|
Data General Extended BASIC
Data General Extended BASIC, also widely known as Nova Extended BASIC, was a BASIC programming language interpreter for the Data General Nova series minicomputers. It was based on the seminal Dartmouth BASIC, including the Fifth Edition's string variables and powerful commands for matrix manipulation. In contrast to the compile-and-go Dartmouth BASIC, Extended BASIC was an interpreter. To this, Extended BASIC added substring manipulation using array slicing, which was common on BASICs of the era, found on HP Time-Shared BASIC, Sinclair BASIC, Atari BASIC and others. This contrasts with the Microsoft BASIC style which uses string functions like , and thus makes porting string code somewhat difficult. Data General later purchased rights to a much-expanded BASIC which was released as Data General Business Basic. This added powerful database functionality and largely replaced Extended BASIC on DG platforms. Description Mathematics The internal floating point number format norma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data General
Data General Corporation was one of the first minicomputer firms of the late 1960s. Three of the four founders were former employees of Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC). Their first product, 1969's Data General Nova, was a 16-bit minicomputer intended to both outperform and cost less than the equivalent from DEC, the 12-bit PDP-8. A basic Nova system cost or less than a similar PDP-8 while running faster, offering easy expandability, being significantly smaller, and proving more reliable in the field. Combined with Data General RDOS (DG/RDOS) and programming languages like Data General Business Basic, Novas provided a multi-user platform far ahead of many contemporary systems. A series of updated Nova machines were released through the early 1970s that kept the Nova line at the front of the 16-bit mini world. The Nova was followed by the Eclipse series which offered much larger memory capacity while still being able to run Nova code without modification. The Eclipse launch wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data General Business Basic
Data General Business Basic was a BASIC interpreter (based on a version from MAI Basic Four) marketed by Data General for their Nova minicomputer in the 1970s, and later ported to the Data General Eclipse MV and AViiON computers. Most business applications for the Nova were developed in Business Basic. Business Basic was an integer-only language inspired by COBOL, and contained powerful string-handling functions and the ability to manipulate indexed files very quickly. It also provided full control over the display screen, with cursor positioning, attribute setting, and region-blanking commands. Business Basic could interface to Data General's INFOS II database, and make calls directly to the operating system. A lock server gave multiple concurrent users efficient access to database records. Small business programs could be developed and debugged rapidly with Business Basic because of the interactive nature of the interpreter, but the language did not provide many structu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operating System
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware, software resources, and provides common services for computer programs. Time-sharing operating systems schedule tasks for efficient use of the system and may also include accounting software for cost allocation of processor time, mass storage, printing, and other resources. For hardware functions such as input and output and memory allocation, the operating system acts as an intermediary between programs and the computer hardware, although the application code is usually executed directly by the hardware and frequently makes system calls to an OS function or is interrupted by it. Operating systems are found on many devices that contain a computer from cellular phones and video game consoles to web servers and supercomputers. The dominant general-purpose personal computer operating system is Microsoft Windows with a market share of around 74.99%. macOS by Apple Inc. is in second place (14.84%), and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Card Punch
A computer punched card reader or just computer card reader is a computer input device used to read computer programs in either source or executable form and data from punched cards. A computer card punch is a computer output device that punches holes in cards. Sometimes computer punch card readers were combined with computer card punches and, later, other devices to form multifunction machines. It is a input device and also an output device. Most early computers, such as the ENIAC, and the IBM NORC, provided for punched card input/output. Card readers and punches, either connected to computers or in off-line card to/from magnetic tape configurations, were ubiquitous through the mid-1970s. Punched cards had been in use since the 1890s; their technology was mature and reliable. Card readers and punches developed for punched card machines were readily adaptable for computer use. Businesses were familiar with storing data on punched cards and keypunch machines were widely emplo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
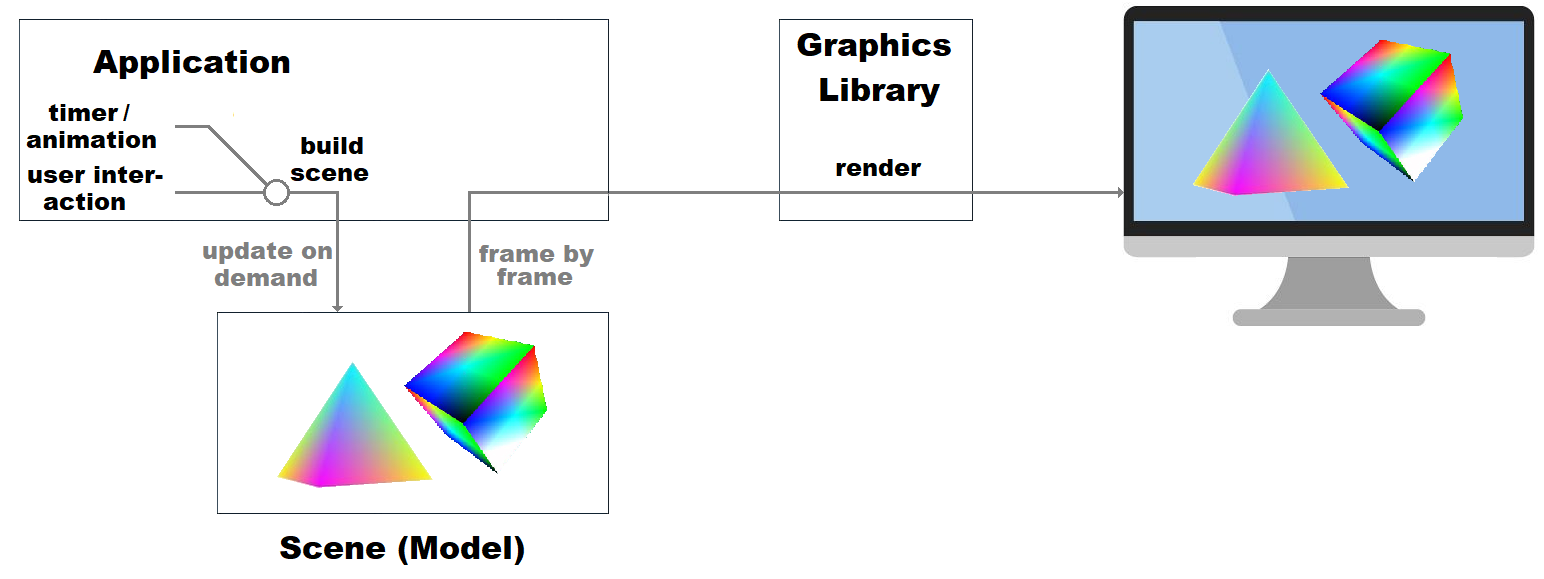
Immediate Mode (computer Graphics)
Immediate mode in computer graphics is a design pattern of API design in graphics libraries, in which * the client calls directly cause rendering of graphics objects to the display, or in which * the data to describe rendering primitives is inserted frame by frame directly from the client into a command list (in the case of '' immediate mode primitive rendering''), without the use of extensive indirection – thus'' immediate ''– to retained resources. It does not preclude the use of double-buffering. Retained mode is an alternative approach. Historically, retained mode has been the dominant style in GUI libraries; however, both can coexist in the same library and are not necessarily exclusive in practice. Overview In immediate mode, the scene (complete object model of the rendering primitives) is retained in the memory space of the client, instead of the graphics library. This implies that in an immediate mode application the lists of graphical objects to be rendered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ASCII
ASCII ( ), abbreviated from American Standard Code for Information Interchange, is a character encoding standard for electronic communication. ASCII codes represent text in computers, telecommunications equipment, and other devices. Because of technical limitations of computer systems at the time it was invented, ASCII has just 128 code points, of which only 95 are , which severely limited its scope. All modern computer systems instead use Unicode, which has millions of code points, but the first 128 of these are the same as the ASCII set. The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) prefers the name US-ASCII for this character encoding. ASCII is one of the List of IEEE milestones, IEEE milestones. Overview ASCII was developed from telegraph code. Its first commercial use was as a seven-bit teleprinter code promoted by Bell data services. Work on the ASCII standard began in May 1961, with the first meeting of the American Standards Association's (ASA) (now the American Nat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Identity Matrix
In linear algebra, the identity matrix of size n is the n\times n square matrix with ones on the main diagonal and zeros elsewhere. Terminology and notation The identity matrix is often denoted by I_n, or simply by I if the size is immaterial or can be trivially determined by the context. I_1 = \begin 1 \end ,\ I_2 = \begin 1 & 0 \\ 0 & 1 \end ,\ I_3 = \begin 1 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 1 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 1 \end ,\ \dots ,\ I_n = \begin 1 & 0 & 0 & \cdots & 0 \\ 0 & 1 & 0 & \cdots & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 1 & \cdots & 0 \\ \vdots & \vdots & \vdots & \ddots & \vdots \\ 0 & 0 & 0 & \cdots & 1 \end. The term unit matrix has also been widely used, but the term ''identity matrix'' is now standard. The term ''unit matrix'' is ambiguous, because it is also used for a matrix of ones and for any unit of the ring of all n\times n matrices. In some fields, such as group theory or quantum mechanics, the identity matrix is sometimes denoted by a boldface one, \mathbf, or called "id" (short for identity). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macro (computer Science)
In computer programming, a macro (short for "macro instruction"; ) is a rule or pattern that specifies how a certain input should be mapped to a replacement output. Applying a macro to an input is known as macro expansion. The input and output may be a sequence of lexical tokens or characters, or a syntax tree. Character macros are supported in software applications to make it easy to invoke common command sequences. Token and tree macros are supported in some programming languages to enable code reuse or to extend the language, sometimes for domain-specific languages. Macros are used to make a sequence of computing instructions available to the programmer as a single program statement, making the programming task less tedious and less error-prone. (Thus, they are called "macros" because a "big" block of code can be expanded from a "small" sequence of characters.) Macros often allow positional or keyword parameters that dictate what the conditional assembler program generates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Significand
The significand (also mantissa or coefficient, sometimes also argument, or ambiguously fraction or characteristic) is part of a number in scientific notation or in floating-point representation, consisting of its significant digits. Depending on the interpretation of the exponent, the significand may represent an integer or a fraction. Example The number 123.45 can be represented as a decimal floating-point number with the integer 12345 as the significand and a 10−2 power term, also called characteristics, where −2 is the exponent (and 10 is the base). Its value is given by the following arithmetic: : 123.45 = 12345 × 10−2. The same value can also be represented in normalized form with 1.2345 as the fractional coefficient, and +2 as the exponent (and 10 as the base): : 123.45 = 1.2345 × 10+2. Schmid, however, called this representation with a significand ranging between 1.0 and 10 a modified normalized form. For base 2, this 1.xxxx form is also called a normalized ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Offset Binary
Offset binary, also referred to as excess-K, excess-''N'', excess-e, excess code or biased representation, is a method for signed number representation where a signed number n is represented by the bit pattern corresponding to the unsigned number n+K, K being the ''biasing value'' or ''offset''. There is no standard for offset binary, but most often the ''K'' for an ''n''-bit binary word is ''K'' = 2''n''−1 (for example, the offset for a four-digit binary number would be 23=8). This has the consequence that the minimal negative value is represented by all-zeros, the "zero" value is represented by a 1 in the most significant bit and zero in all other bits, and the maximal positive value is represented by all-ones (conveniently, this is the same as using two's complement but with the most significant bit inverted). It also has the consequence that in a logical comparison operation, one gets the same result as with a true form numerical comparison operation, whereas, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exponent
Exponentiation is a mathematical operation, written as , involving two numbers, the '' base'' and the ''exponent'' or ''power'' , and pronounced as " (raised) to the (power of) ". When is a positive integer, exponentiation corresponds to repeated multiplication of the base: that is, is the product of multiplying bases: b^n = \underbrace_. The exponent is usually shown as a superscript to the right of the base. In that case, is called "''b'' raised to the ''n''th power", "''b'' (raised) to the power of ''n''", "the ''n''th power of ''b''", "''b'' to the ''n''th power", or most briefly as "''b'' to the ''n''th". Starting from the basic fact stated above that, for any positive integer n, b^n is n occurrences of b all multiplied by each other, several other properties of exponentiation directly follow. In particular: \begin b^ & = \underbrace_ \\ ex& = \underbrace_ \times \underbrace_ \\ ex& = b^n \times b^m \end In other words, when multiplying a base raised to one exp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
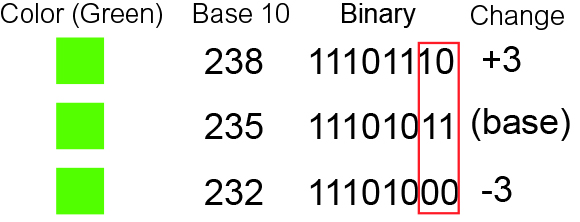
Least Significant Bit
In computing, bit numbering is the convention used to identify the bit positions in a binary number. Bit significance and indexing In computing, the least significant bit (LSB) is the bit position in a binary integer representing the binary 1s place of the integer. Similarly, the most significant bit (MSB) represents the highest-order place of the binary integer. The LSB is sometimes referred to as the ''low-order bit'' or ''right-most bit'', due to the convention in positional notation of writing less significant digits further to the right. The MSB is similarly referred to as the ''high-order bit'' or ''left-most bit''. In both cases, the LSB and MSB correlate directly to the least significant digit and most significant digit of a decimal integer. Bit indexing correlates to the positional notation of the value in base 2. For this reason, bit index is not affected by how the value is stored on the device, such as the value's byte order. Rather, it is a property of the numeri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |