|
Decidua
The decidua is the modified mucosal lining of the uterus (that is, modified endometrium) that forms every month, in preparation for pregnancy. It is shed off each month when there is no fertilised egg to support. The decidua is under the influence of progesterone. Endometrial cells become highly characteristic. The decidua forms the maternal part of the placenta and remains for the duration of the pregnancy. After birth the decidua is shed together with the placenta. Structure The part of the decidua that interacts with the trophoblast is the ''decidua basalis'' (also called ''decidua placentalis''), while the ''decidua capsularis'' grows over the embryo on the luminal side, enclosing it into the endometrium. The remainder of the decidua is termed the ''decidua parietalis'' or ''decidua vera'', and it will fuse with the decidua capsularis by the fourth month of gestation. Three morphologically distinct layers of the decidua basalis can then be described: * Compact outer laye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decidualization
Decidualization is a process that results in significant changes to cells of the endometrium in preparation for, and during, pregnancy. This includes morphological and functional changes (the decidual reaction) to endometrial stromal cells (ESCs), the presence of decidual white blood cells (leukocytes), and vascular changes to maternal arteries. The sum of these changes results in the endometrium changing into a structure called the decidua. In humans, the decidua is shed during childbirth. Decidualization plays an important role in promoting placenta formation between a mother and her fetus by mediating the invasiveness of trophoblast cells. It also triggers the production of cellular and molecular factors that result in structural changes, or remodeling, of maternal spiral arteries. Decidualization is required in some mammalian species where embryo implantation and trophoblast cell invasion of the endometrium occurs, also known as hemochorial placentation. This allows materna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decidualization
Decidualization is a process that results in significant changes to cells of the endometrium in preparation for, and during, pregnancy. This includes morphological and functional changes (the decidual reaction) to endometrial stromal cells (ESCs), the presence of decidual white blood cells (leukocytes), and vascular changes to maternal arteries. The sum of these changes results in the endometrium changing into a structure called the decidua. In humans, the decidua is shed during childbirth. Decidualization plays an important role in promoting placenta formation between a mother and her fetus by mediating the invasiveness of trophoblast cells. It also triggers the production of cellular and molecular factors that result in structural changes, or remodeling, of maternal spiral arteries. Decidualization is required in some mammalian species where embryo implantation and trophoblast cell invasion of the endometrium occurs, also known as hemochorial placentation. This allows materna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Implantation (human Embryo)
Implantation (nidation) is the stage in the embryonic development of Placental mammal, mammals in which the blastocyst hatches as the embryo, adheres, and invades into the wall of the female's uterus. Implantation is the first stage of gestation, and when successful the female is considered to be pregnancy, pregnant. In a woman, an implanted embryo is detected by the presence of increased levels of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) in a pregnancy test. The implanted embryo will receive oxygen and nutrients in order to grow. There is an extensive variation in the type of Trophoblast, trophoblast cells, and structures of the placenta across the different species of mammals. Of the five recognised stages of implantation including two pre-implantation stages that precede placentation, the first four are similar across the species. The five stages are migration and hatching, pre-contact, attachment, adhesion, and invasion. The two pre-implantation stages are associated with the Pre-em ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
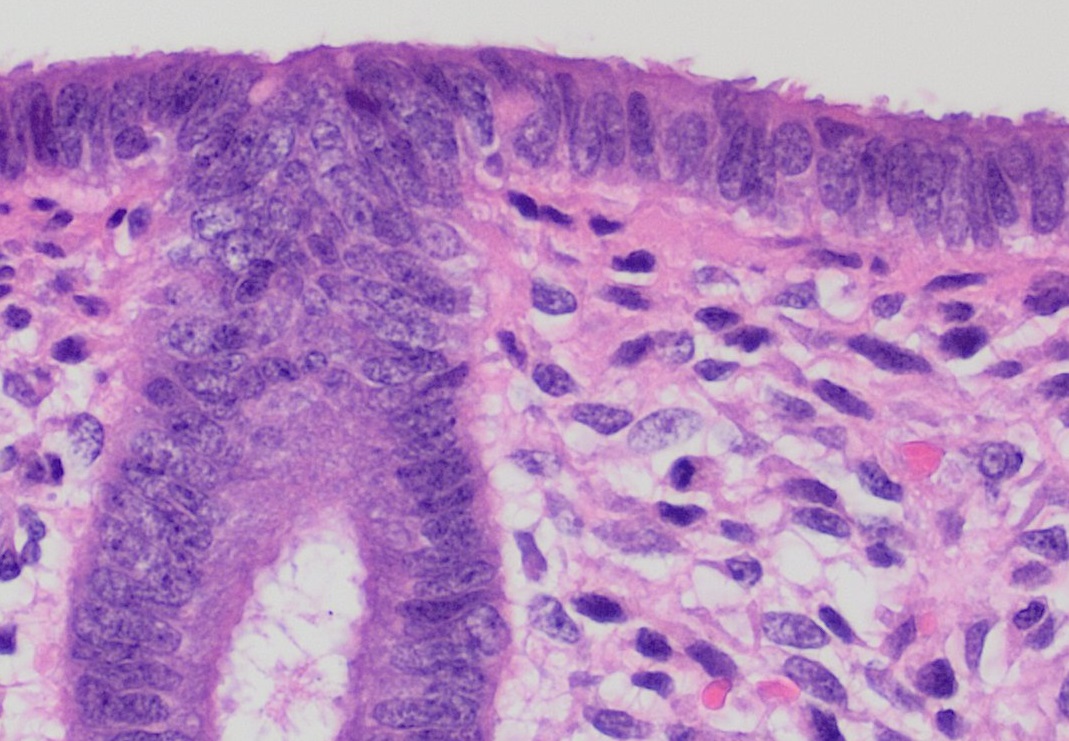
Endometrium Ocp Use3
The endometrium is the inner epithelial layer, along with its mucous membrane, of the mammalian uterus. It has a basal layer and a functional layer: the basal layer contains stem cells which regenerate the functional layer. The functional layer thickens and then is shed during menstruation in humans and some other mammals, including apes, Old World monkeys, some species of bat, the elephant shrew and the Cairo spiny mouse. In most other mammals, the endometrium is reabsorbed in the estrous cycle. During pregnancy, the glands and blood vessels in the endometrium further increase in size and number. Vascular spaces fuse and become interconnected, forming the placenta, which supplies oxygen and nutrition to the embryo and fetus.Blue Histology - Female Reproductive System . ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endometrium
The endometrium is the inner epithelial layer, along with its mucous membrane, of the mammalian uterus. It has a basal layer and a functional layer: the basal layer contains stem cells which regenerate the functional layer. The functional layer thickens and then is shed during menstruation in humans and some other mammals, including apes, Old World monkeys, some species of bat, the elephant shrew and the Cairo spiny mouse. In most other mammals, the endometrium is reabsorbed in the estrous cycle. During pregnancy, the glands and blood vessels in the endometrium further increase in size and number. Vascular spaces fuse and become interconnected, forming the placenta, which supplies oxygen and nutrition to the embryo and fetus.Blue Histology - Female Reproductive System . School ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decidual Cells
Before the fertilized ovum reaches the uterus, the mucous membrane of the body of the uterus undergoes important changes and is then known as the decidua. The thickness and vascularity of the mucous membrane are greatly increased; its glands are elongated and open on its free surface by funnel-shaped orifices, while their deeper portions are tortuous and dilated into irregular spaces. The interglandular tissue is also increased in quantity, and is crowded with large round, oval, or polygonal cells, termed decidual cells. Their enlargement is due to glycogen and lipid accumulation in the cytoplasm allowing these cells to provide a rich source of nutrition for the developing embryo. Decidual cells are also thought to control the invasion of the endometrium by trophoblast cells. Experimentally, human endometrial stromal cells can be decidualized in culture by using analogs of cAMP and progesterone. The cells will exhibit a decidualized phenotype and display upregulation of common deci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemochorial Placentation
Placentation refers to the formation, type and structure, or arrangement of the placenta. The function of placentation is to transfer nutrients, respiratory gases, and water from maternal tissue to a growing embryo, and in some instances to remove waste from the embryo. Placentation is best known in live-bearing mammals ( theria), but also occurs in some fish, reptiles, amphibians, a diversity of invertebrates, and flowering plants. In vertebrates, placentas have evolved more than 100 times independently, with the majority of these instances occurring in squamate reptiles. The placenta can be defined as an organ formed by the sustained apposition or fusion of fetal membranes and parental tissue for physiological exchange. This definition is modified from the original Mossman (1937) definition, which constrained placentation in animals to only those instances where it occurred in the uterus. In mammals In live bearing mammals, the placenta forms after the embryo implants into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Menstrual Cycle
The menstrual cycle is a series of natural changes in hormone production and the structures of the uterus and ovaries of the female reproductive system that make pregnancy possible. The ovarian cycle controls the production and release of eggs and the cyclic release of estrogen and progesterone. The uterine cycle governs the preparation and maintenance of the lining of the uterus (womb) to receive an embryo. These cycles are concurrent and coordinated, normally last between 21 and 35 days, with a median length of 28 days, and continue for about 30–45 years. Naturally occurring hormones drive the cycles; the cyclical rise and fall of the follicle stimulating hormone prompts the production and growth of oocytes (immature egg cells). The hormone estrogen stimulates the uterus lining ( endometrium) to thicken to accommodate an embryo should fertilization occur. The blood supply of the thickened lining provides nutrients to a successfully implanted embryo. If implantation does n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Placenta
The placenta is a temporary embryonic and later fetal organ that begins developing from the blastocyst shortly after implantation. It plays critical roles in facilitating nutrient, gas and waste exchange between the physically separate maternal and fetal circulations, and is an important endocrine organ, producing hormones that regulate both maternal and fetal physiology during pregnancy. The placenta connects to the fetus via the umbilical cord, and on the opposite aspect to the maternal uterus in a species-dependent manner. In humans, a thin layer of maternal decidual (endometrial) tissue comes away with the placenta when it is expelled from the uterus following birth (sometimes incorrectly referred to as the 'maternal part' of the placenta). Placentas are a defining characteristic of placental mammals, but are also found in marsupials and some non-mammals with varying levels of development. Mammalian placentas probably first evolved about 150 million to 200 million years ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Placenta Accreta
Placenta accreta occurs when all or part of the placenta attaches abnormally to the ''myometrium'' (the muscular layer of the uterine wall). Three grades of abnormal placental attachment are defined according to the depth of attachment and invasion into the muscular layers of the uterus: # ''Accreta – chorionic villi'' attached to the myometrium, rather than being restricted within the ''decidua basalis''. # ''Increta – chorionic villi'' invaded into the ''myometrium''. # ''Percreta – chorionic villi'' invaded through the '' perimetrium'' (uterine serosa). Because of abnormal attachment to the myometrium, placenta accreta is associated with an increased risk of heavy bleeding at the time of attempted vaginal delivery. The need for transfusion of blood products is frequent, and surgical removal of the uterus ( hysterectomy) is sometimes required to control life-threatening bleeding. Rates of placenta accreta are increasing. As of 2016, placenta accreta affects an estimated 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uterine Natural Killer Cells
Uterine natural killer cells make up approximately 70% of maternal lymphocytes during pregnancy, occupying both the decidua basalis of the endometrium at the implantation site and the mesometrial lymphoid aggregate of pregnancy (MLAp) that surrounds the blood vessels supplying the placenta. This number is at its peak in early pregnancy but declines at parturition. Morphology General Most studies of uterine natural killer cells use murine cells to model the human equivalent: unless stated otherwise, this section focuses on murine uterine natural killer cells. Uterine natural killer cells are large, granular, rounded or oval lymphocytes. On microscopic examination, they may have one or more cytoplasmic projections and/or be binucleate. Characteristically they contain eosinophilic granules that stain darkly with PAS, indicating the presence of glycoproteins. These granules usually appear regular (but some can be irregularly shaped), and they grow in size and number until appro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trophoblast
The trophoblast (from Greek : to feed; and : germinator) is the outer layer of cells of the blastocyst. Trophoblasts are present four days after fertilization in humans. They provide nutrients to the embryo and develop into a large part of the placenta. They form during the first stage of pregnancy and are the first cells to differentiate from the fertilized egg to become extraembryonic structures that do not directly contribute to the embryo. After gastrulation, the trophoblast is contiguous with the ectoderm of the embryo and is referred to as the trophectoderm. After the first differentiation, the cells in the human embryo lose their totipotency and are no longer totipotent stem cells because they cannot form a trophoblast. They are now pluripotent stem cells. Structure The trophoblast proliferates and differentiates into two cell layers at approximately six days after fertilization for humans. Function Trophoblasts are specialized cells of the placenta that play an i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |