|
Darkhad
The Darkhad, Darqads,. Dalhut, or Darhut ( Mongolian for "Untouchables", "Protected Ones", or "Workmen of Darkhan"; Chinese: 达尔扈特, pinyin: Dá'ěrhùtè) are a subgroup of Mongol people living mainly in northern Mongolia, in the Bayanzürkh, Ulaan-Uul, Renchinlkhümbe, Tsagaannuur sums of Khövsgöl Province; as well as Inner Mongolia in northern China. The Darkhad valley is named after them. The regional variant of Mongol language is the Darkhad dialect. In the 2000 census, 16,268 people identified themselves as Darkhad. The Darkhad were originally part of the Oirat or Khotgoid tribes. Between 1549 and 1686, they were subjects of Zasagt Khan aimag and the Khotgoid Altan Khan. In 1786 they became part of the Jebtsundamba Khutuktu's shabi otog. At roughly the same time they became known as ''Black Darkhad''. In 1947, 2071 people from 462 households were eligible to be Darkhad. They were liable for maintaining the Great Khan's mausoleum at their own expense prior ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mausoleum Of Genghis Khan
The Mausoleum of Genghis Khan is a temple dedicated to Genghis Khan, where he is worshipped as ancestor, dynastic founder, and deity. The temple is better called the Lord's Enclosure (i.e. shrine), the traditional name among the Mongols, as it has never truly contained the Khan's body. It is the main centre of the worship of Genghis Khan, a growing practice in the Mongolian shamanism of both Inner Mongolia, where the temple is located, and Mongolia. The temple is located in the Kandehuo Enclosure in the town of Xinjie, in the Ejin Horo Banner in the Ordos Prefecture of Inner Mongolia, in China. The main hall is actually a cenotaph where the coffin contains no body (only headdresses and accessories), because the actual tomb of Genghis Khan has never been discovered. The present structure was built between 1954 and 1956 by the government of the People's Republic of China in the traditional Mongol style. It was desecrated and its relics destroyed during the Cultural Revolution, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Darkhad Dialect
Darkhad (also "Darkhat") is a dialect in-between Central Mongolian and Oirat still variously seen as closer to Oirat or as a dialect of Khalkha Mongolian with some Oirat features. However, it seems to have substantially assimilated to the Khalkha dialect since it first was described by Sanžeev, and some classificational differences seem to be due to what historical (or even ideal) state got classified. ''Ethnologue'' reports a population of without providing a date. Speakers live mainly in the west of Lake Khövsgöl in the sums Bayanzürkh, Ulaan-Uul and Rinchinlkhümbe in the Khövsgöl Province of Mongolia. Phonetics and phonology In contrast to Oirat, it has and and a diphthongized equivalent of *ai. However, monophthongized reflexes of *ai can be encountered and more so in older language material, so it can be assumed that due to Khalkha influence. Somewhat similar developments can be observed for other vowels, but as at least and can get palatalized, it is pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Darkhad Language
Darkhad (also "Darkhat") is a dialect in-between Central Mongolian and Oirat still variously seen as closer to Oirat or as a dialect of Khalkha Mongolian with some Oirat features. However, it seems to have substantially assimilated to the Khalkha dialect since it first was described by Sanžeev, and some classificational differences seem to be due to what historical (or even ideal) state got classified. ''Ethnologue'' reports a population of without providing a date. Speakers live mainly in the west of Lake Khövsgöl in the sums Bayanzürkh, Ulaan-Uul and Rinchinlkhümbe in the Khövsgöl Province of Mongolia. Phonetics and phonology In contrast to Oirat, it has and and a diphthongized equivalent of *ai. However, monophthongized reflexes of *ai can be encountered and more so in older language material, so it can be assumed that due to Khalkha influence. Somewhat similar developments can be observed for other vowels, but as at least and can get palatalized, it is pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Darkhad Valley
The Darkhad Valley ( mn, Дархадын хотгор, transl.: ''Darhadyn hotgor'') is a large valley in northwestern Khövsgöl aimag, Mongolia. It is situated between the Ulaan Taiga and Khoridol Saridag ranges at an altitude of about 1600 m, about 160 km long and 40 km wide. The area is 4270 km². It was transferred from the People's Republic of Tannu Tuva to the Mongolian People's Republic in 1925 as a Soviet concession to the Mongolians, who had wanted to incorporate the territory of Tannu Uriankhai into their country. The valley is rich in lakes and rivers, the biggest of which are Dood Tsagaan Lake and Shishged River, respectively. The area is noted for its natural environment, but relatively remote and inaccessible even by Mongolian standards. The Darkhad valley is divided between the Ulaan-Uul, Renchinlkhümbe, and Tsagaannuur '' sums''. Inhabitants are mainly Darkhad The Darkhad, Darqads,. Dalhut, or Darhut ( Mongolian for "Untouchables", "Pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mongolian Language
Mongolian is the official language of Mongolia and both the most widely spoken and best-known member of the Mongolic language family. The number of speakers across all its dialects may be 5.2 million, including the vast majority of the residents of Mongolia and many of the ethnic Mongol residents of the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region of the People's Republic of China.Estimate from Svantesson ''et al.'' (2005): 141. In Mongolia, Khalkha Mongolian is predominant, and is currently written in both Cyrillic and traditional Mongolian script. In Inner Mongolia, the language is dialectally more diverse and is written in the traditional Mongolian script. However, Mongols in both countries often use the Latin script for convenience on the Internet. In the discussion of grammar to follow, the variety of Mongolian treated is the standard written Khalkha formalized in the writing conventions and in grammar as taught in schools, but much of what is to be said is also valid for vernacular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mongol Peoples
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member of the large family of Mongolic peoples. The Oirats in Western Mongolia as well as the Buryats and Kalmyks of Russia are classified either as distinct ethno-linguistic groups or subgroups of Mongols. The Mongols are bound together by a common heritage and ethnic identity. Their indigenous dialects are collectively known as the Mongolian language. The ancestors of the modern-day Mongols are referred to as Proto-Mongols. Definition Broadly defined, the term includes the Mongols proper (also known as the Khalkha Mongols), Buryats, Oirats, the Kalmyk people and the Southern Mongols. The latter comprises the Abaga Mongols, Abaganar, Aohans, Baarins, Chahars, Eastern Dorbets, Gorlos Mongols, Jalaids, Jaruud, Kharchins, Khishigten, Khorchins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mongols
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member of the large family of Mongolic peoples. The Oirats in Western Mongolia as well as the Buryats and Kalmyks of Russia are classified either as distinct ethno-linguistic groups or subgroups of Mongols. The Mongols are bound together by a common heritage and ethnic identity. Their indigenous dialects are collectively known as the Mongolian language. The ancestors of the modern-day Mongols are referred to as Proto-Mongols. Definition Broadly defined, the term includes the Mongols proper (also known as the Khalkha Mongols), Buryats, Oirats, the Kalmyk people and the Southern Mongols. The latter comprises the Abaga Mongols, Abaganar, Aohans, Baarins, Chahars, Eastern Dorbets, Gorlos Mongols, Jalaids, Jaruud, Kharchins, Khishig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
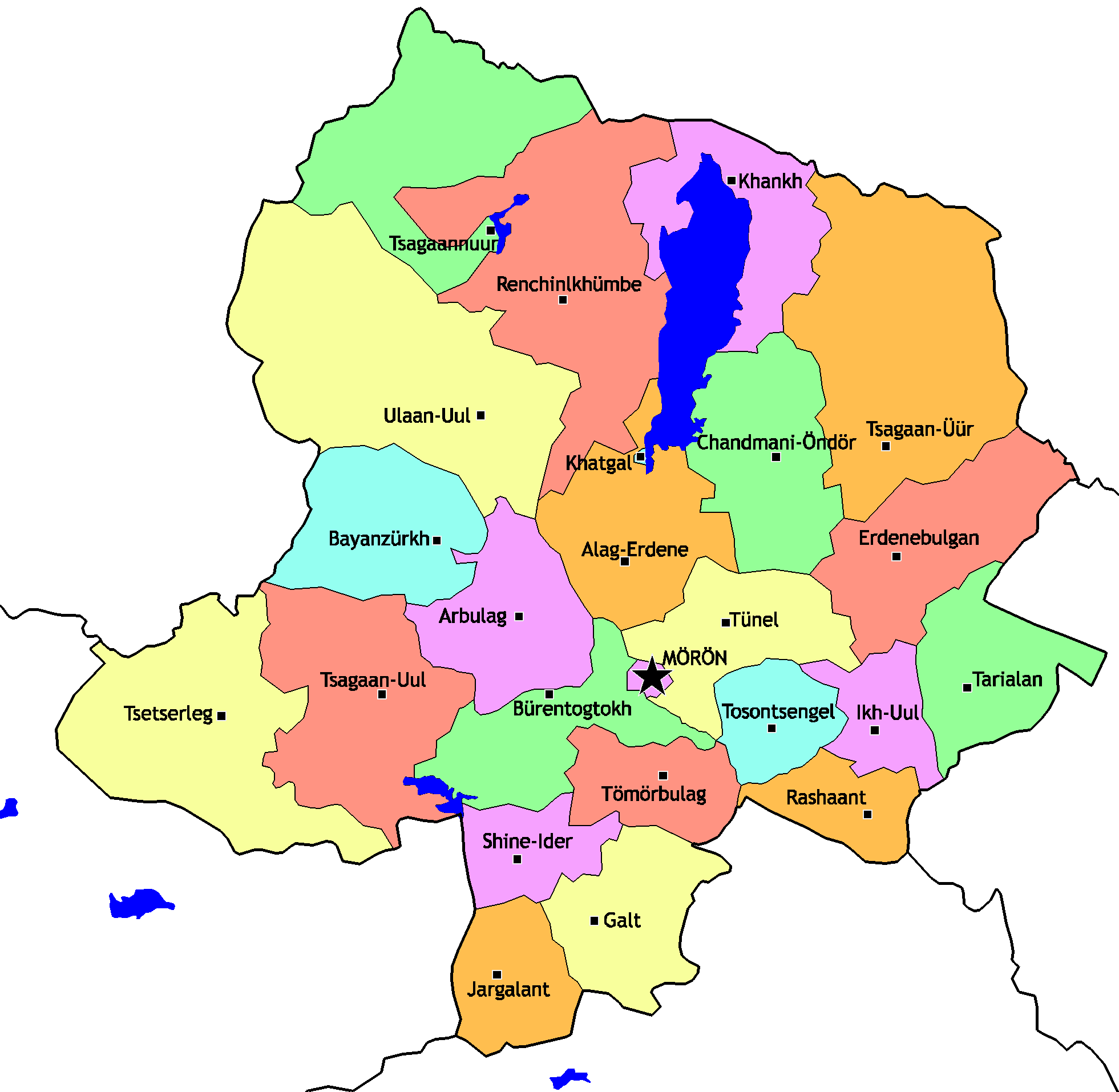
Tsagaannuur, Khövsgöl
Tsagaannuur ( mn, Цагааннуур, ''white lake'') is a sum of Khövsgöl aimag. The area is 5,410 km2. In 2000, Tsagaannuur had a population of 1,317 people, of which most identified themselves as Darkhad. There were 269 inhabitants who identified themselves as Tsaatan ethnicity. The sum center, officially named ''Gurvansaikhan'' ( mn, Гурвансайхан), is located at the shore of Dood Tsagaan nuur, 279 km north-north-east of Mörön and 1048 km from Ulaanbaatar. History The Tsagaannuur sum was split off from Renchinlkhümbe, Khövsgöl in 1985. Economy In 2004, there were about 8,000 heads of livestock, among them 2,400 goats, 2,100 sheep, 2,300 cattle and yaks, 1,100 horses, 6 camels, and 632 reindeer. Tsagaannuur houses the only commercial fishing enterprise in Mongolia. According to the statistics provided by the Tsagaan Nuur Sum government on November 13, 2014, in a general assembly with residents of the sum's Xarmai district, the tota ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taiga (1992 Film)
''Taiga'' (1992) is an eight-hour ethnographic film directed and photographed by Ulrike Ottinger. It focuses on the life and rituals of nomadic peoples in Northern Mongolia, specifically the Darkhad nomads and the Soyon Uriankhai. It is divided into 38 parts: # Der Oul-Paß mit Obo-Heiligtum - Wächter zum Darkhad-Tal # Das Tal der Darkhad-Nomaden # Nomaden am Altrag-Fluß # Im einsamen Höjen-Tal lebt die Schamanin Baldshir # Die schamanistische Seance beginnt um Mitternacht # Bei Jura - Die Hochzeit # Bei Jura - Die weißen Speisen # Juras Nachbarn - Der Sänger und Schmied Dawadschi # Heiliger Baum # Suren Hör erzählt das Märchen vom nackten Jungen im Erdloch # Der Jäger und Stiefelmacher Ölziibajar # Das Öwtschuunii-Naadam - Fest des Hammelbrustknochens # Ringer und Lobpreissänger # Aufbruch der Nomaden ins Winterlager # Unterwegs nach Tsagaan Nor (Weißer See) # Der Jäger Tscholoo # Tsagaan Nor City # Held der Arbeit # Holzfäller Sanji # Örgöl-Heiligtum # Wie die ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khövsgöl Province
Khövsgöl ( mn, Хөвсгөл) is the northernmost of the 21 aimags (provinces) of Mongolia. The name is derived from Lake Khövsgöl. Geography and history The round-topped Tarvagatai, Bulnain and Erchim sub-ranges of the Khangai massif dominate the south and southwest of the largely mountainous province, and north and west of Lake Khövsgöl, lie the alpine Khoridol Saridag, Ulaan Taiga, and Mönkh Saridag mountains. The center and eastern parts of the province are less mountainous, but still hilly. The region is well known in Mongolia for its natural environment, and Lake Khövsgöl is one of the country's major tourist attractions. The largest forests of Mongolia are located around and to the north of the lake, extending the South Siberian taiga. The aimag was founded in 1931. Khatgal was the administrative center until 1933; since then it has been Mörön. Population The region is home to many ethnic minority groups: Darkhad, Khotgoid, Uriankhai, Buriad, and Tsaat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Administrative Divisions Of Mongolia During Qing
The Qing dynasty of China ruled over the Mongolian Plateau, including Inner Mongolia and Outer Mongolia. Both regions, however, were separately administered within the empire. The estate of Jebtsundamba Khutugtu, the Great (from Mongolian , disciple) in 1723, became independent from the four in the sense that its subjects were exempt from most taxes and corvees. The did not—except the three Darkhad in Khövsgöl—control territory. Rather, its subjects mostly lived among the general population. Similar existed for other high lamas. Direct control The direct-controlled Mongols () were banners () controlled by provinces, generals and ambasa. The following regions were directly controlled by the Manchu: * Chakhar (Zhili Province) * Dariganga - Qing emperor's pasture, where the best horses from both Inner and Outer Mongolia were collected and mastered by the Dariganga tribe. It was controlled from Kalgan. Today's location is Dariganga , Sukhbaatar province, Mongolia. * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethnic Groups In Mongolia
This is a demography of Mongolia including population density, Ethnic group, ethnicity, education level, health of the populace, economic status, religious affiliations and other aspects of the population. Segments Youth Vital statistics UN estimates Registered births and deaths Current vital statistics Life expectancy Source: ''UN World Population Prospects'' Structure of the population Ethnicity and languages The demonym for the people of Mongolia is ''Mongolian''. The name ''Mongol'' usually accounts for people of the Mongols, Mongol ethnic group, thus excluding Turkic groups such as Kazakhs and Tuvans. Ethnic Mongols account for about 96% of the population and consist of Khalka Mongols, Khalkh and other groups, all distinguished primarily by dialects of the Mongolian language. The Khalkhs make up 86% of the ethnic Mongol population. The remaining 14% include Oirats, Buryats and others. Ethnic distinctions among the Mongol subgroups are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_p67-68_PLATE22._MONGOLIA_(14597137480).jpg)