|
Decretals
Decretals ( la, litterae decretales) are letters of a pope that formulate decisions in ecclesiastical law of the Catholic Church.McGurk. ''Dictionary of Medieval Terms''. p. 10 They are generally given in answer to consultations but are sometimes given due to the initiative of the pope himself. These furnish, with the canons of the councils, the chief source of the legislation of the Church, and formed the greater part of the '' Corpus Iuris Canonici'' before they were formally replaced by the ''Codex Iuris Canonici'' of 1917. However, Cardinal Pietro Gasparri led the papal commission for the revision of canon law and later on published a guide to the ''fontes'' (sources) used in the 1917 code. Many canons in this code can easily be retraced in their relationship to and dependency on medieval decretals as well as Roman law. In themselves, the medieval decretals form a very special source which throws light on medieval conflicts and the approaches to their solution. They are some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corpus Iuris Canonici
The ''Corpus Juris Canonici'' ( lit. 'Body of Canon Law') is a collection of significant sources of the canon law of the Catholic Church that was applicable to the Latin Church. It was replaced by the 1917 Code of Canon Law which went into effect in 1918. The 1917 Code was later replaced by the 1983 Code of Canon Law, the codification of canon law currently in effect for the Latin Church. In 1990, Eastern Catholic canon law was codified in the Code of Canons of the Eastern Churches, which is currently in effect for the Eastern Catholic Churches. The ''Corpus juris canonici'' was used in canonical courts of the Catholic Church such as those in each diocese and in the courts of appeal at the Roman Curia such as the ''Roman Rota''. Definitions The term ''corpus juris canonici'' was used to denote the system of canonical law beginning in the thirteenth century. The term ''corpus'' (Latin for 'body') here denotes a collection of documents; ''corpus juris'', a collection of laws ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decretales Gregorii IX
The Decretals of Gregory IX ( la, Decretales Gregorii IX), also collectively called the , are a source of medieval Catholic canon law. In 1230, Pope Gregory IX ordered his chaplain and confessor, St. Raymond of Penyafort, a Dominican, to form a new canonical collection destined to replace the , which was the chief collection of legal writings for the church for over 90 years. It has been said that the pope used these letters to emphasize his power over the Universal Church. Political circumstances During Gregory's papacy, the church had established a prominent role in the temporal and spiritual affairs of Europe. Following his predecessor, Pope Honorius III, Gregory maintained papal supremacy. Nevertheless, the utility of a new collection was so evident that there may be no other motives than those the pope gives in the Bull "Rex pacificus" of 5 September 1234, viz., the inconvenience of referring to several collections containing decisions most diverse and sometimes contradic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
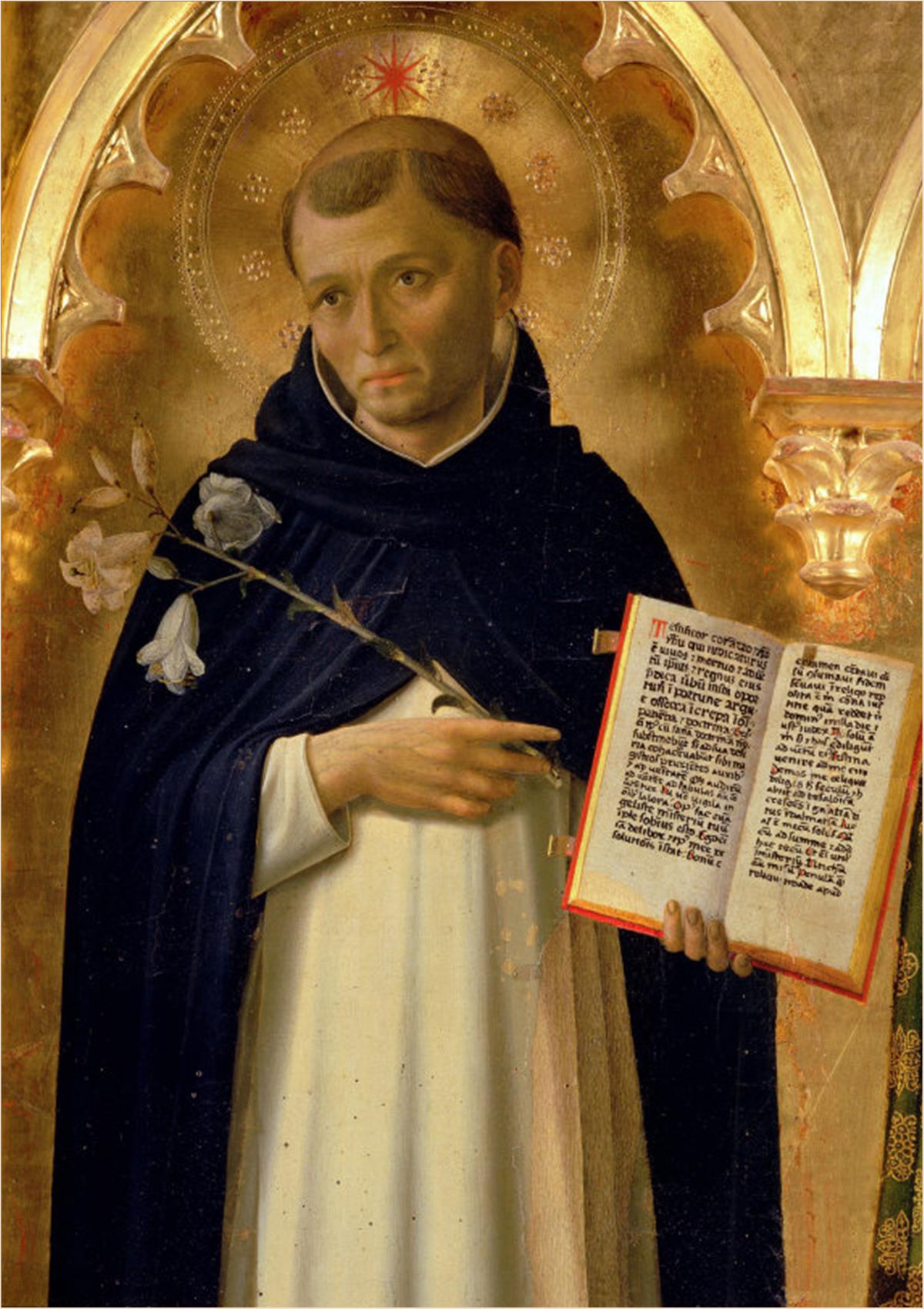
Raymund Of Peñafort
Raymond of Penyafort ( ca, Sant Ramon de Penyafort, ; es, San Raimundo de Peñafort; 1175 – 6 January 1275) was a Catalan Dominican friar in the 13th century, who compiled the Decretals of Gregory IX, a collection of canonical laws that remained a major part of Church law until the 1917 Code of Canon Law abrogated it. He is honored as a saint in the Catholic Church and is the patron saint of canon lawyers. Life Raymond of Penyafort was born in Vilafranca del Penedès, a small town near Barcelona, Principality of Catalonia, around 1175. Descended from a noble family with ties to the royal house of Aragon, he was educated in Barcelona and at the University of Bologna, where he received doctorates in both civil and canon law. From 1195 to 1210, he taught canon law. In 1210, he moved to Bologna, where he remained until 1222, including three years occupying the Chair of canon law at the university. He came to know the newly founded Dominican Order there. Raymond was attra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pope Gregory IX
Pope Gregory IX ( la, Gregorius IX; born Ugolino di Conti; c. 1145 or before 1170 – 22 August 1241) was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 19 March 1227 until his death in 1241. He is known for issuing the '' Decretales'' and instituting the Papal Inquisition, in response to the failures of the episcopal inquisitions established during the time of Pope Lucius III, by means of the papal bull '' Ad abolendam'', issued in 1184. The successor of Honorius III, he fully inherited the traditions of Gregory VII and of his own cousin Innocent III and zealously continued their policy of papal supremacy. Early life Ugolino (Hugh) was born in Anagni. The date of his birth varies in sources between c. 1145 and 1170. He received his education at the Universities of Paris and Bologna. He was created Cardinal-Deacon of the church of Sant'Eustachio by his cousin Innocent III in December 1198. In 1206 he was promoted to the rank of Cardinal Bishop of Osti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decretum Of Gratian
The ''Decretum Gratiani'', also known as the ''Concordia discordantium canonum'' or ''Concordantia discordantium canonum'' or simply as the ''Decretum'', is a collection of canon law compiled and written in the 12th century as a legal textbook by the jurist known as Gratian. It forms the first part of the collection of six legal texts, which together became known as the ''Corpus Juris Canonici''. It was used as the main source of law by canonists of the Roman Catholic Church until the ''Decretals'', promulgated by Pope Gregory IX in 1234, obtained legal force, after which it was the cornerstone of the Corpus Juris Canonici, in force until 1917. Overview In the first half of the 12th century Gratian, ''clusinus episcopus'',Reali, Francesco (ed.), Graziano da Chiusi e la sua opera, 2009, pg. 63-73 and pg. 244 has found and re-evaluated a Kalendarium of the Sienese Church owned by the Library of the Intronati of Siena (Ms FI2, f. 5v) in which, in Carolina minuscule writing with a d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canon Law (Catholic Church)
The canon law of the Catholic Church ("canon law" comes from Latin ') is "how the Church organizes and governs herself". It is the system of laws and ecclesiastical legal principles made and enforced by the hierarchical authorities of the Catholic Church to regulate its external organization and government and to order and direct the activities of Catholics toward the mission of the Church. It was the first modern Western legal system and is the oldest continuously functioning legal system in the West, while the unique traditions of Eastern Catholic canon law govern the 23 Eastern Catholic Churches, Eastern Catholic particular churches ''.'' Positive ecclesiastical laws, based directly or indirectly upon immutable divine law or natural law, derive formal authority in the case of universal laws from Promulgation (Catholic canon law), promulgation by the supreme legislator—the supreme pontiff, who possesses the totality of legislative, executive, and judicial power in his person ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decretists
In the history of canon law, a decretist was a student and interpreter of the ''Decretum Gratiani''. Like Gratian, the decretists sought to provide "a harmony of discordant canons" (''concordia discordantium canonum''), and they worked towards this through glosses (''glossae'') and summaries (''summae'') on Gratian.Rhidian Jones, ''The Canon Law of the Roman Catholic Church and the Church of England: A Handbook'' (T&T Clark, 2000), 45–46. They are contrasted with the decretalists, whose work primarily focused on papal decretals. Early decretists of the Italian school include Paucapalea, a pupil of Gratian's; Rufinus, who wrote the ''Summa Decretorum''; and Huguccio, who wrote the ''Summa super Decreta'', the most extensive decretist work. There was also a French school of decretists starting with Stephen of Tournai Stephen of Tournai, (18 March 1128 - 11 September 1203), was a Canon regular of Sainte-Geneviève (Paris), and Roman Catholic canonist who became bishop of Tournai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pope
The pope ( la, papa, from el, πάππας, translit=pappas, 'father'), also known as supreme pontiff ( or ), Roman pontiff () or sovereign pontiff, is the bishop of Rome (or historically the patriarch of Rome), head of the worldwide Catholic Church, and has also served as the head of state or sovereign of the Papal States and later the Vatican City State since the eighth century. From a Catholic viewpoint, the primacy of the bishop of Rome is largely derived from his role as the apostolic successor to Saint Peter, to whom Petrine primacy, primacy was conferred by Jesus, who gave Peter the Keys of Heaven and the powers of "binding and loosing", naming him as the "rock" upon which the Church would be built. The current pope is Pope Francis, Francis, who was 2013 papal conclave, elected on 13 March 2013. While his office is called the papacy, the ecclesiastical jurisdiction, jurisdiction of the episcopal see is called the Holy See. It is the Holy See that is the sovereign enti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dominican Order
The Order of Preachers ( la, Ordo Praedicatorum) abbreviated OP, also known as the Dominicans, is a Catholic mendicant order of Pontifical Right for men founded in Toulouse, France, by the Spanish priest, saint and mystic Dominic of Caleruega. It was approved by Pope Honorius III via the papal bull '' Religiosam vitam'' on 22 December 1216. Members of the order, who are referred to as ''Dominicans'', generally carry the letters ''OP'' after their names, standing for ''Ordinis Praedicatorum'', meaning ''of the Order of Preachers''. Membership in the order includes friars, nuns, active sisters, and lay or secular Dominicans (formerly known as tertiaries). More recently there has been a growing number of associates of the religious sisters who are unrelated to the tertiaries. Founded to preach the Gospel and to oppose heresy, the teaching activity of the order and its scholastic organisation placed the Preachers in the forefront of the intellectual life of the M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Bologna
The University of Bologna ( it, Alma Mater Studiorum – Università di Bologna, UNIBO) is a public research university in Bologna, Italy. Founded in 1088 by an organised guild of students (''studiorum''), it is the oldest university in continuous operation in the world, and the first degree-awarding institution of higher learning. At its foundation, the word ''universitas'' was first coined.Hunt Janin: "The university in medieval life, 1179–1499", McFarland, 2008, , p. 55f.de Ridder-Symoens, Hilde''A History of the University in Europe: Volume 1, Universities in the Middle Ages'' Cambridge University Press, 1992, , pp. 47–55 With over 90,000 students, it is the second largest university in Italy after La Sapienza in Rome. It was the first place of study to use the term ''universitas'' for the corporations of students and masters, which came to define the institution (especially its law school) located in Bologna. The university's emblem carries the motto, ''Alma Mater Studio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pope Honorius III
Pope Honorius III (c. 1150 – 18 March 1227), born Cencio Savelli, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 18 July 1216 to his death. A canon at the Basilica di Santa Maria Maggiore, he came to hold a number of important administrative positions, including that of Camerlengo. In 1197, he became tutor to the young Frederick II. As pope, he worked to promote the Fifth Crusade, which had been planned under his predecessor, Innocent III. Honorius repeatedly exhorted King Andrew II of Hungary and Emperor Frederick II to fulfill their vows to participate. He also gave approval to the recently formed Dominican and Franciscan religious orders. Early work He was born in Rome as a son of Aimerico, a member of the Roman Savelli family. For a time canon at the church of Santa Maria Maggiore, he later became Camerlengo of the Holy Roman Church in December 5, 1189 and Cardinal Deacon of Santa Lucia in Silice on 20 February 1193. Under Pope Clement III an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tancred Of Bologna
Tancred of Bologna or of Germany (c. 1185 – 1230/1236), commonly just Tancredus, was a Dominican preacher and canonist. He is easily conflated with a contemporary Dominican, Tancred Tancredi, and the two are sometimes indistinguishable in the sources and have been treated as one person, though this is known to be false. Tancred's origins lie in Germany, where, if his hagiographers are to be believed, he was a soldier of middle rank at the court of the Emperor Frederick II. He was educated under John of Wales at the University of Bologna. He wrote an important gloss on the '' Compilatio tertia'' and the ''Summa de matrimonio'' (Summary of Marriage), which was influential to Ramon de Penyafort, as well as the ''Ordo iudiciarius'', completed in 1216, which was the culmination of the procedural literature of the glossators and was translated into both German and French, indicating its importance for medieval legal practice.Rosamond McKitterick et al., ''The New Cambridge Mediev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |