|
David Barclay Of Youngsbury
David Barclay of Youngsbury (1729–1809), also known as David Barclay of Walthamstow or David Barclay of Walthamstow and Youngsbury, was an English Quaker merchant, banker, and philanthropist. He is notable for an experiment in "gratuitous manumission", in which he freed an estate of Jamaican slaves, and arranged for better futures for them in Pennsylvania. His legacy was as one of the founders of the present-day Barclays Bank, a century ahead of its formation under that name, and in the brewing industry. Family background He was the son of Scottish banker and merchant David Barclay of Cheapside (1682–1769), second son of Robert Barclay, eminent Quaker writer, and Priscilla Freame, daughter of the banker John Freame. The Barclay family bank The origins of the Freame Bank, in which Barclay and his brother John inherited shares through their mother, go back at least to the first quarter of the 18th century. The name of the bank changed frequently, but it was generally known ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Earlom
Richard Earlom (baptised 14 May 17439 October 1822) was an England, English mezzotinter. Biography Earlom was born and died in London. His natural faculty for art appears to have been first called into exercise by his admiration for the lord mayor's state coach, which had just been decorated by Giovanni Battista Cipriani. He tried to copy the paintings, and was sent to study under Cipriani. He displayed great skill as a drawing, draughtsman, and at the same time acquired without assistance the art of mezzotint. In 1765, Earlom was employed by John Boydell, Alderman Boydell, a publisher and promoter of the fine arts, to make a series of drawings from the pictures at Houghton Hall; and these he engraved in mezzotint. His best works are perhaps the fruit and flower pieces after the Dutch artists Van Os and Jan van Huysum. Among his historical and figure subjects are ''Agrippina'', after Benjamin West; ''Love in Bondage'', after Guido Reni; the ''Royal Academy'', the ''Embassy of Hy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Hunter Morris
Robert Hunter Morris ( – 27 January 1764), was a prominent governmental figure in Colonial Pennsylvania, serving as governor of Pennsylvania and Chief Justice of the New Jersey Supreme Court. Early life and education Morris was born in 1700 in Trenton, New Jersey. He was the second son of Lewis Morris and Isabella ( née Graham) Morris and named after his father's friend the future colonial governor Robert Hunter. His older brother was Lewis Morris Jr. who served as a member and speaker of the New York General Assembly. His father was very prominent in public life and variously served as chief justice of New York and as the 8th Colonial Governor of New Jersey. His paternal grandparents were Sarah (née Pole) Morris and Richard Morris, who was originally from Monmouthshire, Wales. His grandparents bought Morrisania from Samuel Edsall in 1670 and moved there from Barbados. His mother was the eldest daughter of James Graham, who served as the first Speaker of the N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Perkins (bibliophile)
Henry Perkins (c.1777–1855) was an English brewer, known as a bibliophile. Early life He was the son of John Perkins (died 1812), and his wife Amelia, John being a partner in the Anchor Brewery, Southwark with the Quaker group of David Barclay of Youngsbury, Robert Barclay, and Silvanus Bevan III, Amelia's relations. The Thrale family were involved in the sale, and Henry and his brother Frederick Perkins (1780–1860) have been identified as the sons of John Perkins who were tutored by Samuel Parr, at the expense of Hester Thrale. Perkins himself became a partner in the firm of Barclay, Perkins, & Co., brewers. He had a 12.5% share, in what was a lucrative business, but was not very active in its management. Perkins was elected a fellow of the Linnean Society in 1825, and was also a fellow of the Geological Society and Horticultural Society of London. Family Perkins married in 1803 Susannah Latham; they had one son and three daughters. Of the daughters: *Matilda married fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
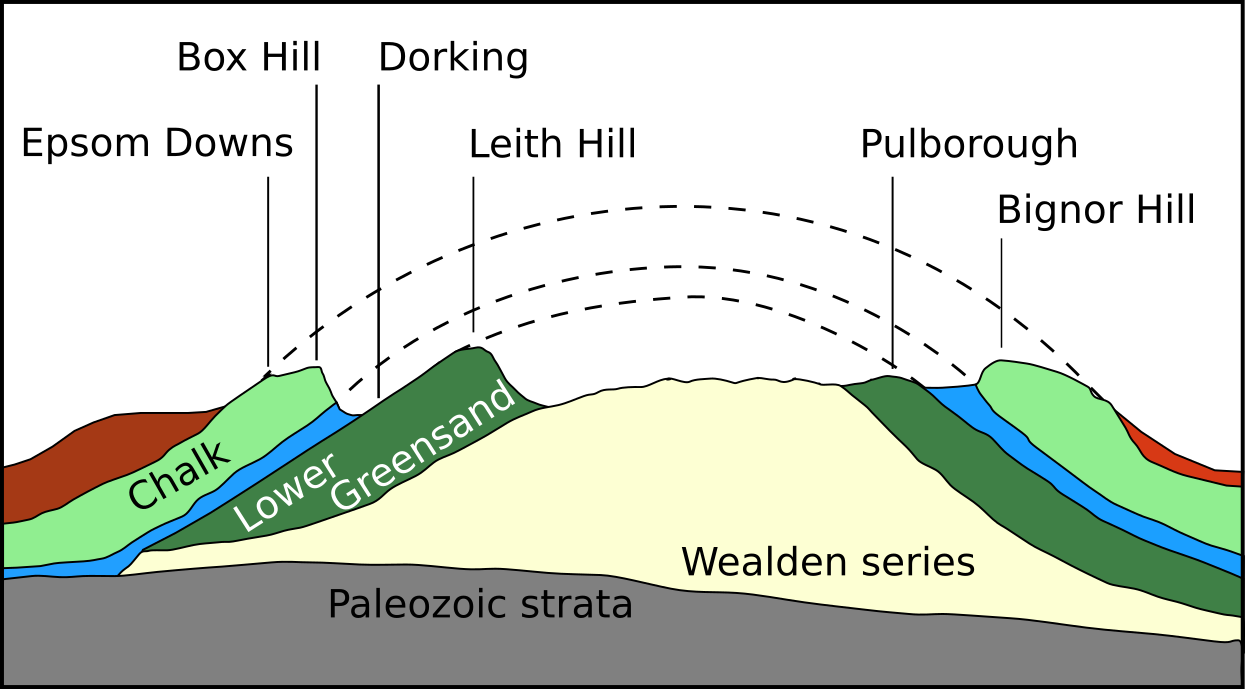
Dorking
Dorking () is a market town in Surrey in South East England, about south of London. It is in Mole Valley District and the council headquarters are to the east of the centre. The High Street runs roughly east–west, parallel to the Pipp Brook and along the northern face of an outcrop of Lower Greensand. The town is surrounded on three sides by the Surrey Hills Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty and is close to Box Hill and Leith Hill. The earliest archaeological evidence of human activity is from the Mesolithic and Neolithic periods, and there are several Bronze Age bowl barrows in the local area. The town may have been the site of a staging post on Stane Street during Roman times, however the name 'Dorking' suggests an Anglo-Saxon origin for the modern settlement. A market is thought to have been held at least weekly since early medieval times and was highly regarded for the poultry traded there. The Dorking breed of domestic chicken is named after the town. The loca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hester Thrale
Hester Lynch Thrale Piozzi (née Salusbury; later Piozzi; 27 January 1741 or 16 January 1740 – 2 May 1821),Contemporary records, which used the Julian calendar and the Annunciation Style of enumerating years, recorded her birth as 16 January 1740. The provisions of the British Calendar (New Style) Act 1750, implemented in 1752, altered the official British dating method to the Gregorian calendar with the start of the year on 1 January (it had been 25 March). These changes resulted in dates being moved forward 11 days, and for those between 1 January and 25 March, an advance of one year. For further explanation, see: Old Style and New Style dates. a Welsh-born diarist, author and patron of the arts, is an important source on Samuel Johnson and 18th-century English life. She belonged to the prominent Salusbury family, Anglo-Welsh landowners, and married first a wealthy brewer, Henry Thrale, then a music teacher, Gabriel Mario Piozzi. Her '' Anecdotes of the Late Samuel Johnson' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Thrale
Henry Thrale (1724/1730?–4 April 1781) was a British politician who sat in the House of Commons from 1765 to 1780. He was a close friend of Samuel Johnson. Like his father, he was the proprietor of the large London brewery H. Thrale & Co. Born at the Alehouse in Harrow Corner, Southwark, he was the son of the rich brewer Ralph Thrale (1698–1758) and Mary Thrale. He married Hester Lynch Salusbury on 11 October 1763; they had 12 children, and she outlived him. He was MP for Southwark 23 December 1765 – September 1780, an Alderman, and Sheriff of the City of London: a respected, religious man who was a good hunter and sportsman with a taste for gambling. Education Thrale was educated at Eton College and University College, Oxford, where he matriculated on 4 June 1744. He travelled in Europe with Lord William Henry Lyttleton Westcote (1724–1808). Friendship with Samuel Johnson Johnson first met the Thrales on the 9 or 10 January 1765, and immediately became almost a p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anchor Brewery, Southwark
The Anchor Brewery was a brewery in Park Street, Southwark, London, England. Established in 1616, by the early nineteenth century it was the largest brewery in the world. From 1781 it was operated by Barclay Perkins & Co, who in 1955 merged with the Courage Brewery, which already owned the nearby Anchor Brewhouse. The Park Street brewery was demolished in 1981. History The brewery was established in 1616 by James Monger Sr. in Southwark, on land adjacent to the Globe Theatre. On his death, the brewery passed to his godson, James Monger Jr. James Child acquired the brewery after the younger Monger's death in 1670, and owned it until his death in 1696. His son in law, Edmund Halsey, managed the business with James Child from 1693, and subsequently as sole proprietor until his death in 1729. The brewery was then purchased by Ralph Thrale, the brewery manager and a nephew of Halsey, for £30,000 in instalments over 11 years. Barclay Perkins & Co was founded in July 1781 after ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abolitionism In The United Kingdom
Abolitionism in the United Kingdom was the movement in the late 18th and early 19th centuries to end the practice of slavery, whether formal or informal, in the United Kingdom, the British Empire and the world, including ending the Atlantic slave trade. It was part of a wider abolitionism movement in Western Europe and the Americas. The buying and selling of slaves was made illegal across the British Empire in 1807, but owning slaves was permitted until it was outlawed completely in 1833, beginning a process where from 1834 slaves became indentured "apprentices" to their former owners until emancipation was achieved for the majority by 1840 and for remaining exceptions by 1843. Former slave owners received formal compensation for their losses from the British government, known as compensated emancipation. Origins In the 17th and early 18th centuries, English Quakers and a few evangelical religious groups condemned slavery (by then applied mostly to Africans) as un-Christian. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abolitionism In The United States
In the United States, abolitionism, the movement that sought to end slavery in the country, was active from the late colonial era until the American Civil War, the end of which brought about the abolition of American slavery through the Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution (ratified 1865). The anti-slavery movement originated during the Age of Enlightenment, focused on ending the trans-Atlantic slave trade. In Colonial America, a few German Quakers issued the 1688 Germantown Quaker Petition Against Slavery, which marks the beginning of the American abolitionist movement. Before the Revolutionary War, evangelical colonists were the primary advocates for the opposition to slavery and the slave trade, doing so on humanitarian grounds. James Oglethorpe, the founder of the colony of Georgia, originally tried to prohibit slavery upon its founding, a decision that was eventually reversed. During the Revolutionary era, all states abolished the international sla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lord North
Frederick North, 2nd Earl of Guilford (13 April 17325 August 1792), better known by his courtesy title Lord North, which he used from 1752 to 1790, was 12th Prime Minister of Great Britain from 1770 to 1782. He led Great Britain through most of the American War of Independence. He also held a number of other cabinet posts, including Home Secretary and Chancellor of the Exchequer. North's reputation among historians has swung back and forth. It reached its lowest point in the late nineteenth century, when he was depicted as a creature of the king and an incompetent who lost the American colonies. In the early twentieth century, a revised view emerged emphasising his strengths in administering the Treasury, handling the House of Commons, and in defending the Church of England. Historian Herbert Butterfield, however, argued that his indolence was a barrier to efficient crisis management; he neglected his role in supervising the entire war effort. Early life (1732–1754) North wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boston Tea Party
The Boston Tea Party was an American political and mercantile protest by the Sons of Liberty in Boston, Massachusetts, on December 16, 1773. The target was the Tea Act of May 10, 1773, which allowed the British East India Company to sell tea from China in American colonies without paying taxes apart from those imposed by the Townshend Acts. The Sons of Liberty strongly opposed the taxes in the Townshend Act as a violation of their rights. Protesters, some disguised as Indigenous Americans, destroyed an entire shipment of tea sent by the East India Company. The demonstrators boarded the ships and threw the chests of tea into the Boston Harbor. The British government considered the protest an act of treason and responded harshly. The episode escalated into the American Revolution, becoming an iconic event of American history. Since then other political protests such as the Tea Party movement have referred to themselves as historical successors to the Boston protest of 1773. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Fothergill (physician)
John Fothergill FRS (8 March 1712 – 26 December 1780) was an English physician, plant collector, philanthropist and Quaker. His medical writings were influential, and he built up a sizeable botanic garden in what is now West Ham Park in London. Life and work Fothergill was born at Carr End, near Bainbridge in Yorkshire, the son of John Fothergill (1676–1745), a Quaker preacher and farmer, and his first wife, Margaret Hough (1677–1719). After studying at Sedbergh School, Fothergill was apprenticed to an apothecary. In 1736, he obtained the degree of Doctor of Medicine at Edinburgh and followed this by further studies at St Thomas's Hospital, London. After visiting continental Europe in 1740, he settled in London, where he gained an extensive practice. During the influenza epidemics of 1775 and 1776 he is said to have treated 60 patients a day. In 1745, Fothergill gave a brief lecture to the Royal Society of London, citing the work of a Scottish physician and surgeon, Wil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)

.jpg)

