|
Deferasirox
Deferasirox, sold under the brand name Exjade & Asunra (in injectable form) & Oleptiss (Tablet formulation) both by Novartis among others, is an oral iron chelator. Its main use is to reduce chronic iron overload in patients who are receiving long-term blood transfusions for conditions such as beta- thalassemia and other chronic anemias.https://www.novartis.com/research-development/research-loc .... References External links * {{Portal bar , Medicine Chelating agents Chelating agents used as drugs Orphan drugs Novartis brands Antidotes Triazoles Benzoic acids Phenols ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deferasirox Synthesis
Deferasirox, sold under the brand name Exjade & Asunra (in injectable form) & Oleptiss (Tablet formulation) both by Novartis among others, is an oral iron Chelation therapy, chelator. Its main use is to reduce Iron overload disorder, chronic iron overload in patients who are receiving long-term blood transfusions for conditions such as beta-thalassemia and other chronic anemias.Free full text It is the first oral medication approved in the United States for this purpose. It was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in November 2005. According to the FDA (May 2007), kidney failure and cytopenias have been reported in patients receiving deferasirox tablets for oral suspension. It is approved in the European Union by the European Medicines Agency ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Novartis Brands
Novartis AG is a Swiss-American multinational pharmaceutical corporation based in Basel, Switzerland and Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States (global research).name="novartis.com">https://www.novartis.com/research-development/research-locations It is one of the largest pharmaceutical companies in the world. Novartis manufactures the drugs clozapine (Clozaril), diclofenac (Voltaren; sold to GlaxoSmithKline in 2015 deal), carbamazepine (Tegretol), valsartan (Diovan), imatinib mesylate (Gleevec/Glivec), cyclosporine (Neoral/Sandimmune), letrozole (Femara), methylphenidate (Ritalin; production ceased 2020), terbinafine (Lamisil), deferasirox (Exjade), and others. In March 1996, the companies Ciba-Geigy and Sandoz merged to form Novartis; the pharmaceutical and agrochemical divisions of both companies formed Novartis as an independent entity. Other Ciba-Geigy and Sandoz businesses were sold, or, like Ciba Specialty Chemicals, spun off as independent companies. The Sandoz bran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thalassemia
Thalassemias are inherited blood disorders characterized by decreased hemoglobin production. Symptoms depend on the type and can vary from none to severe. Often there is mild to severe anemia (low red blood cells or hemoglobin). Anemia can result in feeling tired and pale skin. There may also be bone problems, an enlarged spleen, yellowish skin, and dark urine. Slow growth may occur in children. Thalassemias are genetic disorders inherited from a person's parents. There are two main types, alpha thalassemia and beta thalassemia. The severity of alpha and beta thalassemia depends on how many of the four genes for alpha globin or two genes for beta globin are missing. Diagnosis is typically by blood tests including a complete blood count, special hemoglobin tests, and genetic tests. Diagnosis may occur before birth through prenatal testing. Treatment depends on the type and severity. Treatment for those with more severe disease often includes regular blood transfusions, iron chel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Novartis
Novartis AG is a Swiss-American multinational pharmaceutical corporation based in Basel, Switzerland and Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States (global research).name="novartis.com">https://www.novartis.com/research-development/research-locations It is one of the largest pharmaceutical companies in the world. Novartis manufactures the drugs clozapine (Clozaril), diclofenac (Voltaren; sold to GlaxoSmithKline in 2015 deal), carbamazepine (Tegretol), valsartan (Diovan), imatinib mesylate (Gleevec/Glivec), cyclosporine (Neoral/Sandimmune), letrozole (Femara), methylphenidate (Ritalin; production ceased 2020), terbinafine (Lamisil), deferasirox (Exjade), and others. In March 1996, the companies Ciba-Geigy and Sandoz merged to form Novartis; the pharmaceutical and agrochemical divisions of both companies formed Novartis as an independent entity. Other Ciba-Geigy and Sandoz businesses were sold, or, like Ciba Specialty Chemicals, spun off as independent companies. The Sandoz brand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron Overload Disorder
Iron overload or hemochromatosis (also spelled ''haemochromatosis'' in British English) indicates increased total accumulation of iron in the body from any cause and resulting organ damage. The most important causes are hereditary haemochromatosis (HH or HHC), a genetic disorder, and transfusional iron overload, which can result from repeated blood transfusions. Signs and symptoms Organs most commonly affected by hemochromatosis include the liver, heart, and endocrine glands. Hemochromatosis may present with the following clinical syndromes: * liver: chronic liver disease and cirrhosis of the liver. * heart: heart failure, cardiac arrhythmia. * hormones: diabetes (see below) and hypogonadism (insufficiency of the sex hormone producing glands) which leads to low sex drive and/or loss of fertility in men and loss of menstrual cycle in women. * metabolism: diabetes in people with iron overload occurs as a result of selective iron deposition in islet beta cells in the pancreas lead ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WHO Model List Of Essential Medicines
The WHO Model List of Essential Medicines (aka Essential Medicines List or EML), published by the World Health Organization (WHO), contains the medications considered to be most effective and safe to meet the most important needs in a health system. The list is frequently used by countries to help develop their own local lists of essential medicines. , more than 155 countries have created national lists of essential medicines based on the World Health Organization's model list. This includes both developed and developing countries. The list is divided into core items and complementary items. The core items are deemed to be the most cost-effective options for key health problems and are usable with little additional health care resources. The complementary items either require additional infrastructure such as specially trained health care providers or diagnostic equipment or have a lower cost–benefit ratio. About 25% of items are in the complementary list. Some medicatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chelation Therapy
Chelation therapy is a medical procedure that involves the administration of Chelation, chelating agents to remove heavy metals from the body. Chelation therapy has a long history of use in clinical toxicology and remains in use for some very specific medical treatments, although it is administered under very careful medical supervision due to various inherent risks, including the mobilization of mercury and other metals through the brain and other parts of the body by the use of weak chelating agents that unbind with metals before elimination, exacerbating existing damage. To avoid mobilization, some practitioners of chelation use strong chelators, such as selenium, taken at low doses over a long period of time. Chelation therapy must be administered with care as it has a number of possible side effects, including death. In response to increasing use of chelation therapy as alternative medicine and in circumstances in which the therapy should not be used in conventional medicine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antidotes
An antidote is a substance that can counteract a form of poisoning. The term ultimately derives from the Greek term φάρμακον ἀντίδοτον ''(pharmakon) antidoton'', "(medicine) given as a remedy". Antidotes for anticoagulants are sometimes referred to as reversal agents. The antidotes for some particular toxins are manufactured by injecting the toxin into an animal in small doses and extracting the resulting antibodies from the host animals' blood. This results in an antivenom that can be used to counteract venom produced by certain species of snakes, spiders, and other venomous animals. Some animal venoms, especially those produced by arthropods (such as certain spiders, scorpions, and bees) are only potentially lethal when they provoke allergic reactions and induce anaphylactic shock; as such, there is no "antidote" for these venoms; however anaphylactic shock can be treated (e.g. with epinephrine). Some other toxins have no known antidote. For example, the pois ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deferiprone
Deferiprone, sold under the brand name Ferriprox among others, is a medication that chelates iron and is used to treat iron overload in thalassaemia major. It was first approved and indicated for use in treating thalassaemia major in 1994 and had been licensed for use in the European Union for many years while awaiting approval in Canada and in the United States. On October 14, 2011, it was approved for use in the US under the FDA's accelerated approval program. The most common side effects include red-brown urine (showing that iron is being removed through the urine), nausea (feeling sick), abdominal pain (stomach ache) and vomiting. Text was copied from this source which is © European Medicines Agency. Reproduction is authorized provided the source is acknowledged. Less common but more serious side effects are agranulocytosis (very low levels of granulocytes, a type of white blood cell) and neutropenia (low levels of neutrophils, a type of white blood cell that fights infec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
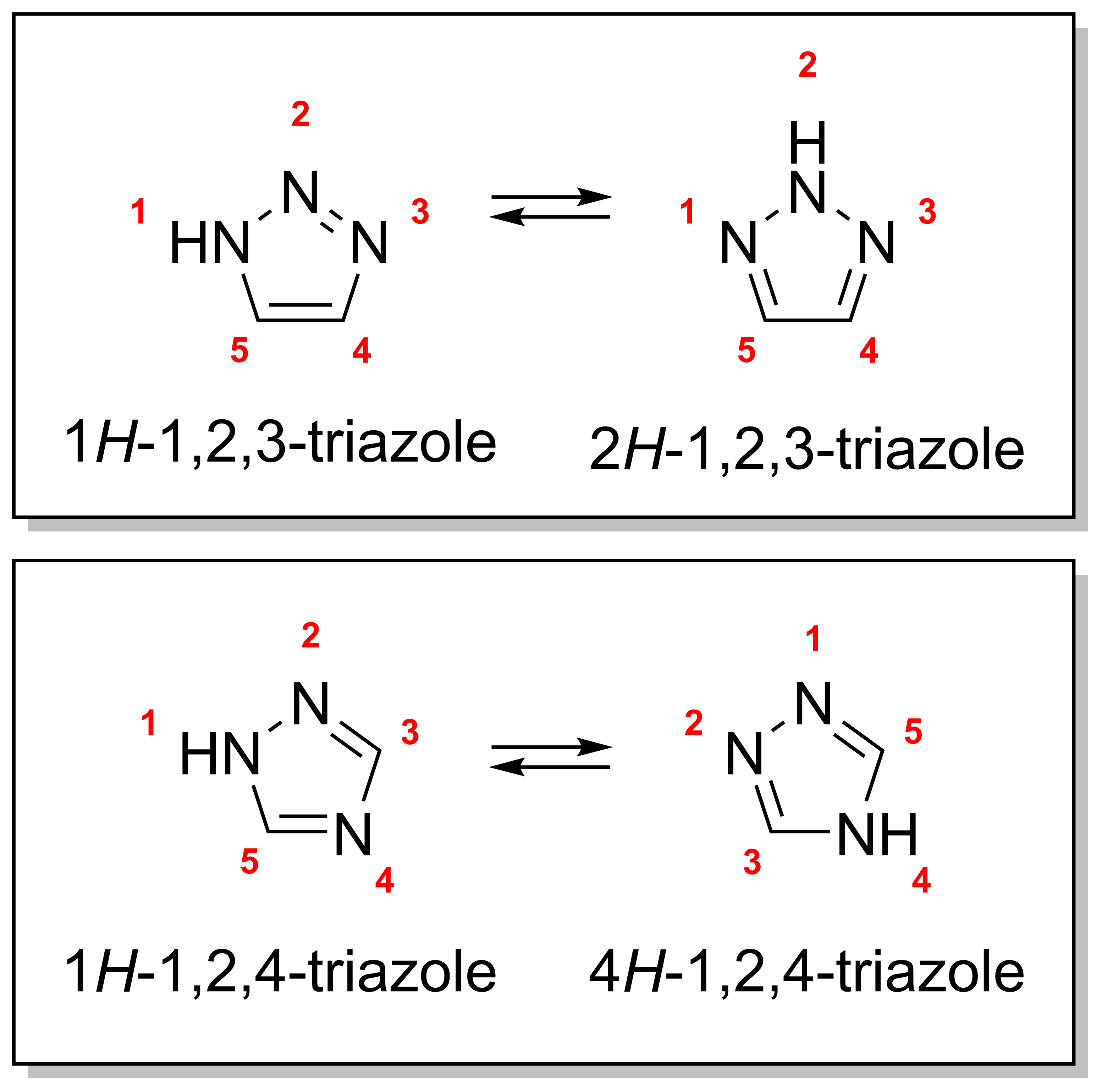
Triazoles
A triazole is a heterocyclic compound featuring a five-membered ring of two carbon atoms and three nitrogen atoms with molecular formula C2H3N3. Triazoles exhibit substantial isomerism, depending on the positioning of the nitrogen atoms within the ring. Many triazoles are versatile, biologically active compounds commonly used as fungicides and plant retardants. However, triazoles are also useful in bioorthogonal chemistry, because the large number of nitrogen atoms causes triazoles to react similar to azides. Lastly, the many free lone pairs in triazoles make them useful as coordination compounds, although not typically as haptic ligands. Isomerism There are four triazole isomers, which are conventionally divided into two pairs of tautomers. In the 1,2,3-triazoles, the three nitrogen atoms are adjacent; in the 1,2,4-triazoles, an interstitial carbon separates out one nitrogen atom. Each category has two tautomers that differ by which nitrogen has a hydrogen bonded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chelating Agents Used As Drugs
Chelation is a type of bonding of ions and molecules to metal ions. It involves the formation or presence of two or more separate coordinate bonds between a polydentate (multiple bonded) ligand and a single central metal atom. These ligands are called chelants, chelators, chelating agents, or sequestering agents. They are usually organic compounds, but this is not a necessity, as in the case of zinc and its use as a maintenance therapy to prevent the absorption of copper in people with Wilson's disease. Chelation is useful in applications such as providing nutritional supplements, in chelation therapy to remove toxic metals from the body, as contrast agents in MRI scanning, in manufacturing using homogeneous catalysts, in chemical water treatment to assist in the removal of metals, and in fertilizers. Chelate effect The chelate effect is the greater affinity of chelating ligands for a metal ion than that of similar nonchelating (monodentate) ligands for the same metal. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chelating Agents
Chelation is a type of bonding of ions and molecules to metal ions. It involves the formation or presence of two or more separate coordinate bonds between a polydentate (multiple bonded) ligand and a single central metal atom. These ligands are called chelants, chelators, chelating agents, or sequestering agents. They are usually organic compounds, but this is not a necessity, as in the case of zinc and its use as a maintenance therapy to prevent the absorption of copper in people with Wilson's disease. Chelation is useful in applications such as providing nutritional supplements, in chelation therapy to remove toxic metals from the body, as contrast agents in MRI scanning, in manufacturing using homogeneous catalysts, in chemical water treatment to assist in the removal of metals, and in fertilizers. Chelate effect The chelate effect is the greater affinity of chelating ligands for a metal ion than that of similar nonchelating (monodentate) ligands for the same metal. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |