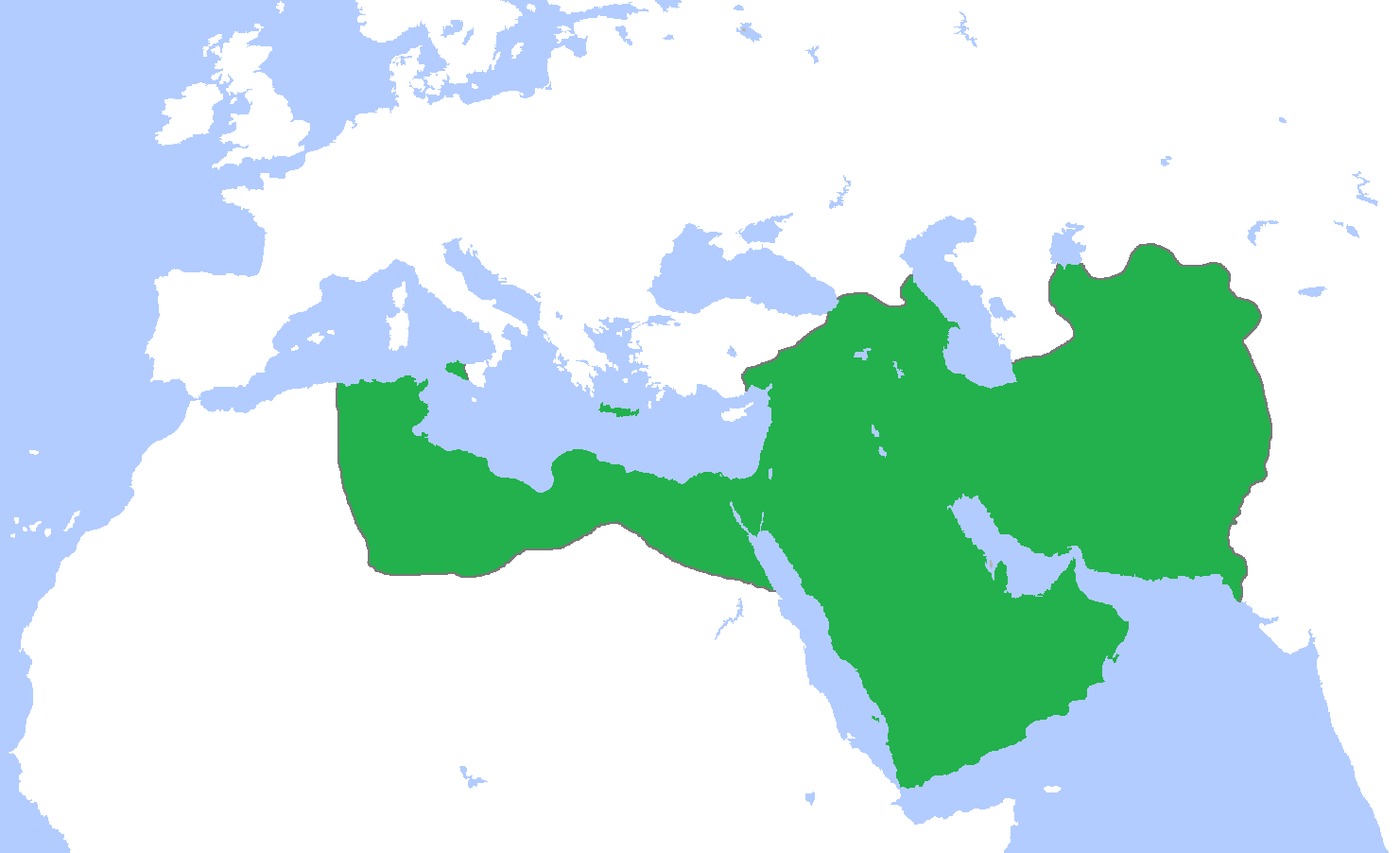
Abbasid Architecture
Abbasid architecture developed in the Abbasid Caliphate between 750 and 1227, primarily in its heartland of Mesopotamia (modern Iraq). The great changes of the Abbasid era can be characterized as at the same time political, geo-political and cultural. The Abbasid period starts with the destruction of the Umayyad ruling family and its replacement by the Abbasids, and the position of power is shifted to the Mesopotamian area, and as a result in a corresponding displacement of the influence of classical and Byzantine artistic and cultural standards in favor of local Mesopotamian models as well as Persian. The Abbasids evolved distinctive styles of their own, particularly in decoration of their buildings. They favoured mud brick and baked brick for construction, allowing for enormous architectural complexes to be built at relatively low cost, as most clearly exemplified by Samarra, a 9th-century capital city made up of vast palaces and monumental mosques spread across some . The arch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hair Braids
A braid (also referred to as a plait) is a complex structure or pattern formed by interlacing two or more strands of flexible material such as textile yarns, wire, or hair. The simplest and most common version is a flat, solid, three-stranded structure. More complex patterns can be constructed from an arbitrary number of strands to create a wider range of structures (such as a fishtail braid, a five-stranded braid, rope braid, a French braid and a waterfall braid). The structure is usually long and narrow with each component strand functionally equivalent in zigzagging forward through the overlapping mass of the others. It can be compared with the process of weaving, which usually involves two separate perpendicular groups of strands (warp and weft). Historically, the materials used have depended on the indigenous plants and animals available in the local area. During the Industrial Revolution, mechanized braiding equipment was invented to increase production. The braiding te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pick Axe
A pickaxe, pick-axe, or pick is a generally T-shaped hand tool used for Leverage (mechanics), prying. Its head is typically metal, attached perpendicularly to a longer handle, traditionally made of wood, occasionally metal, and increasingly fiberglass. A standard pickaxe, similar to a "mattock, pick mattock", has a pointed end on one side of its head and a broad flat "axe" blade opposite. A gradual curve characteristically spans the length of the head. The next most common configuration features two spikes, one slightly longer than the other. The pointed end is used both for breaking and prying, the axe for hoeing, skimming, and chopping through roots. Developed as agricultural tools in prehistoric times, picks have evolved into other tools such as the plough and the mattock. They also have been used in general construction and traditional mining, mining, and adapted to warfare. Etymology The Oxford Dictionary of English states that both "pick" and "pickaxe" have the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
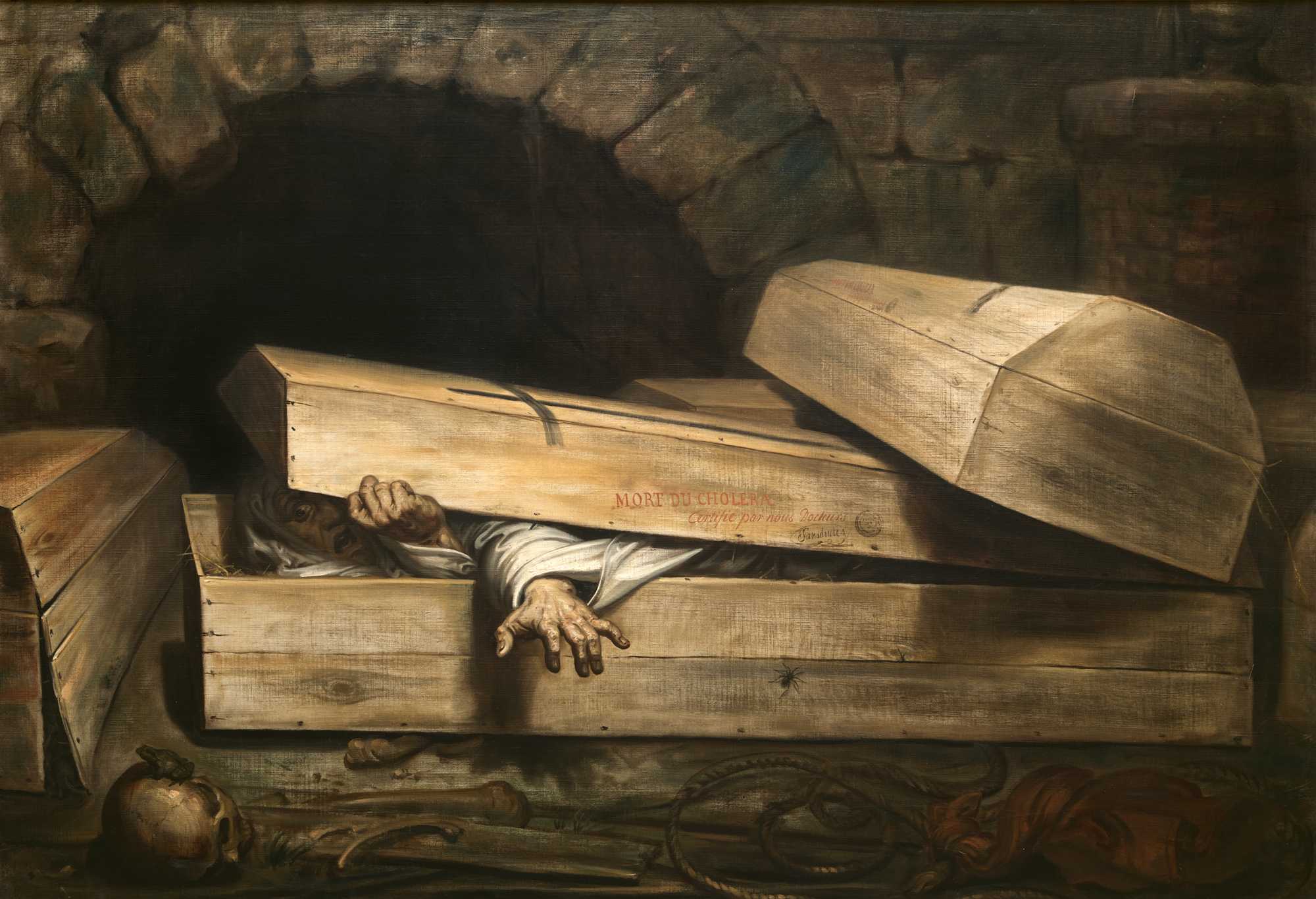
Buried Alive
Premature burial, also known as live burial, burial alive, or vivisepulture, means to be buried while still alive. Animals or humans may be buried alive accidentally on the mistaken assumption that they are dead, or intentionally as a form of torture, murder, or execution. It may also occur with the consent of the victim as a part of a stunt, with the intention to escape. Fear of being buried alive is reported to be among the most common phobias. Physiology Premature burial can lead to death through the following: asphyxiation, dehydration, starvation, or (in cold climates) hypothermia. A person trapped with fresh air to breathe can last a considerable time and burial has been used as a very cruel method of execution (as in cases of Vestal Virgins who violated the oath of celibacy), lasting sufficiently long for the victim to comprehend and imagine every stage of what is happening (being trapped in total darkness with very limited or no movement) and to experience great ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fainting
Syncope, commonly known as fainting, or passing out, is a loss of consciousness and muscle strength characterized by a fast onset, short duration, and spontaneous recovery. It is caused by a decrease in blood flow to the brain, typically from low blood pressure. There are sometimes symptoms before the loss of consciousness such as lightheadedness, sweating, pale skin Pallor is a pale color of the skin that can be caused by illness, emotional shock or stress, stimulant use, or anemia, and is the result of a reduced amount of oxyhaemoglobin and may also be visible as pallor of the conjunctivae of the eyes o ..., blurred vision, nausea, vomiting, or feeling warm. Syncope may also be associated with a short episode of muscle twitching. Psychiatric causes can also be determined when a patient experiences fear, anxiety, or panic; particularly before a stressful event usually medical in nature. When consciousness and muscle strength are not completely lost, it is called presy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sacrifice
Sacrifice is the offering of material possessions or the lives of animals or humans to a deity as an act of propitiation or worship. Evidence of ritual animal sacrifice has been seen at least since ancient Hebrews and Greeks, and possibly existed before that. Evidence of ritual human sacrifice can also be found back to at least pre-Columbian civilizations of Mesoamerica as well as in European civilizations. Varieties of ritual non-human sacrifices are practiced by numerous religions today. Terminology The Latin term ''sacrificium'' (a sacrifice) derived from Latin ''sacrificus'' (performing priestly functions or sacrifices), which combined the concepts ''sacra'' (sacred things) and ''facere'' (to do or perform). The Latin word ''sacrificium'' came to apply to the Christian eucharist in particular, sometimes named a "bloodless sacrifice" to distinguish it from blood sacrifices. In individual non-Christian ethnic religions, terms translated as "sacrifice" include the Indic ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fortune Teller
Fortune telling is the practice of predicting information about a person's life. Melton, J. Gordon. (2008). ''The Encyclopedia of Religious Phenomena''. Visible Ink Press. pp. 115-116. The scope of fortune telling is in principle identical with the practice of divination. The difference is that divination is the term used for predictions considered part of a religious ritual, invoking deities or spirits, while the term fortune telling implies a less serious or formal setting, even one of popular culture, where belief in occult workings behind the prediction is less prominent than the concept of suggestion, spiritual or practical advisory or affirmation. Historically, Pliny the Elder describes use of the crystal ball in the 1st century CE by soothsayers (''"crystallum orbis"'', later written in Medieval Latin by scribes as ''orbuculum''). Contemporary Western images of fortune telling grow out of folkloristic reception of Renaissance magic, specifically associated with R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)