|
Deconfinement
In physics, deconfinement (in contrast to confinement) is a phase of matter in which certain particles are allowed to exist as free excitations, rather than only within bound states. Examples Various examples exist in particle physics where certain gauge theories exhibit transitions between confining and deconfining phases. A prominent example, and the first case considered as such in theoretical physics, occurs at high energy in quantum chromodynamics when quarks and gluons are free to move over distances larger than a femtometer (the size of a hadron). This phase is also called the quark–gluon plasma. These ideas have been adopted in many-body theory of matter with a distinguished example developed in the context fractional quantum Hall effect. See also *Onset of deconfinement * Colour confinement *Quark–gluon plasma Quark–gluon plasma (QGP) or quark soup is an interacting localized assembly of quarks and gluons at thermal (local kinetic) and (close to) chemical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quark Matter
Quark matter or QCD matter (quantum chromodynamics, quantum chromodynamic) refers to any of a number of hypothetical phase (matter), phases of matter whose degrees of freedom (physics and chemistry), degrees of freedom include quarks and gluons, of which the prominent example is Quark–gluon plasma, quark-gluon plasma. Several series of conferences in 2019, 2020, and 2021 were devoted to this topic. Quarks are liberated into quark matter at extremely high temperatures and/or densities, and some of them are still only theoretical as they require conditions so extreme that they cannot be produced in any laboratory, especially not at equilibrium conditions. Under these extreme conditions, the familiar structure of matter, where the basic constituents are atomic nucleus, nuclei (consisting of nucleons which are bound states of quarks) and electrons, is disrupted. In quark matter it is more appropriate to treat the quarks themselves as the basic degrees of freedom. In the standard mode ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quark–gluon Plasma
Quark–gluon plasma (QGP) or quark soup is an interacting localized assembly of quarks and gluons at thermal (local kinetic) and (close to) chemical (abundance) equilibrium. The word ''plasma'' signals that free color charges are allowed. In a 1987 summary, Léon van Hove pointed out the equivalence of the three terms: quark gluon plasma, quark matter and a new state of matter. Since the temperature is above the Hagedorn temperature—and thus above the scale of light u,d-quark mass—the pressure exhibits the relativistic Stefan-Boltzmann format governed by temperature to the fourth power ( T^) and many practically massless quark and gluon constituents. It can be said that QGP emerges to be the new phase of strongly interacting matter which manifests its physical properties in terms of nearly free dynamics of practically massless gluons and quarks. Both quarks and gluons must be present in conditions near chemical (yield) equilibrium with their colour charge ''open'' for a new s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quark–gluon Plasma
Quark–gluon plasma (QGP) or quark soup is an interacting localized assembly of quarks and gluons at thermal (local kinetic) and (close to) chemical (abundance) equilibrium. The word ''plasma'' signals that free color charges are allowed. In a 1987 summary, Léon van Hove pointed out the equivalence of the three terms: quark gluon plasma, quark matter and a new state of matter. Since the temperature is above the Hagedorn temperature—and thus above the scale of light u,d-quark mass—the pressure exhibits the relativistic Stefan-Boltzmann format governed by temperature to the fourth power ( T^) and many practically massless quark and gluon constituents. It can be said that QGP emerges to be the new phase of strongly interacting matter which manifests its physical properties in terms of nearly free dynamics of practically massless gluons and quarks. Both quarks and gluons must be present in conditions near chemical (yield) equilibrium with their colour charge ''open'' for a new s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gluon
A gluon ( ) is an elementary particle that acts as the exchange particle (or gauge boson) for the strong force between quarks. It is analogous to the exchange of photons in the electromagnetic force between two charged particles. Gluons bind quarks together, forming hadrons such as protons and neutrons. Gluons are vector gauge bosons that mediate strong interactions of quarks in quantum chromodynamics (QCD). Gluons themselves carry the color charge of the strong interaction. This is unlike the photon, which mediates the electromagnetic interaction but lacks an electric charge. Gluons therefore participate in the strong interaction in addition to mediating it, making QCD significantly harder to analyze than quantum electrodynamics (QED). Properties The gluon is a vector boson, which means, like the photon, it has a spin of 1. While massive spin-1 particles have three polarization states, massless gauge bosons like the gluon have only two polarization states because gauge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bound State
Bound or bounds may refer to: Mathematics * Bound variable * Upper and lower bounds, observed limits of mathematical functions Physics * Bound state, a particle that has a tendency to remain localized in one or more regions of space Geography *Bound Brook (Raritan River), a tributary of the Raritan River in New Jersey * Bound Brook, New Jersey, a borough in Somerset County People *Bound (surname) *Bounds (surname) Arts, entertainment, and media Films * ''Bound'' (1996 film), an American neo-noir film by the Wachowskis * ''Bound'' (2015 film), an American erotic thriller film by Jared Cohn * ''Bound'' (2018 film), a Nigerian romantic drama film by Frank Rajah Arase Television * "Bound" (''Fringe''), an episode of ''Fringe'' * "Bound" (''The Secret Circle''), an episode of ''The Secret Circle'' * "Bound" (''Star Trek: Enterprise''), an episode of ''Star Trek: Enterprise'' Other arts, entertainment, and media * ''Bound'' (video game), a PlayStation 4 game * "Bound", a song ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Excited State
In quantum mechanics, an excited state of a system (such as an atom, molecule or nucleus) is any quantum state of the system that has a higher energy than the ground state (that is, more energy than the absolute minimum). Excitation refers to an increase in energy level above a chosen starting point, usually the ground state, but sometimes an already excited state. The temperature of a group of particles is indicative of the level of excitation (with the notable exception of systems that exhibit negative temperature). The lifetime of a system in an excited state is usually short: spontaneous or induced emission of a quantum of energy (such as a photon or a phonon) usually occurs shortly after the system is promoted to the excited state, returning the system to a state with lower energy (a less excited state or the ground state). This return to a lower energy level is often loosely described as decay and is the inverse of excitation. Long-lived excited states are often called ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fractionalization
In quantum mechanics, fractionalization is the phenomenon whereby the quasiparticles of a system cannot be constructed as combinations of its elementary constituents. One of the earliest and most prominent examples is the fractional quantum Hall effect, where the constituent particles are electrons but the quasiparticles carry fractions of the electron charge. Fractionalization can be understood as deconfinement of quasiparticles that together are viewed as comprising the elementary constituents. In the case of spin–charge separation, for example, the electron can be viewed as a bound state of a 'spinon' and a ' chargon', which under certain conditions can become free to move separately. History Quantized Hall conductance was discovered in 1980, related to the electron charge. Laughlin proposed a fluid of fractional charges in 1983, to explain the Fractional quantum Hall effect seen in 1982, for which he shared the 1998 Physics Nobel Prize. In 1997, experiments directly observ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quark-nova
A quark-nova is the hypothetical violent explosion resulting from the conversion of a neutron star to a quark star. Analogous to a supernova heralding the birth of a neutron star, a quark nova signals the creation of a quark star. The term quark-novae was coined in 2002 by Dr. Rachid Ouyed (currently at the University of Calgary, Canada) and Drs. J. Dey and M. Dey (Calcutta University, India). The nova process When a neutron star spins down, it may convert to a quark star through a process known as quark deconfinement. The resultant star would have quark matter in its interior. The process would release immense amounts of energy, perhaps explaining the most energetic explosions in the universe; calculations have estimated that as much as 1046 J could be released from the phase transition inside a neutron star. Quark-novae may be one cause of gamma ray bursts. According to Jaikumar ''et al.'', they may also be involved in producing heavy elements such as platinum through r-pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phase Of Matter
In the physical sciences, a phase is a region of space (a thermodynamic system), throughout which all physical properties of a material are essentially uniform. Examples of physical properties include density, index of refraction, magnetization and chemical composition. A simple description is that a phase is a region of material that is chemically uniform, physically distinct, and (often) mechanically separable. In a system consisting of ice and water in a glass jar, the ice cubes are one phase, the water is a second phase, and the humid air is a third phase over the ice and water. The glass of the jar is another separate phase. (See ) The term ''phase'' is sometimes used as a synonym for state of matter, but there can be several immiscible phases of the same state of matter. Also, the term ''phase'' is sometimes used to refer to a set of equilibrium states demarcated in terms of state variables such as pressure and temperature by a phase boundary on a phase diagram. Becaus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colour Confinement
In quantum chromodynamics (QCD), color confinement, often simply called confinement, is the phenomenon that color-charged particles (such as quarks and gluons) cannot be isolated, and therefore cannot be directly observed in normal conditions below the Hagedorn temperature of approximately 2 terakelvin (corresponding to energies of approximately 130–140 MeV per particle). Quarks and gluons must clump together to form hadrons. The two main types of hadron are the mesons (one quark, one antiquark) and the baryons (three quarks). In addition, colorless glueballs formed only of gluons are also consistent with confinement, though difficult to identify experimentally. Quarks and gluons cannot be separated from their parent hadron without producing new hadrons. Origin There is not yet an analytic proof of color confinement in any non-abelian gauge theory. The phenomenon can be understood qualitatively by noting that the force-carrying gluons of QCD have color charge, unlike the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
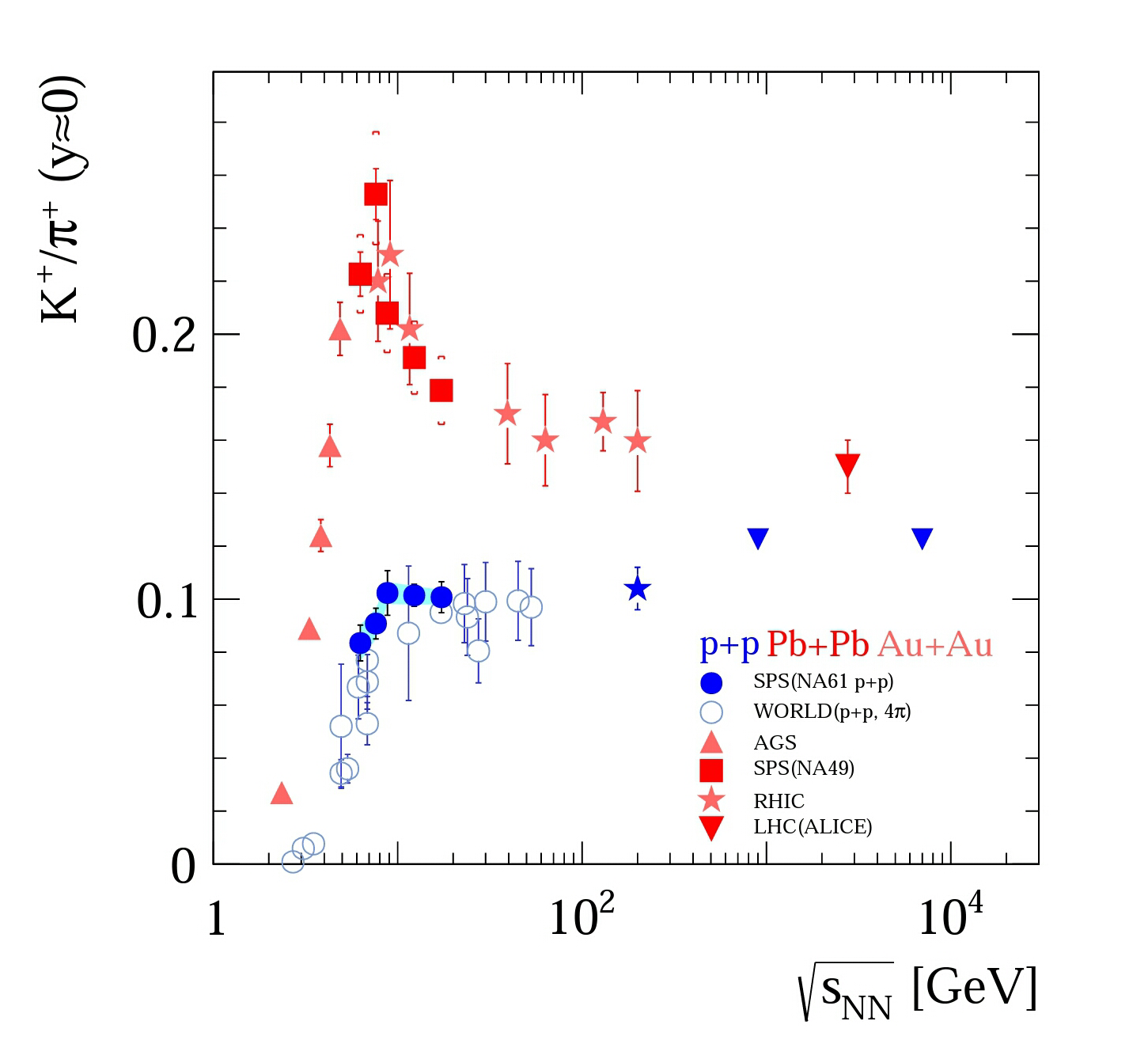
Onset Of Deconfinement
The onset of deconfinement refers to the beginning of the creation of deconfined states of strongly interacting matter produced in nucleus-nucleus collisions with increasing collision energy (a quark–gluon plasma). The onset of deconfinement was predicted by Marek Gazdzicki and Mark I. Gorenstein to be located in the low energy range of the Super Proton Synchrotron (SPS) at the European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN). These predictions have been confirmed by the NA49 experiment at the CERN SPS within the energy scan programme. The most famous of these is the "horn" in the ratio of mean multiplicities of positively charged kaons and pions observed in collisions of two lead nuclei at the low energies of the SPS. Strangeness production In particle physics, strangeness ("''S''") is a property of particles, expressed as a quantum number, for describing decay of particles in strong and electromagnetic interactions which occur in a short period of time. The str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fractional Quantum Hall Effect
The fractional quantum Hall effect (FQHE) is a physical phenomenon in which the Hall conductance of 2-dimensional (2D) electrons shows precisely quantized plateaus at fractional values of e^2/h. It is a property of a collective state in which electrons bind magnetic flux lines to make new quasiparticles, and excitations have a fractional elementary charge and possibly also fractional statistics. The 1998 Nobel Prize in Physics was awarded to Robert Laughlin, Horst Störmer, and Daniel Tsui "for their discovery of a new form of quantum fluid with fractionally charged excitations" Laughlin's explanation only applies to fillings \nu = 1/m where m is an odd integer. The microscopic origin of the FQHE is a major research topic in condensed matter physics. Introduction The fractional quantum Hall effect (FQHE) is a collective behavior in a 2D system of electrons. In particular magnetic fields, the electron gas condenses into a remarkable liquid state, which is very delicate, requ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |