|
Dalhousie Square
B. B. D. Bagh, formerly called Tank Square and then Dalhousie Square (1847 to 1856), is the shortened version for Benoy-Badal-Dinesh Bagh. It is the seat of power of the state government, as well as the central business district of Kolkata in Kolkata district in the Indian state of West Bengal. Origin of name B. B. D. stands for three young Indian independence activists — Benoy Basu, Badal Gupta and Dinesh Gupta — who on 8 December 1930 assassinated the Inspector General of Prisons, N.S. Simpson, in the balconies of the Writers' Building of the then Dalhousie Square. The square had been named after Lord Dalhousie, Governor General of India from 1847 to 1856. At different times it has been called ‘The Green before the Fort’ and the Tank Square. Geography The B.B.D. Bagh area is near the Hooghly River in the western part of Central Kolkata and is a square built around the old Lal Dighi tank. The old fort built by the British was near where the General Post Of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
States And Territories Of India
India is a federal union comprising 28 states and 8 union territories, with a total of 36 entities. The states and union territories are further subdivided into districts and smaller administrative divisions. History Pre-independence The Indian subcontinent has been ruled by many different ethnic groups throughout its history, each instituting their own policies of administrative division in the region. The British Raj The British Raj (; from Hindi language, Hindi ''rāj'': kingdom, realm, state, or empire) was the rule of the British The Crown, Crown on the Indian subcontinent; * * it is also called Crown rule in India, * * * * or Direct rule in India, * Q ... mostly retained the administrative structure of the preceding Mughal Empire. India was divided into provinces (also called Presidencies), directly governed by the British, and princely states, which were nominally controlled by a local prince or raja loyal to the British Empire, which held ''de f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
India
India, officially the Republic of India ( Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the southwest, and the Bay of Bengal on the southeast, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north; and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is in the vicinity of Sri Lanka and the Maldives; its Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand, Myanmar, and Indonesia. Modern humans arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa no later than 55,000 years ago., "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by modern humans originating in Africa. ... Coalescence dates for most non-European populations average to between 73–55 ka.", "Modern human beings—''Homo sapiens''—originated in Africa. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dalhousie 1870s
Dalhousie ( ) may refer to: Buildings *Dalhousie Castle, a castle near Bonnyrigg, Scotland * Dalhousie Obelisk, a monument in Empress Place, Singapore * Dalhousie Station (Montreal), a former passenger rail station in Montreal, Quebec * Dalhousie station (Calgary), a LRT station in Calgary, Alberta Institutions * Dalhousie Hilltop School, Dalhousie, India *Dalhousie School, a former prep school in Scotland *Dalhousie University, located in Halifax, Nova Scotia *HMIS (later INS) Dalhousie, the initial name of INS Angre, the naval base at Mumbai, India Ships * ''Dalhousie'', later name of People and clans *Clan Ramsay (Dalhousie), a branch of the main line of Scottish Ramsays *Earl of Dalhousie, a title created in the Peerage of Scotland in 1633 *James Broun-Ramsay, 1st Marquess of Dalhousie, (1812–1860) a Governor-General of India *George Ramsay, 9th Earl of Dalhousie, a Governor of Nova Scotia and of British North America Places Australia *County of Dalhousie, Victoria * Cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
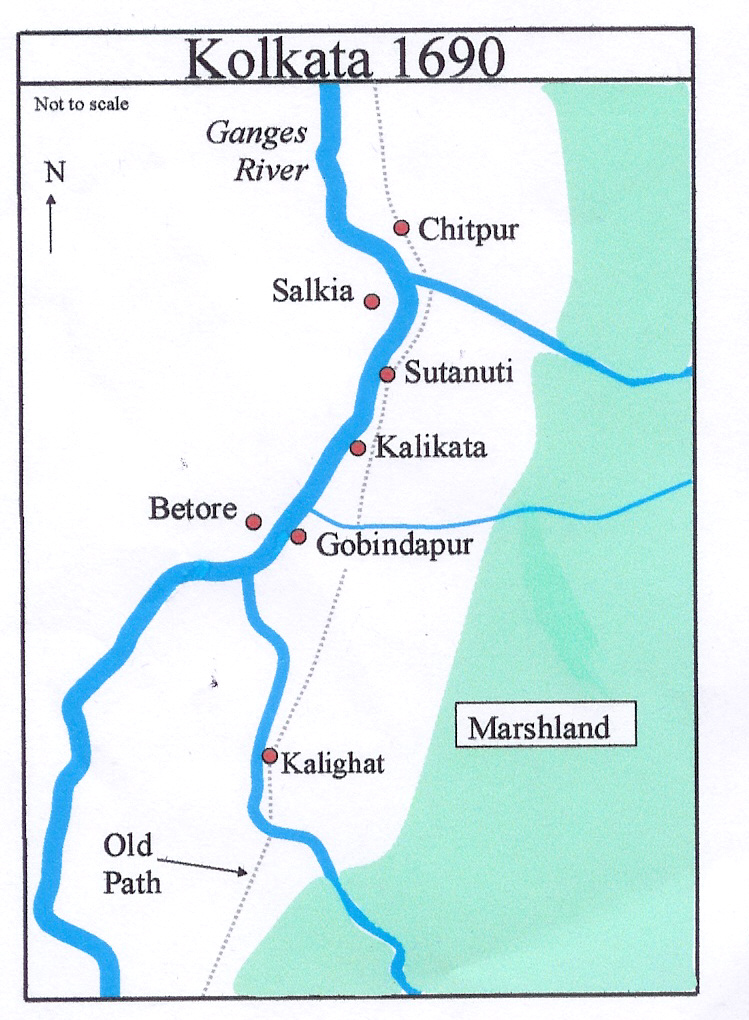
Kalikata
Kalikata was one of the three villages which were merged to form the city of Kolkata (formerly Calcutta) in India. The other two villages were Gobindapur and Sutanuti. Job Charnock, an administrator with the British East India Company is traditionally credited with the honour of founding the city. He settled in the village of Sutanuti. Kalikata was much less important than Sutanuti and Gobindapur, and this, along with the consequent abundance of space, afforded the British room to settle there.Cotton, H.E.A., ''Calcutta Old and New'', 1909/1980, p. 1, General Printers and Publishers Pvt. Ltd. While both Sutanati and Gobindapur appear on old maps like Thomas Bowrey's of 1687 and George Herron's of 1690, Kalikata situated between the two is not depicted.Cotton, H.E.A., p. 11 However, one variant of the name, "Kalkatâ", is shown in Abu'l Fazal's ''Ain-i-Akbari'' (around 1590). History English trader Job Charnock landed at Sutanuti on 24 August 1690 with the objective of estab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lal Dighi
Lal Dighi, also called the Tank Square or Dalhousie Square () is a man-made water tank in Kolkata, India. Etymology The park was referred to as Lal Bagh or Lall Bagh, due to the name of the surrounding neighbourhood, when it was first established in the area. An anecdote can be found interlinked in the name of this thing. Because of the celebration of Holi, which resulted in the pond turning a red or crimson colour, the park became known as Lal Dighi. This name comes from the colour of the pond after the festival. Specification Lal Dighi is a wide body of water in the area of BBD Bagh. Some of the heritage buildings including Andrew's Church, Writers' Building, High Court, General Post Office The General Post Office (GPO) was the state mail, postal system and telecommunications carrier of the United Kingdom until 1969. Before the Acts of Union 1707, it was the postal system of the Kingdom of England, established by Charles II of En ... are situated nearby to the tank ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hooghly River
The Bhagirathi Hooghly River (Anglicized alternatively spelled ''Hoogli'' or ''Hugli'') or the 'Bhāgirathi-Hooghly', called the Ganga or the Kati-Ganga in mythological texts, is the eastern distributary of the Ganges River in West Bengal, India, rising close to Giria in Murshidabad. The main distributary of the Ganges then flows into Bangladesh as the Padma. Today there is a man-made canal called the Farakka Feeder Canal connecting the Ganges to the Bhagirathi. The river flows through the Rarh region, the lower deltaic districts of West Bengal, and eventually into the Bay of Bengal. The upper riparian zone of the river is called Bhagirathi while the lower riparian zone is called Hooghly. Major rivers that drain into the Bhagirathi-Hooghly include Mayurakshi, Jalangi , Ajay, Damodar, Rupnarayan and Haldi rivers other than the Ganges. Hugli-Chinsura, Bandel, Chandannagar, Srirampur, Barrackpur, Rishra, Uttarpara, Titagarh, Kamarhati, Agarpara, Baranagar and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis De Grandpré
Louis Marie Joseph Ohier de Grandpré (May 7, 1761 - January 7, 1846) was a French naval officer and slave trader. Between 1789 and 1790, Grandpré toured the Indian Ocean, beginning at Île de France (Mauritius), and included visits to India, the Seychelles, Vietnam (then Cochin China), Yemen, and Sri Lanka. Early years Grandpré was born in Saint-Malo, France on May 7, 1761. His father, Louis Athanase Ohier, was slave ship captain of Irish descent. His mother, Nicole Marie Louise, came from a family from the Valais canton in Switzerland. At age six, Grandpré began school in Rennes. He left school at an early age to pursue his interest in sailing, later demonstrating his ability as a sailor in the American Revolutionary War. In March 1781, while serving in Viceadmiral Pierre André de Suffren's fleet, he traveled from Brest to India, where the French engaged the British fleet. On November 29, 1783, he married Marie Thérèse de Jehannot Penquer (1762-1837) on the island of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Governor General Of India
The Governor-General of India (1773–1950, from 1858 to 1947 the Viceroy and Governor-General of India, commonly shortened to Viceroy of India) was the representative of the monarch of the United Kingdom and after Indian independence in 1947, the representative of the British monarch. The office was created in 1773, with the title of Governor-General of the Presidency of Fort William. The officer had direct control only over Fort William but supervised other East India Company officials in India. Complete authority over all of British territory in the Indian subcontinent was granted in 1833, and the official came to be known as the "Governor-General of India". In 1858, because of the Indian Rebellion the previous year, the territories and assets of the East India Company came under the direct control of the British Crown; as a consequence, the Company rule in India was succeeded by the British Raj. The governor-general (now also the Viceroy) headed the central government o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Broun-Ramsay, 1st Marquess Of Dalhousie
James Andrew Broun-Ramsay, 1st Marquess of Dalhousie (22 April 1812 – 19 December 1860), also known as Lord Dalhousie, styled Lord Ramsay until 1838 and known as The Earl of Dalhousie between 1838 and 1849, was a Scottish statesman and colonial administrator in British India. He served as Governor-General of India from 1848 to 1856. He established the foundations of the modern educational system in India by adding mass education in addition to elite higher education. He introduced passenger trains to the railways, the electric telegraph and uniform postage, which he described as the "three great engines of social improvement". He also founded the Public Works Department in India To his supporters he stands out as the far-sighted Governor-General who consolidated East India Company rule in India, laid the foundations of its later administration, and by his sound policy enabled his successors to stem the tide of rebellion. His period of rule in India directly preceded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Writers' Building
The Writers' Buildings, often shortened to just Writers, is the official secretariat building of the state government of West Bengal in Kolkata, India. The 150-meter long building covers the entire northern stretch of the iconic Lal Dighi pond at the centre of historic B.B.D. Bagh, long considered as the administrative and business hub of the city. It originally served as the principal administrative office for writers (junior clerks) of the British East India Company (EIC). Designed by Thomas Lyon in 1777, the Writers' Building has gone through a long series of extensions over the centuries. Since India's independence in 1947, it housed the office of the Chief Minister of West Bengal, cabinet ministers and other senior officials, until 4 October 2013, when a major restoration of the building was announced. The majority of government departments were subsequently moved out to a new repurposed building named Nabanna in Howrah on a temporary basis. The building has been called ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinesh Gupta
Dinesh Chandra Gupta ( bn, দিনেশ চন্দ্র গুপ্ত ''Dinesh Chôndro Gupto'') or Dinesh Gupta (6 December 1911 – 7 July 1931) was an Indian revolutionary against British rule in India, who is noted for launching an attack on the Secretariat Building - the Writers' Building in the Dalhousie square in Calcutta, along with Badal Gupta and Benoy Basu. Rabindrasangeet exponent and trainer Maya Sen (maiden name Gupta) was his own niece. Even he suggested his sister-in-law Ashalata Gupta to let Maya learn Rabindrasangeet. His nephew and Maya's brother Dr. Tapan Gupta was a doctor and established 'the Tagoreans' in London. Mr. Gupta's daughter is an MBE, Tanika Gupta, a playwright and regularly works for BBC and the stage in England. Early activities Dinesh Gupta was born on 6 December 1911 in Josholong in Munshiganj District, now in Bangladesh. While he was studying in Dhaka College, Dinesh joined Bengal Volunteers - a group organised by Subhas Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Badal Gupta
Badal Gupta ( bn, বাদল গুপ্ত ''Badol Gupto''), real name Sudhir Gupta (1912 – 8 December 1930), was an Indian revolutionary against British rule in India, who is noted for launching an attack on the Secretariat Building - the Writers' Building in the Dalhousie square in Calcutta, along with Benoy Basu and Dinesh Gupta. Early activities Badal Gupta was born in the village Purba Shimulia (East Shimulia) in the Bikrampur region of Dhaka, now in Munshiganj District, Bangladesh. Badal Gupta was also influenced by the revolutionary activities of his two paternal uncles Late Dharaninath Gupta and Nagendranath Gupta, who were involved in the Alipore Bomb Case and were imprisoned along with Rishi Aurobindo Ghosh. Badal Gupta joined the Bengal Volunteers in 1928. He had also known Kanailal Bhattacharjee, who too was a Bengal Volunteer. The battle at Writers' Building Bengal Volunteers targeted Lt Col NS Simpson, the Inspector General of Prisons, who was infamous fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |