|
Decision Curve Analysis
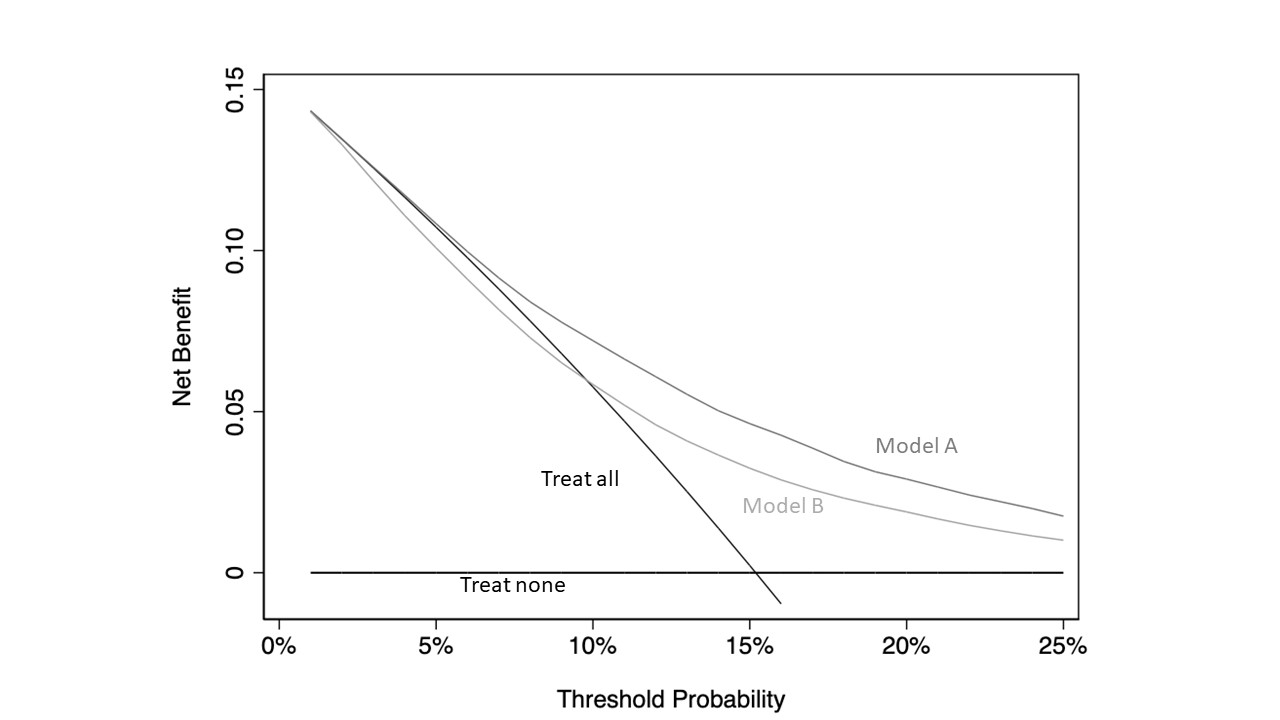
Decision curve analysis evaluates a predictor for an event as a probability threshold is varied, typically by showing a graphical plot of net benefit against threshold probability. By convention, the default strategies of assuming that all or no observations are positive are also plotted. Decision curve analysis is distinguished from other statistical methods like receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves by the ability to assess the clinical value of a predictor. Applying decision curve analysis can determine whether using a predictor to make clinical decisions like performing biopsy will provide benefit over alternative decision criteria, given a specified threshold probability. Threshold probability is defined as the minimum probability of an event at which a decision-maker would take a given action, for instance, the probability of cancer at which a doctor would order a biopsy. A lower threshold probability implies a greater concern about the event (e.g. a patient w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graph Of A Function
In mathematics, the graph of a function f is the set of ordered pairs (x, y), where f(x) = y. In the common case where x and f(x) are real numbers, these pairs are Cartesian coordinates of points in two-dimensional space and thus form a subset of this plane. In the case of functions of two variables, that is functions whose domain consists of pairs (x, y), the graph usually refers to the set of ordered triples (x, y, z) where f(x,y) = z, instead of the pairs ((x, y), z) as in the definition above. This set is a subset of three-dimensional space; for a continuous real-valued function of two real variables, it is a surface. In science, engineering, technology, finance, and other areas, graphs are tools used for many purposes. In the simplest case one variable is plotted as a function of another, typically using rectangular axes; see '' Plot (graphics)'' for details. A graph of a function is a special case of a relation. In the modern foundations of mathematics, and, typicall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Receiver Operating Characteristic
A receiver operating characteristic curve, or ROC curve, is a graphical plot that illustrates the diagnostic ability of a binary classifier system as its discrimination threshold is varied. The method was originally developed for operators of military radar receivers starting in 1941, which led to its name. The ROC curve is created by plotting the true positive rate (TPR) against the false positive rate (FPR) at various threshold settings. The true-positive rate is also known as sensitivity, recall or ''probability of detection''. The false-positive rate is also known as ''probability of false alarm'' and can be calculated as (1 − specificity). The ROC can also be thought of as a plot of the power as a function of the Type I Error of the decision rule (when the performance is calculated from just a sample of the population, it can be thought of as estimators of these quantities). The ROC curve is thus the sensitivity or recall as a function of fall-out. In general, if the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binary Classification
Binary classification is the task of classifying the elements of a set into two groups (each called ''class'') on the basis of a classification rule. Typical binary classification problems include: * Medical testing to determine if a patient has certain disease or not; * Quality control in industry, deciding whether a specification has been met; * In information retrieval, deciding whether a page should be in the result set of a search or not. Binary classification is dichotomization applied to a practical situation. In many practical binary classification problems, the two groups are not symmetric, and rather than overall accuracy, the relative proportion of different types of errors is of interest. For example, in medical testing, detecting a disease when it is not present (a ''false positive'') is considered differently from not detecting a disease when it is present (a ''false negative''). Statistical binary classification Statistical classification is a problem studied in ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decision Theory
Decision theory (or the theory of choice; not to be confused with choice theory) is a branch of applied probability theory concerned with the theory of making decisions based on assigning probabilities to various factors and assigning numerical consequences to the outcome. There are three branches of decision theory: # Normative decision theory: Concerned with the identification of optimal decisions, where optimality is often determined by considering an ideal decision-maker who is able to calculate with perfect accuracy and is in some sense fully rational. # Prescriptive decision theory: Concerned with describing observed behaviors through the use of conceptual models, under the assumption that those making the decisions are behaving under some consistent rules. # Descriptive decision theory: Analyzes how individuals actually make the decisions that they do. Decision theory is closely related to the field of game theory and is an interdisciplinary topic, studied by econom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Expected Value
In probability theory, the expected value (also called expectation, expectancy, mathematical expectation, mean, average, or first moment) is a generalization of the weighted average. Informally, the expected value is the arithmetic mean of a large number of independently selected outcomes of a random variable. The expected value of a random variable with a finite number of outcomes is a weighted average of all possible outcomes. In the case of a continuum of possible outcomes, the expectation is defined by integration. In the axiomatic foundation for probability provided by measure theory, the expectation is given by Lebesgue integration. The expected value of a random variable is often denoted by , , or , with also often stylized as or \mathbb. History The idea of the expected value originated in the middle of the 17th century from the study of the so-called problem of points, which seeks to divide the stakes ''in a fair way'' between two players, who have to end th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Utility
As a topic of economics, utility is used to model worth or value. Its usage has evolved significantly over time. The term was introduced initially as a measure of pleasure or happiness as part of the theory of utilitarianism by moral philosophers such as Jeremy Bentham and John Stuart Mill. The term has been adapted and reapplied within neoclassical economics, which dominates modern economic theory, as a utility function that represents a single consumer's preference ordering over a choice set but is not comparable across consumers. This concept of utility is personal and based on choice rather than on pleasure received, and so is specified more rigorously than the original concept but makes it less useful (and controversial) for ethical decisions. Utility function Consider a set of alternatives among which a person can make a preference ordering. The utility obtained from these alternatives is an unknown function of the utilities obtained from each alternative, not the sum of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decision Analysis
Decision analysis (DA) is the discipline comprising the philosophy, methodology, and professional practice necessary to address important decisions in a formal manner. Decision analysis includes many procedures, methods, and tools for identifying, clearly representing, and formally assessing important aspects of a decision; for prescribing a recommended course of action by applying the maximum expected-utility axiom to a well-formed representation of the decision; and for translating the formal representation of a decision and its corresponding recommendation into insight for the decision maker, and other corporate and non-corporate stakeholders. History In 1931, mathematical philosopher Frank Ramsey pioneered the idea of subjective probability as a representation of an individual’s beliefs or uncertainties. Then, in the 1940s, mathematician John von Neumann and economist Oskar Morgenstern developed an axiomatic basis for utility theory as a way of expressing an individual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Utility
As a topic of economics, utility is used to model worth or value. Its usage has evolved significantly over time. The term was introduced initially as a measure of pleasure or happiness as part of the theory of utilitarianism by moral philosophers such as Jeremy Bentham and John Stuart Mill. The term has been adapted and reapplied within neoclassical economics, which dominates modern economic theory, as a utility function that represents a single consumer's preference ordering over a choice set but is not comparable across consumers. This concept of utility is personal and based on choice rather than on pleasure received, and so is specified more rigorously than the original concept but makes it less useful (and controversial) for ethical decisions. Utility function Consider a set of alternatives among which a person can make a preference ordering. The utility obtained from these alternatives is an unknown function of the utilities obtained from each alternative, not the sum of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dca Example 2
DCA may refer to: Computers * Document Content Architecture, an IBM document standard * Dynamic Channel Allocation/Assignment, in wireless networks * DTS Coherent Acoustics in DTS (sound system) Military * Defence Cyber Agency, a tri-service command of the Indian Armed Forces * Defense Communications Agency, former name of US Defense Information Systems Agency * Defensive counter air (''Défense contre les aéronefs''), French term for air defense * Deputy Commandant for Aviation, principle advisor on all aviation matters in the United States Marine Corps Organizations * California Department of Consumer Affairs * Department for Constitutional Affairs of the UK government, 2003-2007 * DCA Design * Department of Civil Aviation (Australia) * Department of Civil Aviation (Thailand) * Digital Communications Associates, US company * Diyanet Center of America, Lanham, Maryland * Drum Corps Associates, a governing body of drum corps in North America * Dundee Contemporary Arts, Sco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statistical Analysis
Statistical inference is the process of using data analysis to infer properties of an underlying distribution of probability.Upton, G., Cook, I. (2008) ''Oxford Dictionary of Statistics'', OUP. . Inferential statistical analysis infers properties of a population, for example by testing hypotheses and deriving estimates. It is assumed that the observed data set is sampled from a larger population. Inferential statistics can be contrasted with descriptive statistics. Descriptive statistics is solely concerned with properties of the observed data, and it does not rest on the assumption that the data come from a larger population. In machine learning, the term ''inference'' is sometimes used instead to mean "make a prediction, by evaluating an already trained model"; in this context inferring properties of the model is referred to as ''training'' or ''learning'' (rather than ''inference''), and using a model for prediction is referred to as ''inference'' (instead of ''prediction''); ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decision Analysis
Decision analysis (DA) is the discipline comprising the philosophy, methodology, and professional practice necessary to address important decisions in a formal manner. Decision analysis includes many procedures, methods, and tools for identifying, clearly representing, and formally assessing important aspects of a decision; for prescribing a recommended course of action by applying the maximum expected-utility axiom to a well-formed representation of the decision; and for translating the formal representation of a decision and its corresponding recommendation into insight for the decision maker, and other corporate and non-corporate stakeholders. History In 1931, mathematical philosopher Frank Ramsey pioneered the idea of subjective probability as a representation of an individual’s beliefs or uncertainties. Then, in the 1940s, mathematician John von Neumann and economist Oskar Morgenstern developed an axiomatic basis for utility theory as a way of expressing an individual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |