|
Daphnia (Daphnia)
''Daphnia'' is one of the three subgenera of the genus ''Daphnia'', the others being '' Australodaphnia'' and '' Ctenodaphnia''. Species *'' Daphnia ambigua'' Scourfield, 1947 *'' Daphnia arenata'' Hebert, 1995 *'' Daphnia catawba'' Coker, 1926 *'' Daphnia cavicervix'' Ekman, 1900 *'' Daphnia cheraphila'' Hebert & Finston, 1996 *'' Daphnia commutata'' Ekman, 1900 *'' Daphnia cristata'' Sars, 1862 *'' Daphnia cucullata'' Sars, 1862 *'' Daphnia curvirostris'' Eylmann, 1887 *'' Daphnia dentifera'' Forbes, 1893 *'' Daphnia dubia'' Herrick, 1883 *'' Daphnia galeata'' Sars, 1864 *'' Daphnia gessneri'' Herbst, 1967 *'' Daphnia hyalina'' Leydig, 1860 *'' Daphnia lacustris'' Sars, 1862 *'' Daphnia laevis'' Birge, 1879 *'' Daphnia latispina'' Kořínek & Hebert, 1996 *''Daphnia longiremis'' Sars, 1862 *''Daphnia longispina'' (O. F. Müller, 1776) *''Daphnia lumholtzi'' Sars, 1885 *'' Daphnia marcahuasensis'' (Valdivia Villar & Burger, 1989) *'' Daphnia melanica'' Hebert, 1995 *'' Daphnia m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
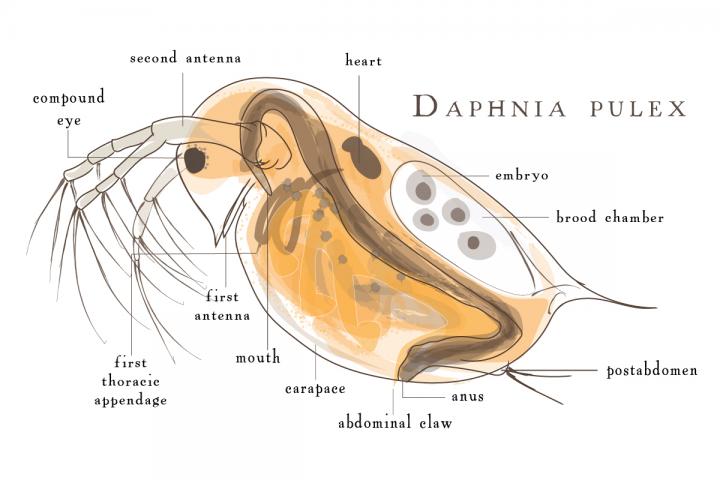
Daphnia Pulex
''Daphnia pulex'' is the most common species of water flea. It has a cosmopolitan distribution: the species is found throughout the Americas, Europe, and Australia. It is a model species, and was the first crustacean to have its genome sequenced. Description ''D. pulex'' is an arthropod whose body segments are difficult to distinguish. It can only be recognised by its appendages (only ever one pair per segment), and by studying its internal anatomy. The head is distinct and is made up of six segments, which are fused together even as an embryo. It bears the mouthparts, and two pairs of antennae, the second pair of which is enlarged into powerful organs used for swimming. No clear division is seen between the thorax and abdomen, which collectively bear five pairs of appendages. The shell surrounding the animal extends posteriorly into a spine. Like most other ''Daphnia'' species, ''D. pulex'' reproduces by cyclical parthenogenesis, alternating between sexual and asexual reprodu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daphnia Gessneri
''Daphnia'' is a genus of small planktonic crustaceans, in length. ''Daphnia'' are members of the order Anomopoda, and are one of the several small aquatic crustaceans commonly called water fleas because their saltatory swimming style resembles the movements of fleas. ''Daphnia'' spp. live in various aquatic environments ranging from acidic swamps to freshwater lakes and ponds. The two most commonly found species of ''Daphnia'' are '' D. pulex'' (small and most common) and '' D. magna'' (large). They are often associated with a related genus in the order Cladocera: ''Moina'', which is in the Moinidae family instead of the Daphniidae, and is much smaller than ''D. pulex'' (roughly half the maximum length). Appearance and characteristics The body of a ''Daphnia'' species is usually long, and is divided into segments, although this division is not visible. The head is fused, and is generally bent down towards the body with a visible notch separating the two. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daphnia Morsei
''Daphnia'' is a genus of small planktonic crustaceans, in length. ''Daphnia'' are members of the order Anomopoda, and are one of the several small aquatic crustaceans commonly called water fleas because their saltatory swimming style resembles the movements of fleas. ''Daphnia'' spp. live in various aquatic environments ranging from acidic swamps to freshwater lakes and ponds. The two most commonly found species of ''Daphnia'' are '' D. pulex'' (small and most common) and '' D. magna'' (large). They are often associated with a related genus in the order Cladocera: ''Moina'', which is in the Moinidae family instead of the Daphniidae, and is much smaller than ''D. pulex'' (roughly half the maximum length). Appearance and characteristics The body of a ''Daphnia'' species is usually long, and is divided into segments, although this division is not visible. The head is fused, and is generally bent down towards the body with a visible notch separating the two. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daphnia Minnehaha
''Daphnia'' is a genus of small planktonic crustaceans, in length. ''Daphnia'' are members of the order Anomopoda, and are one of the several small aquatic crustaceans commonly called water fleas because their saltatory swimming style resembles the movements of fleas. ''Daphnia'' spp. live in various aquatic environments ranging from acidic swamps to freshwater lakes and ponds. The two most commonly found species of ''Daphnia'' are '' D. pulex'' (small and most common) and '' D. magna'' (large). They are often associated with a related genus in the order Cladocera: ''Moina'', which is in the Moinidae family instead of the Daphniidae, and is much smaller than ''D. pulex'' (roughly half the maximum length). Appearance and characteristics The body of a ''Daphnia'' species is usually long, and is divided into segments, although this division is not visible. The head is fused, and is generally bent down towards the body with a visible notch separating the two. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daphnia Middendorffiana
''Daphnia'' is a genus of small planktonic crustaceans, in length. ''Daphnia'' are members of the order Anomopoda, and are one of the several small aquatic crustaceans commonly called water fleas because their saltatory swimming style resembles the movements of fleas. ''Daphnia'' spp. live in various aquatic environments ranging from acidic swamps to freshwater lakes and ponds. The two most commonly found species of ''Daphnia'' are '' D. pulex'' (small and most common) and '' D. magna'' (large). They are often associated with a related genus in the order Cladocera: ''Moina'', which is in the Moinidae family instead of the Daphniidae, and is much smaller than ''D. pulex'' (roughly half the maximum length). Appearance and characteristics The body of a ''Daphnia'' species is usually long, and is divided into segments, although this division is not visible. The head is fused, and is generally bent down towards the body with a visible notch separating the two. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daphnia Mendotae
''Daphnia'' is a genus of small planktonic crustaceans, in length. ''Daphnia'' are members of the order Anomopoda, and are one of the several small aquatic crustaceans commonly called water fleas because their saltatory swimming style resembles the movements of fleas. ''Daphnia'' spp. live in various aquatic environments ranging from acidic swamps to freshwater lakes and ponds. The two most commonly found species of ''Daphnia'' are '' D. pulex'' (small and most common) and '' D. magna'' (large). They are often associated with a related genus in the order Cladocera: ''Moina'', which is in the Moinidae family instead of the Daphniidae, and is much smaller than ''D. pulex'' (roughly half the maximum length). Appearance and characteristics The body of a ''Daphnia'' species is usually long, and is divided into segments, although this division is not visible. The head is fused, and is generally bent down towards the body with a visible notch separating the two. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daphnia Melanica
''Daphnia'' is a genus of small planktonic crustaceans, in length. ''Daphnia'' are members of the order Anomopoda, and are one of the several small aquatic crustaceans commonly called water fleas because their saltatory swimming style resembles the movements of fleas. ''Daphnia'' spp. live in various aquatic environments ranging from acidic swamps to freshwater lakes and ponds. The two most commonly found species of ''Daphnia'' are '' D. pulex'' (small and most common) and '' D. magna'' (large). They are often associated with a related genus in the order Cladocera: ''Moina'', which is in the Moinidae family instead of the Daphniidae, and is much smaller than ''D. pulex'' (roughly half the maximum length). Appearance and characteristics The body of a ''Daphnia'' species is usually long, and is divided into segments, although this division is not visible. The head is fused, and is generally bent down towards the body with a visible notch separating the two. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daphnia Marcahuasensis
''Daphnia'' is a genus of small planktonic crustaceans, in length. ''Daphnia'' are members of the order Anomopoda, and are one of the several small aquatic crustaceans commonly called water fleas because their saltatory swimming style resembles the movements of fleas. ''Daphnia'' spp. live in various aquatic environments ranging from acidic swamps to freshwater lakes and ponds. The two most commonly found species of ''Daphnia'' are '' D. pulex'' (small and most common) and '' D. magna'' (large). They are often associated with a related genus in the order Cladocera: ''Moina'', which is in the Moinidae family instead of the Daphniidae, and is much smaller than ''D. pulex'' (roughly half the maximum length). Appearance and characteristics The body of a ''Daphnia'' species is usually long, and is divided into segments, although this division is not visible. The head is fused, and is generally bent down towards the body with a visible notch separating the two. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daphnia Lumholtzi
''Daphnia lumholtzi'' is a species of small, invasive water fleas that originates in the tropical and subtropical lakes of Africa, Asia, and Australia. As an invasive species, ''Daphnia lumholtzi'' disrupts aquatic habitats by spreading throughout the warmer waters of lakes and reservoirs. Description ''Daphnia lumholtzi'' is a small crustacean that is 2–3 mm in length. It has a large helmet and a long tailspine, usually longer than the length of its body, that fluctuates in size. Its body structure is arched, extending to a sharp point. There are roughly 10 prominent spines on the margin of the abdominal shield covering. Ecology Temperature ''Daphnia lumholtzi'' is typically found in the warm, shallow regions of bodies of water with larger surface areas. While most species of ''Daphnia'' see high mortality at temperatures greater than 25 °C, ''D. lumholtzi'' individuals can survive and reproduce at temperatures up to 30 °C, with a thermal optimum occurring ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daphnia Longispina
''Daphnia longispina'' is a planktonic crustacean of the family Daphniidae, a cladoceran freshwater water flea. It is native to Eurasia. ''D. longispina'' is similar in size and sometimes confused with the often sympatric '' D. pulex'' (a very common species), but much smaller than '' D. magna''. ''D. longispina'' is found in a wide range of standing freshwater bodies from small, ephemeral rock-pools to large lakes. Life history Like all ''Daphnia'' species, ''D. longispina'' is a filter feeder, collecting particles of about 2 to 40 µm suspended in the water. The main food are green algae. At 20 °C maturity is reached within about 6 to 12 days, followed by a period of regular reproduction in about 3-4 day intervals. ''D. longispina'' reproduces either asexually (''parthenogenesis'') or sexually. For the later, females need to produce sons asexually. The same or other females can switch at any moment from asexual to sexual reproduction, but producing haploid eggs, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daphnia Longiremis
''Daphnia'' is a genus of small planktonic crustaceans, in length. ''Daphnia'' are members of the order Anomopoda, and are one of the several small aquatic crustaceans commonly called water fleas because their saltatory swimming style resembles the movements of fleas. ''Daphnia'' spp. live in various aquatic environments ranging from acidic swamps to freshwater lakes and ponds. The two most commonly found species of ''Daphnia'' are '' D. pulex'' (small and most common) and '' D. magna'' (large). They are often associated with a related genus in the order Cladocera: ''Moina'', which is in the Moinidae family instead of the Daphniidae, and is much smaller than ''D. pulex'' (roughly half the maximum length). Appearance and characteristics The body of a ''Daphnia'' species is usually long, and is divided into segments, although this division is not visible. The head is fused, and is generally bent down towards the body with a visible notch separating the two. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daphnia Latispina
''Daphnia'' is a genus of small planktonic crustaceans, in length. ''Daphnia'' are members of the order Anomopoda, and are one of the several small aquatic crustaceans commonly called water fleas because their saltatory swimming style resembles the movements of fleas. ''Daphnia'' spp. live in various aquatic environments ranging from acidic swamps to freshwater lakes and ponds. The two most commonly found species of ''Daphnia'' are '' D. pulex'' (small and most common) and '' D. magna'' (large). They are often associated with a related genus in the order Cladocera: ''Moina'', which is in the Moinidae family instead of the Daphniidae, and is much smaller than ''D. pulex'' (roughly half the maximum length). Appearance and characteristics The body of a ''Daphnia'' species is usually long, and is divided into segments, although this division is not visible. The head is fused, and is generally bent down towards the body with a visible notch separating the two. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |