|
Death In 19th-century Mormonism
Death in 19th-century Mormonism involved several unique religious rituals, cultural customs, and eschatological beliefs. In the years of the Church of Christ and, later, in the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (LDS Church), death played a prominent role in the lives of members due to various diseases, forced removal from settlements, the harsh nature of life on the American frontier, and the lack of medical knowledge at the time. Mormon mortality rates climbed through most of the century until a permanent settlement in Utah Territory was established and advances in medical science were made. Before these improvements, the commonality of death in Latter-day Saint communities produced a distinct culture surrounding the death of a member of the community. The dying were either blessed to be healed or to be received into heaven, depending on the person's wishes. A phenomenon known as the "beautiful death" set forth traditions such as family and friends gathering around a pers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Smith
Joseph Smith Jr. (December 23, 1805June 27, 1844) was an American religious leader and founder of Mormonism and the Latter Day Saint movement. When he was 24, Smith published the Book of Mormon. By the time of his death, 14 years later, he had attracted tens of thousands of followers and founded a religion that continues to the present with millions of global adherents. Smith was born in Sharon, Vermont. By 1817, he had moved with his family to Western New York, the site of intense religious revivalism during the Second Great Awakening. Smith said he experienced a series of visions, including one in 1820 during which he saw "two personages" (whom he eventually described as God the Father and Jesus Christ), and another in 1823 in which an angel directed him to a buried book of golden plates inscribed with a Judeo-Christian history of an ancient American civilization. In 1830, Smith published what he said was an English translation of these plates called the ''Book of Mormo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David W
David (; , "beloved one") (traditional spelling), , ''Dāwūd''; grc-koi, Δαυΐδ, Dauíd; la, Davidus, David; gez , ዳዊት, ''Dawit''; xcl, Դաւիթ, ''Dawitʿ''; cu, Давíдъ, ''Davidŭ''; possibly meaning "beloved one". was, according to the Hebrew Bible, the third king of the United Kingdom of Israel. In the Books of Samuel, he is described as a young shepherd and harpist who gains fame by slaying Goliath, a champion of the Philistines, in southern Canaan. David becomes a favourite of Saul, the first king of Israel; he also forges a notably close friendship with Jonathan, a son of Saul. However, under the paranoia that David is seeking to usurp the throne, Saul attempts to kill David, forcing the latter to go into hiding and effectively operate as a fugitive for several years. After Saul and Jonathan are both killed in battle against the Philistines, a 30-year-old David is anointed king over all of Israel and Judah. Following his rise to power, David ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
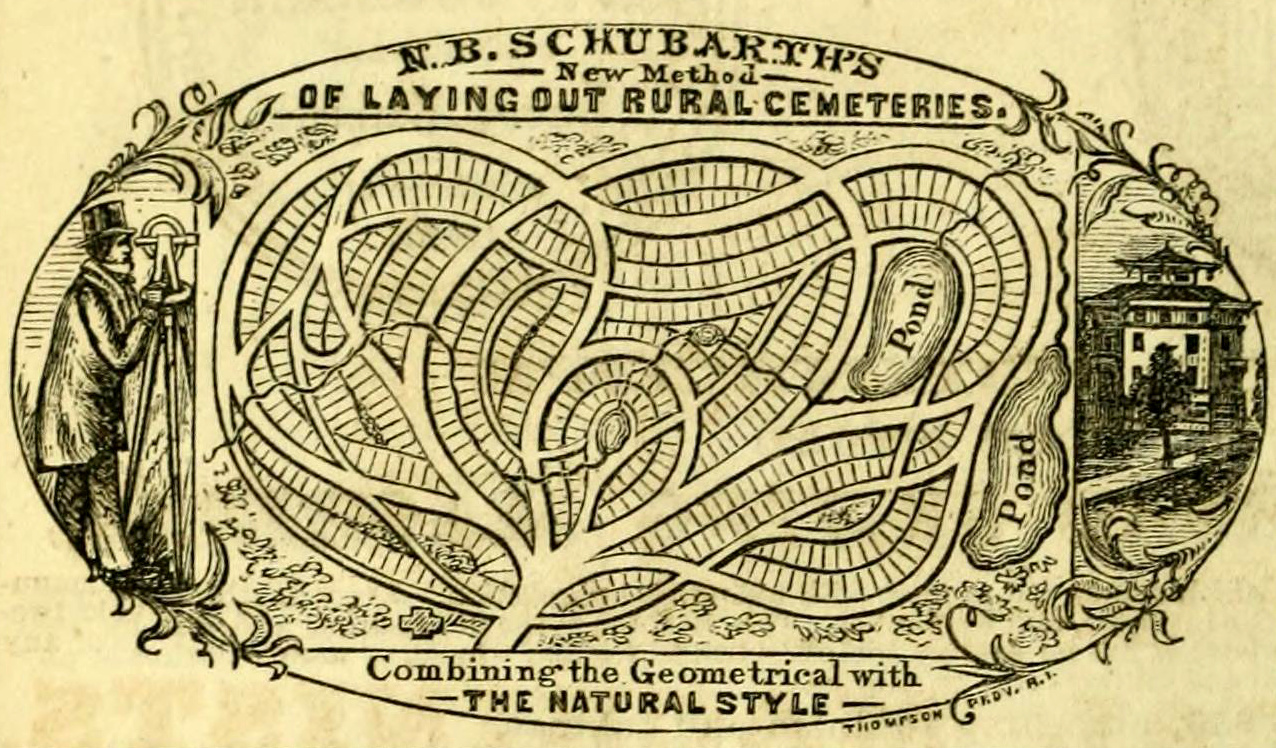
Rural Cemetery
A rural cemetery or garden cemetery is a style of cemetery that became popular in the United States and Europe in the mid-nineteenth century due to the overcrowding and health concerns of urban cemeteries. They were typically built one to five miles outside of the city, far enough to be separated from the city, but close enough for visitors. They often contain elaborate monuments, memorials, and mausoleums in a landscaped park-like setting. The rural cemetery movement mirrored changing attitudes toward death in the nineteenth century. Images of hope and immortality were popular in rural cemeteries in contrast to the puritanical pessimism depicted in earlier cemeteries. Statues and memorials included depictions of angels and cherubs as well as botanical motifs such as ivy representing memory, oak leaves for immortality, poppies for sleep and acorns for life. From their inception, they were intended as civic institutions designed for public use. Before the widespread developmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Far West, Missouri
Far West was a settlement of the Latter Day Saint movement in Caldwell County, Missouri, United States, during the late 1830s. It is recognized as a historic site by the U.S. National Register of Historic Places, added to the register in 1970. It is owned and maintained by the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints. Foundation and early history The town was founded by Missouri leaders of the church, W. W. Phelps and John Whitmer in August 1836 shortly before the county's creation. The town was platted originally as a square area, centered on a public square which was to house a temple. The design of the town resembled the plan of Joseph Smith Jr. (the first modern-day prophet of the Latter Day Saint Movement) for the City of Zion, which had been planned to be built in the town of Independence, Missouri. As the town of Far West grew, the plat was extended to . Early Latter-day Saints began to settle in northwestern Missouri soon after the church was organized in 1830. Acc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statue In Winter Quarters—a Memorial To The Pioneers Who Died
A statue is a free-standing sculpture in which the realistic, full-length figures of persons or animals are carved or cast in a durable material such as wood, metal or stone. Typical statues are life-sized or close to life-size; a sculpture that represents persons or animals in full figure but that is small enough to lift and carry is a statuette or figurine, whilst one more than twice life-size is a colossal statue. Statues have been produced in many cultures from prehistory to the present; the oldest-known statue dating to about 30,000 years ago. Statues represent many different people and animals, real and mythical. Many statues are placed in public places as public art. The world's tallest statue, ''Statue of Unity'', is tall and is located near the Narmada dam in Gujarat, India. Color Ancient statues often show the bare surface of the material of which they are made. For example, many people associate Greek classical art with white marble sculpture, but there is evidenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Word Of Wisdom
The "Word of Wisdom" is the common name of an 1833 section of the Doctrine and Covenants, a book considered by many churches within the Latter Day Saint movement to be a sacred text. The section defines beliefs regarding certain drugs, nutritious ingredients in general, and the counsel to eat meat sparingly; it also offers promises to those who follow the guidance of the Word of Wisdom. As practiced by the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (LDS Church), the largest Latter Day Saint denomination, the Word of Wisdom explicitly prohibits the consumption of alcohol, tobacco, tea, and coffee, and recreational drug use, and encourages healthy practices such as nutritious eating, the sparing use of meat, regular exercise, proper hygiene, and getting sufficient rest. Compliance with the Word of Wisdom is necessary in the LDS Church to become a member and to participate in various church functions, however, violation of the code is not normally cause for a church membership counc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Botanical Medicine
Herbal medicine (also herbalism) is the study of pharmacognosy and the use of medicinal plants, which are a basis of traditional medicine. With worldwide research into pharmacology, some herbal medicines have been translated into modern remedies, such as the anti-malarial group of drugs called artemisinin isolated from ''Artemisia annua'', a herb that was known in Chinese medicine to treat fever. There is limited scientific evidence for the safety and efficacy of plants used in 21st century herbalism, which generally does not provide standards for purity or dosage. The scope of herbal medicine commonly includes fungal and bee products, as well as minerals, shells and certain animal parts. Herbal medicine is also called phytomedicine or phytotherapy. Paraherbalism describes alternative and pseudoscientific practices of using unrefined plant or animal extracts as unproven medicines or health-promoting agents. Paraherbalism relies on the belief that preserving various substances fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alvin Smith (brother Of Joseph Smith)
Alvin Smith (February 11, 1798 – November 19, 1823) was the eldest brother of Joseph Smith, founder of the Latter Day Saint movement. Alvin took a leading role in helping the Smith family work toward paying their debts and building their home. His death at age 25 resulted in his younger brothers Hyrum and Joseph taking more of a leading role in family affairs. A vision by Joseph Smith showed Alvin, who was not baptized while alive, in the celestial kingdom, which is the highest of the degrees of glory. His presence in the life of young Joseph Smith and in that vision played a significant role in the establishment of the Latter Day Saint doctrines of redemption of those who die without a knowledge of the gospel, as well as the practice of baptism for the dead in the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (LDS Church). Early life Alvin Smith was born in 1798, the first surviving child of Joseph Smith Sr. and Lucy Mack Smith. During his youth, Smith worked as a carpenter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calomel
Calomel is a mercury chloride mineral with formula Hg2Cl2 (see mercury(I) chloride). The name derives from Greek ''kalos'' (beautiful) and ''melas'' (black) because it turns black on reaction with ammonia. This was known to alchemists. Calomel occurs as a secondary mineral which forms as an alteration product in mercury deposits. It occurs with native mercury, amalgam, cinnabar, mercurian tetrahedrite, eglestonite, terlinguaite, montroydite, kleinite, moschelite, kadyrelite, kuzminite, chursinite, kelyanite, calcite, limonite and various clay minerals. The type locality is Moschellandsburg, Alsenz-Obermoschel, Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. History The substance later known as calomel was first documented in ancient Persia by medical historian Rhazes in year 850. Only a few of the compounds he mentioned could be positively identified as calomel, as not every alchemist disclosed what compounds they used in their drugs. Calomel first entered Western medical literature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states that had seceded. The central cause of the war was the dispute over whether slavery would be permitted to expand into the western territories, leading to more slave states, or be prevented from doing so, which was widely believed would place slavery on a course of ultimate extinction. Decades of political controversy over slavery were brought to a head by the victory in the 1860 U.S. presidential election of Abraham Lincoln, who opposed slavery's expansion into the west. An initial seven southern slave states responded to Lincoln's victory by seceding from the United States and, in 1861, forming the Confederacy. The Confederacy seized U.S. forts and other federal assets within their borders. Led by Confederate President Jefferson Davis, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)

