|
De Dion-Bouton Tricycle
The De Dion-Bouton tricycle was the most successful motor vehicle in Europe from 1897 until 1901. With about 15,000 copies sold, the de-Dion-Bouton motor tricycle scored the first breakthrough for the distribution of motor vehicles. In particular the fast-running de Dion-Bouton engine set new standards for vehicular motors, and is regarded as the precursor of all motorcycle engines. Development Jules-Albert de Dion, the engineer of Georges Bouton and his brother-in-law Charles-Armand Trépardoux, founded a workshop in 1882 near Paris. The first project was the production of steam boilers, then a fairly successful steam-powered tricycle from 1887, which should have already reached a speed of 65 km/h. Trépardoux, who wished to continue the further development of steam engines, resigned from the company in 1893; De Dion and Bouton opted for the development of gasoline engines after they viewed Daimler's engines at the Paris Exposition of 1889. Motor In 1895, the first four- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1900 De Dion-Bouton Tricycle
Nineteen or 19 may refer to: * 19 (number), the natural number following 18 and preceding 20 * one of the years 19 BC, AD 19, 1919, 2019 Films * ''19'' (film), a 2001 Japanese film * ''Nineteen'' (film), a 1987 science fiction film Music * 19 (band), a Japanese pop music duo Albums * ''19'' (Adele album), 2008 * ''19'', a 2003 album by Alsou * ''19'', a 2006 album by Evan Yo * ''19'', a 2018 album by MHD * ''19'', one half of the double album ''63/19'' by Kool A.D. * ''Number Nineteen'', a 1971 album by American jazz pianist Mal Waldron * ''XIX'' (EP), a 2019 EP by 1the9 Songs * "19" (song), a 1985 song by British musician Paul Hardcastle. * "Nineteen", a song by Bad4Good from the 1992 album ''Refugee'' * "Nineteen", a song by Karma to Burn from the 2001 album ''Almost Heathen''. * "Nineteen" (song), a 2007 song by American singer Billy Ray Cyrus. * "Nineteen", a song by Tegan and Sara from the 2007 album '' The Con''. * "XIX" (song), a 2014 song by Slipknot. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hildebrand & Wolfmüller
The Hildebrand & Wolfmüller was the world's first production motorcycle. Heinrich and Wilhelm Hildebrand were steam-engine engineers before they teamed up with Alois Wolfmüller to produce their internal combustion ''Motorrad'' in Munich in 1894. Mechanical details The Hildebrand & Wolfmüller patent of 20 January 1894, No. 78553 describes a two-cylinder, four-stroke engine, with a bore and stroke of . It produced @ 240 rpm propelling a weight of up to a maximum speed of .The fuel-air mixture from the surface carburettor was regulated by a valve operated by controls on the handlebar. The engine, which was positioned flat in the frame, used hot tube ignition with the tube heater in front of the cylinder heads. The tube heater was ventilated by the lower downtubes while the upper downtubes held lubricating oil. Some design details were carried over from a steam-powered prototype made by the Hildebrand brothers in 1889, including the water tank shaped to form the rear m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adler (automobile)
Adler was a German automobile and motorcycle manufacturer from 1900 until 1957. The'' 'Adler' '' name is German for 'eagle'. History The Adler factory produced bicycles, typewriters, motorcycles and calculators in addition to cars. Before World War I, the company used De Dion two- and four-cylinder engines in cars that ranged from 1032 cc to 9081 cc; beginning in 1902 (the year Edmund Rumpler became technical director), they used their own engines as well. These cars, driven by Erwin Kleyer and Otto Kleyer (sons of the company founder Heinrich Kleyer) and by Alfred Theves won many sporting events. In the 1920s, Karl Irion raced many Adlers; popular models of the period included the 2298 cc, 1550 cc, and 4700 cc four-cylinders and the 2580 cc six-cylinders. A few of the Standard models, built between 1927 and 1934, featured Gropius-designed coachwork. The Adler Standard 6, which entered volume production in 1927, had a 2540 cc or 2916 cc six-cylinder engine, while the Adler ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minerva (automobile)
Minerva was a Belgian firm active from 1902 to 1938 and a manufacturer of luxury automobiles. The company became defunct in 1956. History In 1883, a young Dutchman, Sylvain de Jong (1868–1928) settled in Antwerp, Belgium. Bicycles and motorcycles Minerva started out manufacturing standard safety bicycles in 1897, before in 1900 expanding into light cars and "motocyclettes", particularly motorized bicycles which were a forerunner of motorcycles. They produced lightweight clip-on engines that mounted below the bicycle front down tube, specifically for Minerva bicycles, but also available in kit form suitable for almost any bicycle. The engine drove a belt turning a large gear wheel attached to the side of the rear wheel opposite to the chain. By 1901 the kit engine was a 211cc unit developing 1.5 hp, comfortably cruising at at 1,500 rpm, capable of a top speed of , and getting fuel consumption in the range of . These kits were exported around the world to countries incl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antoine (automobile)
The Antoine was a Belgian automobile manufactured by Victor Antoine of Liège, an engine manufacturer, from 1900 to 1903. At least two models were offered. One was a voiturette A voiturette is a miniature automobile. History ''Voiturette'' was first registered by Léon Bollée in 1895 to name his new motor tricycle. The term became so popular in the early years of the motor industry that it was used by many makers t .... The other, offered in 1903, was a 15/25 hp car. Veteran vehicles Defunct motor vehicle manufacturers of Belgium {{Veteran-auto-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Gold Mark
The German mark (german: Goldmark ; sign: ℳ) was the currency of the German Empire, which spanned from 1871 to 1918. The mark was paired with the minor unit of the pfennig (₰); 100 pfennigs were equivalent to 1 mark. The mark was on the gold standard from 1871–1914, but like most nations during World War I, the German Empire removed the gold backing in August 1914, and gold and silver coins ceased to circulate. After the fall of the Empire due to the November Revolution of 1918, the mark was succeeded by the Weimar Republic's mark, derisively referred to as the Papiermark ("Paper mark") due to hyperinflation in the Weimar Republic from 1918–1923. History The introduction of the German mark in 1873 was the culmination of decades-long efforts to unify the various currencies used by the German Confederation.pp 205-218 https://books.google.com/books?id=GrJCAAAAIAAJ&pg=PA205#v=onepage&q&f=false The Zollverein unified in 1838 the Prussian and South German currenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
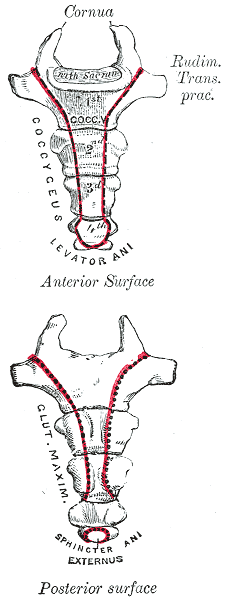
Coccyx
The coccyx ( : coccyges or coccyxes), commonly referred to as the tailbone, is the final segment of the vertebral column in all apes, and analogous structures in certain other mammals such as horses. In tailless primates (e.g. humans and other great apes) since ''Nacholapithecus'' (a Miocene hominoid),Nakatsukasa 2004, ''Acquisition of bipedalism'' (SeFig. 5entitled ''First coccygeal/caudal vertebra in short-tailed or tailless primates.''.) the coccyx is the remnant of a vestigial tail. In animals with bony tails, it is known as ''tailhead'' or ''dock'', in bird anatomy as ''tailfan''. It comprises three to five separate or fused coccygeal vertebrae below the sacrum, attached to the sacrum by a fibrocartilaginous joint, the sacrococcygeal symphysis, which permits limited movement between the sacrum and the coccyx. Structure The coccyx is formed of three, four or five rudimentary vertebrae. It articulates superiorly with the sacrum. In each of the first three segments may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rectum
The rectum is the final straight portion of the large intestine in humans and some other mammals, and the Gastrointestinal tract, gut in others. The adult human rectum is about long, and begins at the rectosigmoid junction (the end of the sigmoid colon) at the level of the third sacral vertebra or the sacral promontory depending upon what definition is used. Its diameter is similar to that of the sigmoid colon at its commencement, but it is dilated near its termination, forming the rectal ampulla. It terminates at the level of the anorectal ring (the level of the puborectalis sling) or the dentate line, again depending upon which definition is used. In humans, the rectum is followed by the anal canal which is about long, before the gastrointestinal tract terminates at the anal verge. The word rectum comes from the Latin ''Wikt:rectum, rectum Wikt:intestinum, intestinum'', meaning ''straight intestine''. Structure The rectum is a part of the lower gastrointestinal tract ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
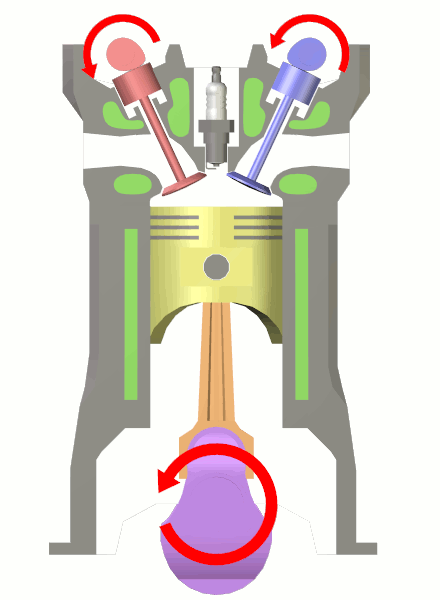
Dead Centre (engineering)
In a reciprocating engine, the dead centre is the position of a piston in which it is either farthest from, or nearest to, the crankshaft. The former is known as Top Dead Centre (TDC) while the latter is known as Bottom Dead Centre (BDC). More generally, the dead centre is any position of a crank where the applied force is straight along its axis, meaning no turning force can be applied. Many sorts of machines are crank driven, including unicycles, bicycles, tricycles, various types of machine presses, gasoline engines, diesel engines, steam locomotives, and other steam engines. Crank-driven machines rely on the energy stored in a flywheel to overcome the dead centre, or are designed, in the case of multi-cylinder engines, so that dead centres can never exist on all cranks at the same time. A steam locomotive is an example of the latter, the connecting rods being arranged such that the dead centre for each cylinder occurs out of phase with the other one (or more) cylinde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snifting Valve
A snifting valve (sometimes snifter valve) is an automatic anti-vacuum valve used in a steam locomotive when coasting. The word ''Snift'' imitates the sound made by the valve. Overview When the driver shuts off the steam to the cylinders of a steam locomotive while it is in motion, the moving pistons could create a partial vacuum in the cylinders. This would give rise to two problems. Firstly, the pumping action would absorb energy and prevent the engine from coasting freely. Secondly, when the exhaust valve opened, soot and cinders from the smokebox could be sucked down the exhaust pipe and into the valve chest or cylinder, causing damage. (The exhaust is open to the smokebox because in normal running the exhaust steam is sent through the blastpipe to draw the fire and eject the combustion products from the chimney.) These problems are avoided by using snifting valves to allow air to be drawn into the cylinder. On railways which did not use snifting valves, drivers were instr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Side Valve
A flathead engine, also known as a sidevalve engine''American Rodder'', 6/94, pp.45 & 93. or valve-in-block engine is an internal combustion engine with its poppet valves contained within the engine block, instead of in the cylinder head, as in an overhead valve engine. Flatheads were widely used internationally by automobile manufacturers from the late 1890s until the mid-1950s but were replaced by more efficient overhead valve and overhead camshaft engines. They are currently experiencing a revival in low-revving aero-engines such as the D-Motor. The side-valve design The valve gear comprises a camshaft sited low in the cylinder block which operates the poppet valves via tappets and short pushrods (or sometimes with no pushrods at all). The flathead system obviates the need for further valvetrain components such as lengthy pushrods, rocker arms, overhead valves or overhead camshafts. The sidevalves are typically adjacent, sited on one side of the cylinder(s), though some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)