|
Deepcar Railway Station
Deepcar railway station, originally "Deep Car", is a disused railway station near Deepcar, South Yorkshire, England. The station, situated on the line built by the Sheffield, Ashton-under-Lyne and Manchester Railway, opened on 14 July 1845. The station was located between Oughtibridge and Wortley and was intended to serve the village of Deepcar, near Sheffield, South Yorkshire. In 1899 the route became part of the Great Central Railway main line from London Marylebone to Manchester. The station was built with two flanking platforms, the main station building being on the Manchester-bound side with a waiting shelter on the other. In the 1870s a short branch line was constructed to serve the Stocksbridge steel works of Samuel Fox and Company. This line ran from the west end of Deepcar station to a set of sidings, where traffic was exchanged with the Stocksbridge Railway. At the west end of the station, to the rear of the main line platform, there was a short bay known as the St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deepcar
Deepcar is a village located on the eastern fringe of the town of Stocksbridge, South Yorkshire, England. It is in the electoral ward of Stocksbridge and Upper Don, approximately north-west of Sheffield city centre.Ordnance survey. 1:25000. c.2012 Geography The village lies south-west of the confluence of the River Don and Little Don River, and near to the junctions of the A616 road and A6102 roads, and the former junction of the ' Woodhead Line' (Sheffield to Penistone section, built for the Sheffield, Ashton-under-Lyne and Manchester Railway) and private Stocksbridge Railways; the village was served by the Deepcar railway station from 1846 to 1959. History The Deepcar archaeological site, which included a structure or 'house', dating to the mesolithic period, and ascribed to the Maglemosian culture was excavated in 1962 close to the junction of the Don and Little Don at Wharncliffe Wood. (). The site's culture has similarities to Star Carr in North Yorkshire, bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel Fox And Company
Samuel Fox and Company was a company operating a major steel complex built in the Upper Don Valley at Stocksbridge, near Sheffield, South Yorkshire, England. History Samuel Fox bought a disused corn mill close by the centre of the town in 1842 and made alterations so that he could produce wire for the manufacture of textile pins. Within 6 years the business began to manufacture wire for umbrella frames and he developed his own variant, the “Paragon” in 1851. Expansion continued and by the mid-1860s furnaces and rolling mills had been built and the production of railway lines and springs begun. Road transport in the area was difficult and with larger products being manufactured a new outlet was required. In the 1870s a short branch line was built to link the works with the Manchester, Sheffield & Lincolnshire Railway at Deepcar. This was known as the Stocksbridge Railway which was a subsidiary of the main company until the early 1990s. The line was still open in 2018 and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railway Stations In Great Britain Closed In 1959
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a prepared flat surface, rail vehicles ( rolling stock) are directionally guided by the tracks on which they run. Tracks usually consist of steel rails, installed on sleepers (ties) set in ballast, on which the rolling stock, usually fitted with metal wheels, moves. Other variations are also possible, such as "slab track", in which the rails are fastened to a concrete foundation resting on a prepared subsurface. Rolling stock in a rail transport system generally encounters lower frictional resistance than rubber-tyred road vehicles, so passenger and freight cars (carriages and wagons) can be coupled into longer trains. The operation is carried out by a railway company, providing transport between train stations or freight customer faci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railway Stations In Great Britain Opened In 1845
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a prepared flat surface, rail vehicles (rolling stock) are directionally guided by the tracks on which they run. Tracks usually consist of steel rails, installed on sleepers (ties) set in ballast, on which the rolling stock, usually fitted with metal wheels, moves. Other variations are also possible, such as "slab track", in which the rails are fastened to a concrete foundation resting on a prepared subsurface. Rolling stock in a rail transport system generally encounters lower frictional resistance than rubber-tyred road vehicles, so passenger and freight cars (carriages and wagons) can be coupled into longer trains. The operation is carried out by a railway company, providing transport between train stations or freight customer faciliti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
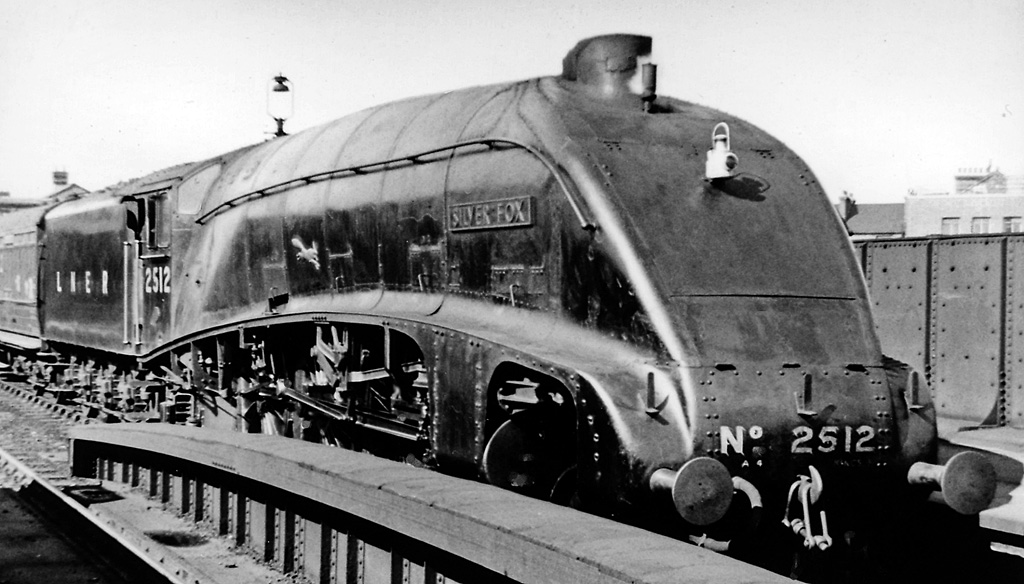
Locomotive Publishing Company
The Locomotive Publishing Company was an English publishing house, specialising in railway topics. It was noted for publishing '' Locomotive Magazine'', amongst many other highly regarded titles. It was also notable as one of the first stock photo libraries, in this case specialising in railway images. History The company was preceded in the final years of the 19th century by 'F. Moore', a railway artist and photographer who published ''Moore's Monthly Magazine'', the first widely popular railway magazine. In actuality, 'F. Moore' was the pseudonymous pen-name for two brothers, A.R. Bell and A. Morton Bell, both apprentices at the Stratford Works of the Great Eastern Railway. They began as a photo library, trading between the increasing number of amateur photographers of railways and the growing interest of enthusiasts. A third brother, Walter John Bell, and another apprentice, A.C.W. Lowe, became involved from 1896 with the launch of ''Moore's Monthly Magazine''. From the 13t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
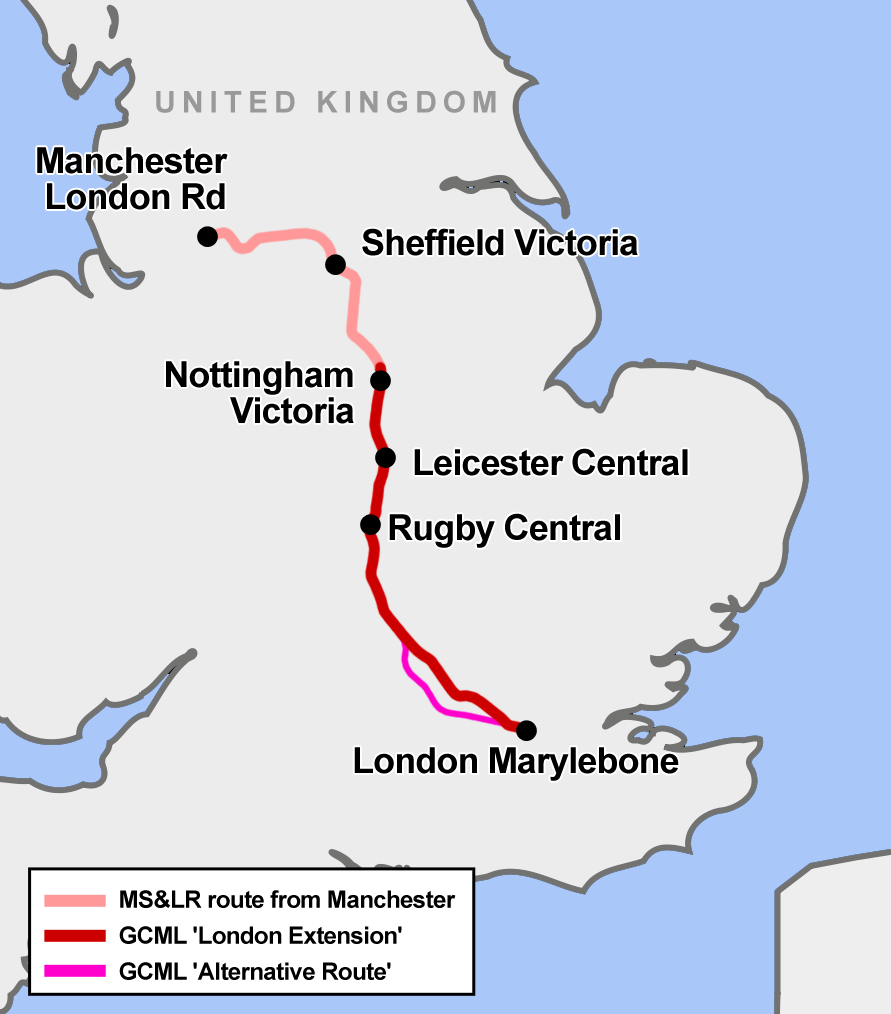
Great Central Main Line
The Great Central Main Line (GCML), also known as the London Extension of the Manchester, Sheffield and Lincolnshire Railway (MS&LR), is a former railway line in the United Kingdom. The line was opened in 1899 and built by the Great Central Railway running from Sheffield in the North of England, southwards through Nottingham and Leicester to Marylebone in London. The GCML was the last main line railway to be built in Britain during the Victorian period. Built by the railway entrepreneur Edward Watkin with the aim to run as a fast trunk route from the North and the East Midlands to London and the south of England. Initially not a financial success, it recovered under the leadership of Sam Fay. Although initially planned for long-distance passenger services, in practice the line's most important function became to carry goods traffic, notably coal. In the 1960s, the line was considered by Dr Beeching as an unnecessary duplication of other lines that served the same places, especial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Railways
British Railways (BR), which from 1965 traded as British Rail, was a state-owned company that operated most of the overground rail transport in Great Britain from 1948 to 1997. It was formed from the nationalisation of the Big Four British railway companies, and was privatised in stages between 1994 and 1997. Originally a trading brand of the Railway Executive of the British Transport Commission, it became an independent statutory corporation in January 1963, when it was formally renamed the British Railways Board. The period of nationalisation saw sweeping changes in the railway. A process of dieselisation and electrification took place, and by 1968 steam locomotives had been entirely replaced by diesel and electric traction, except for the Vale of Rheidol Railway (a narrow-gauge tourist line). Passengers replaced freight as the main source of business, and one-third of the network was closed by the Beeching cuts of the 1960s in an effort to reduce rail subsidies. On privatis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liberty House Group
Liberty Steel Group Holdings UK Ltd (LHG), which is also referred to as Liberty House or Liberty House UK, is a British industrial and metals company founded in the United Kingdom in 1992 by industrialist Sanjeev Gupta. It is headquartered in London, England, and has offices in Dubai, Singapore and Hong Kong. The holding company of Liberty Steel, Liberty House Group PTE Ltd is based in Singapore. The company focuses on ferrous and non-ferrous metal trading, metals recycling, steel and aluminium production, and engineering products and services. Gupta controls it through his vehicle GFG Alliance. History LHG was founded by Sanjeev Gupta in 1992. LHG, together with the SIMEC Group, part of the GFG Alliance, purchased the Lochaber aluminium smelter plant as well as the Laggan Dam from Rio Tinto in November 2016. In February 2017, LHG agreed to purchase the specialty steel division of Tata Steel Europe for £100 million. The purchase included the division's facilities in Rother ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stocksbridge Platform
Stocksbridge was a small railway halt, the terminus of, and only railway station on the Stocksbridge Railway. The platform was a simple wooden affair, nothing more was needed to cater for the service provided. The passenger service, which ran from a west facing bay platform at Deepcar, on the Manchester, Sheffield and Lincolnshire Railways Woodhead Line, commenced operation on 14 April 1877 and ceased in 1931. Operation was undertaken by the Stocksbridge Railway Company who bought two small coaches for the trains, utilising their own locomotive. In the main, passengers consisted of workers going to Samuel Fox and Company Samuel Fox and Company was a company operating a major steel complex built in the Upper Don Valley at Stocksbridge, near Sheffield, South Yorkshire, England. History Samuel Fox bought a disused corn mill close by the centre of the town in 1 ...'s works and school children. References "Great Central", Vol. 2, "Dominion of Watkin", George Dow, Loco. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stocksbridge Railway
The Stocksbridge Railway was a subsidiary of Samuel Fox and Company and linked the company's works at Stocksbridge, near Sheffield, South Yorkshire, England, with the main line of the Manchester, Sheffield and Lincolnshire Railway at Deepcar. As the size of Fox's steelworks expanded, better transport links were needed, and the railway was authorised by an Act of Parliament in 1874. It was completed in 1877, and remained an independent subsidiary until 1992, when it became part of the steelworks operation. When the Woodhead line was closed to the north of Deepcar, the line south to Sheffield was singled, and operates as a long siding. A extension was constructed between 1897 and 1898 by Sheffield Corporation, to service the construction of reservoirs at Langsett and Underbank. It was unusual in that it had a third rail, to allow both standard gauge and -gauge stock to work on it. Reservoir building was completed in 1904, but the locomotive was retained until 1907 when Underbank ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stocksbridge
Stocksbridge is a town and civil parish, in the City of Sheffield, in South Yorkshire, England. Historically part of the West Riding of Yorkshire, it lies just to the east of the Peak District. The town is located in the steep-sided valley of the Little Don River, below the Underbank Reservoir. It blends into the areas of Deepcar, Bolsterstone and the eastern end of Ewden valley around Ewden village, which are also within the civil parish. The population of the civil parish as of the 2011 census was 13,455. Early history Until the early 18th century, what is now Stocksbridge was a deciduously wooded valley, running from Midhopestones at its northwestern extremity to Deepcar at its southeastern end. A river, originally called the Hunshelf Water and later renamed the Little Don, ran through the valley. This river was also, unofficially, called the Porter, probably on account of its peaty colour. A dirt road, connecting Sheffield with Manchester, ran through the woods adjacent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)
