|
David De La Croix
David de la Croix (; born 22 April 1964) is a Belgian scholar and author in the field of economic growth and demographic economics. He is professor at the University of Louvain (UCLouvain). Contributions David de la Croix and his co-authors Raouf Boucekkine and Omar Licandro developed a unified framework encompassing longevity, education and economic growth. The basic link is that a longer life expectancy justifies a greater investment in education (this is called the Ben Porath mechanism in the related literature), which in turn fosters economic growth by promoting human capital accumulation. The resulting model has been taken to several sets of demographic data pertaining to the 17th and 18th centuries, providing evidence on the role of demographics in the Industrial Revolution. This conclusion is reinforced by the work with Omar Licandro on famous people, which provides a broad picture of the evolution of the longevity of the elite over the last centuries, using a database ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belgium
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to the southwest, and the North Sea to the northwest. It covers an area of and has a population of more than 11.5 million, making it the 22nd most densely populated country in the world and the 6th most densely populated country in Europe, with a density of . Belgium is part of an area known as the Low Countries, historically a somewhat larger region than the Benelux group of states, as it also included parts of northern France. The capital and largest city is Brussels; other major cities are Antwerp, Ghent, Charleroi, Liège, Bruges, Namur, and Leuven. Belgium is a sovereign state and a federal constitutional monarchy with a parliamentary system. Its institutional organization is complex and is structured on both regional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going from hand production methods to machines, new chemical manufacturing and iron production processes, the increasing use of steam power and water power, the development of machine tools and the rise of the mechanized factory system. Output greatly increased, and a result was an unprecedented rise in population and in the rate of population growth. Textiles were the dominant industry of the Industrial Revolution in terms of employment, value of output and capital invested. The textile industry was also the first to use modern production methods. The Industrial Revolution began in Great Britain, and many of the technological and architectural innovations were of British origin. By the mid-18th century, Britain was the world's leadi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demography
Demography () is the statistics, statistical study of populations, especially human beings. Demographic analysis examines and measures the dimensions and Population dynamics, dynamics of populations; it can cover whole societies or groups defined by criteria such as education, nationality, religion, and ethnicity. Educational institutions usually treat demography as a field of sociology, though there are a number of independent demography departments. These methods have primarily been developed to study human populations, but are extended to a variety of areas where researchers want to know how populations of Social actions, social actors can change across time through processes of birth, death, and Human migration, migration. In the context of human biological populations, demographic analysis uses Public records, administrative records to develop an independent Approximation, estimate of the population. Demographic analysis estimates are often considered a reliable stan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economics
Economics () is the social science that studies the Production (economics), production, distribution (economics), distribution, and Consumption (economics), consumption of goods and services. Economics focuses on the behaviour and interactions of Agent (economics), economic agents and how economy, economies work. Microeconomics analyzes what's viewed as basic elements in the economy, including individual agents and market (economics), markets, their interactions, and the outcomes of interactions. Individual agents may include, for example, households, firms, buyers, and sellers. Macroeconomics analyzes the economy as a system where production, consumption, saving, and investment interact, and factors affecting it: employment of the resources of labour, capital, and land, currency inflation, economic growth, and public policies that have impact on glossary of economics, these elements. Other broad distinctions within economics include those between positive economics, desc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Demographic Economics
''Journal of Demographic Economics'' (JODE) is a peer-reviewed academic journal at the intersection of demography and economics. It is published by Cambridge University Press and edited by the Institute of Economic and Social Research of the UCLouvain. The Journal of Demographic Economics publishes four issues a year. The Journal of the Demographic Economics (JODE) welcomes both empirical and theoretical papers on issues relevant to Demographic Economics with a preference for combining abstract economic or demographic models together with data to highlight major mechanisms of the interplay between demographics and economics. JODE intends to be the premier demography & economics outlet for empirical contributions that are firmly grounded in theory as well as theoretical papers that are motivated by empirical regularities and findings. The editor-in-chief of JODE is David de la Croix (UClouvain) and Murat Iyigun (University of Colorado at Boulder) is the Co-Editor. In August 2021, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VoxEU
The Centre for Economic Policy Research (CEPR) is an independent, non‐partisan, pan‐European non‐profit organisation. Its mission is to enhance the quality of policy decisions through providing policy‐relevant research, based soundly in economic theory, to policymakers, the private sector and civil society. Rather than adopting the traditional in-house ‘think-tank’ research structure, CEPR appoints Research Fellows and Affiliates who remain in their home institutions (universities, research institutes, central bank research departments, and international organisations). CEPR’s network includes over 1,700 of the world's top economists from over 330 institutions in 30 countries. The results of the research conducted by the Centre's network are disseminated through a variety of publications, public meetings, workshops and conferences. Its headquarters is currently located in London. History CEPR was founded in 1983 by Richard Portes, FBA, CBE, to enhance the qualit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guild
A guild ( ) is an association of artisans and merchants who oversee the practice of their craft/trade in a particular area. The earliest types of guild formed as organizations of tradesmen belonging to a professional association. They sometimes depended on grants of letters patent from a monarch or other ruler to enforce the flow of trade to their self-employed members, and to retain ownership of tools and the supply of materials, but were mostly regulated by the city government. A lasting legacy of traditional guilds are the guildhalls constructed and used as guild meeting-places. Guild members found guilty of cheating the public would be fined or banned from the guild. Typically the key "privilege" was that only guild members were allowed to sell their goods or practice their skill within the city. There might be controls on minimum or maximum prices, hours of trading, numbers of apprentices, and many other things. These rules reduced free competition, but sometimes mainta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quarterly Journal Of Economics
''The Quarterly Journal of Economics'' is a peer-reviewed academic journal published by the Oxford University Press for the Harvard University Department of Economics. Its current editors-in-chief are Robert J. Barro, Lawrence F. Katz, Nathan Nunn, Andrei Shleifer, and Stefanie Stantcheva. History It is the oldest professional journal of economics in the English language, and covers all aspects of the field—from the journal's traditional emphasis on micro-theory to both empirical and theoretical macroeconomics. Reception According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2015 impact factor of 6.662, ranking it first out of 347 journals in the category "Economics". It is generally regarded as one of the top 5 journals in economics, together with the American Economic Review, Econometrica, the Journal of Political Economy, and the Review of Economic Studies. Notable papers Some of the most influential and well-read papers in economics have been published in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polygyny
Polygyny (; from Neoclassical Greek πολυγυνία (); ) is the most common and accepted form of polygamy around the world, entailing the marriage of a man with several women. Incidence Polygyny is more widespread in Africa than in any other continent. Some scholars see the slave trade's impact on the male-to-female sex ratio as a key factor in the emergence and fortification of polygynous practices in regions of Africa. Polygyny is most common in a region known as the "polygamy belt" in West Africa and Central Africa, with the countries estimated to have the highest polygamy prevalence in the world being Burkina Faso, Mali, Gambia, Niger and Nigeria. In the region of sub-Saharan Africa, polygyny is common and deeply rooted in the culture, with 11% of the population of sub-Saharan Africa living in such marriages (25% of the Muslim population and 3% of the Christian population, as of 2019). Polygyny is especially widespread in West Africa, with the countries estimated to h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
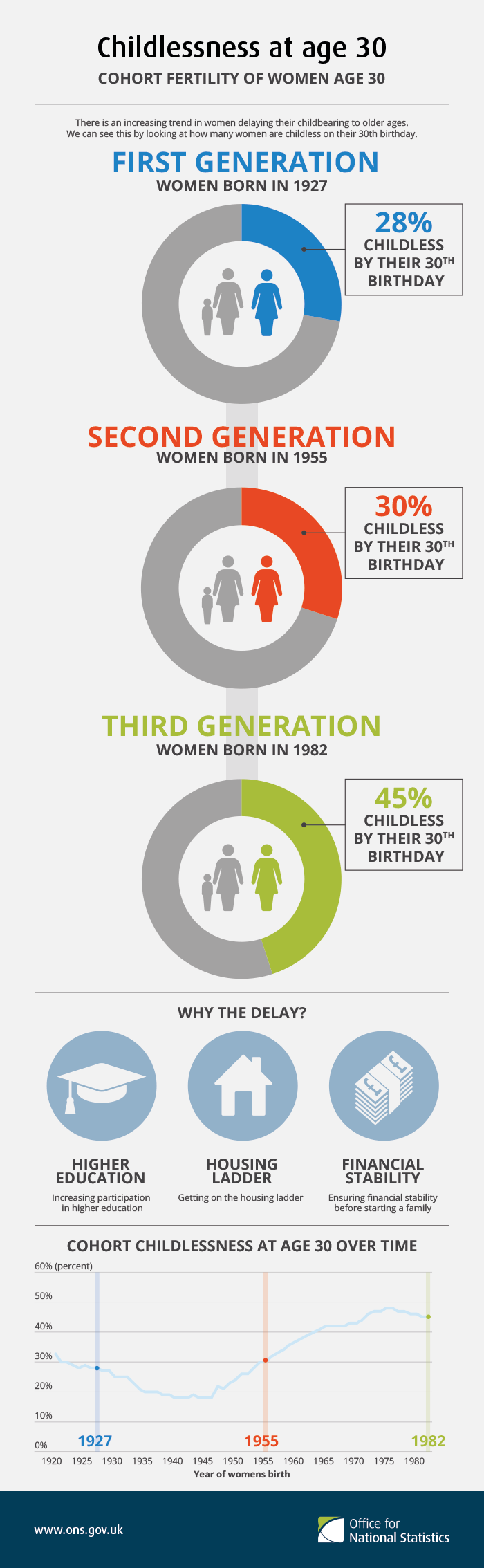
Childlessness
Childlessness is the state of not having children. Childlessness may have personal, social or political significance. Childlessness, which may be by choice or circumstance, is distinguished from voluntary childlessness, which is voluntarily having no children, and from antinatalism, wherein childlessness is promoted. Types Types of childlessness can be classified into several categories: * ''natural sterility'' randomly affects individuals. One can think of it as the minimum level of permanent childlessness that we can observe in any given society, and is of the order of 2 percent, in line with data from the Hutterites, a group established as the demographic standard in the 1950s. * ''social sterility'', which one can also call poverty driven childlessness, or endogenous sterility, describes the situation of poor women whose fecundity has been affected by poor living conditions. * people who are childless by circumstance. These people can be childless because they have not met ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vox EU
The Centre for Economic Policy Research (CEPR) is an independent, non‐partisan, pan‐European non‐profit organisation. Its mission is to enhance the quality of policy decisions through providing policy‐relevant research, based soundly in economic theory, to policymakers, the private sector and civil society. Rather than adopting the traditional in-house ‘think-tank’ research structure, CEPR appoints Research Fellows and Affiliates who remain in their home institutions (universities, research institutes, central bank research departments, and international organisations). CEPR’s network includes over 1,700 of the world's top economists from over 330 institutions in 30 countries. The results of the research conducted by the Centre's network are disseminated through a variety of publications, public meetings, workshops and conferences. Its headquarters is currently located in London. History CEPR was founded in 1983 by Richard Portes, FBA, CBE, to enhance the qualit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |