|
Dale (landform)
A dale is an open valley. ''Dale'' is a synonym of the word '' valley''. The name is used when describing the physical geography of an area. It is used most frequently in the Lowlands of Scotland and in the North of England; the term " fell" commonly refers to the mountains or hills that flank the dale. Etymology The word ''dale'' comes from the Old English word ''dæl'', from which the word "dell" is also derived. It is also related to Old Norse word ''dalr'' (and the modern Icelandic word ''dalur''), which may perhaps have influenced its survival in northern England. The Germanic origin is assumed to be *''dala-''. ''Dal-'' in various combinations is common in placenames in Norway. Modern English valley and French vallée are presumably not related to dale. A distant relative of ''dale'' is currency unit dollar, stemming from German ''thaler'' or ''daler'', short for joachimsthaler coins manufactured in the town of Joachimsthal in Bohemia.Falk, Hjalmar (1991). ''Etymo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valley
A valley is an elongated low area often running between hills or mountains, which will typically contain a river or stream running from one end to the other. Most valleys are formed by erosion of the land surface by rivers or streams over a very long period. Some valleys are formed through erosion by glacial ice. These glaciers may remain present in valleys in high mountains or polar areas. At lower latitudes and altitudes, these glacially formed valleys may have been created or enlarged during ice ages but now are ice-free and occupied by streams or rivers. In desert areas, valleys may be entirely dry or carry a watercourse only rarely. In areas of limestone bedrock, dry valleys may also result from drainage now taking place underground rather than at the surface. Rift valleys arise principally from earth movements, rather than erosion. Many different types of valleys are described by geographers, using terms that may be global in use or else applied only locally. For ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karst
Karst is a topography formed from the dissolution of soluble rocks such as limestone, dolomite, and gypsum. It is characterized by underground drainage systems with sinkholes and caves. It has also been documented for more weathering-resistant rocks, such as quartzite, given the right conditions. Subterranean drainage may limit surface water, with few to no rivers or lakes. However, in regions where the dissolved bedrock is covered (perhaps by debris) or confined by one or more superimposed non-soluble rock strata, distinctive karst features may occur only at subsurface levels and can be totally missing above ground. The study of ''paleokarst'' (buried karst in the stratigraphic column) is important in petroleum geology because as much as 50% of the world's hydrocarbon reserves are hosted in carbonate rock, and much of this is found in porous karst systems. Etymology The English word ''karst'' was borrowed from German in the late 19th century, which entered German ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eskdale, North Yorkshire
Eskdale is a valley running west to east from Westerdale on the North York Moors to Whitby on the Yorkshire Coast of England. Formed during the last major ice age, it has a classic U-shaped valley formation caused by the action of glaciers carving away the rock. Eskdale is named after its river which in Celtic means water or stream. The dale carries the River Esk from the "Esklets" above Westerdale to the sea at Whitby. The tops of its steep-sided valleys are noted for their heather moorland, whilst below the land is mainly split between pasture for cows and Swaledale sheep and arable crops such as Oil seed rape. The Esk Valley Walk is a walk covering starting from the head of the Esk through the valley and down to Whitby. Eskdale School in Whitby is named after the valley. The Esk Valley Line runs through Eskdale from Commondale eastwards towards Whitby and is named after the dale. The river flows through the narrow valley that the water has cut into the soft shale of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
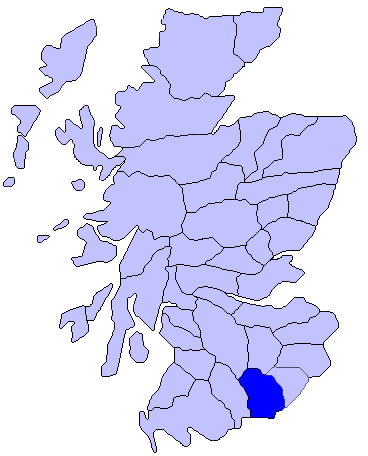
Eskdale, Dumfries And Galloway
Eskdale ( gd, Eisgeadal, IPA: �eʃkʲət̪əɫ̪ is a glen and former lordship in the county of Dumfriesshire, Scotland. The River Esk flows through Eskdale to its estuary at the Solway Firth The Solway Firth ( gd, Tràchd Romhra) is a firth that forms part of the border between England and Scotland, between Cumbria (including the Solway Plain) and Dumfries and Galloway. It stretches from St Bees Head, just south of Whitehaven in .... In 1620, when 13 continuous days of snow occurred in Scotland, on Eskdale Moor only 35 of a flock of 20,000 sheep survived. Sources Glens of Scotland Landforms of Dumfries and Galloway Annandale and Eskdale {{DumfriesGalloway-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eskdale, Cumbria
Eskdale is a glacial valley and civil parish in the western Lake District National Park in Cumbria, England. It forms part of the Borough of Copeland, and in 2001 had a population of 264, increasing to 304 at the 2011 Census. One of the Lake District's most popular tourist attractions, the Ravenglass and Eskdale Railway, runs through the valley, though along with other western valleys of the Lake District, Eskdale is notably quieter during the high summer season than the more accessible eastern areas. Topography The River Esk flows through the valley to its estuary at Ravenglass. The valley is notable in being one of few major valleys in the Lake District not to have its own lake, although several tarns are perched above the valley sides. The main access to the valley is from the western end; however, there is also a steep pass with a motor road leading out of the valley to the east over Hardknott Pass, as well as a road with beautiful views leading southwards over Birk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coquetdale
The River Coquet runs through the county of Northumberland, England, discharging into the North Sea on the east coast at Amble. It rises in the Cheviot Hills on the border between England and Scotland, and follows a winding course across the landscape ("Coquetdale"). The upper reaches are bordered by the Otterburn Ranges military training ground, and are crossed by a number of bridges built in the 20th century. It passes a number of small villages and hamlets, and feeds one of the lakes created by extraction of gravel that form the Caistron Nature Reserve, before reaching the town of Rothbury, where it is crossed by a grade II listed bridge. Below the town is Thrum Mill, the restoration of which was featured on Channel 4 television. It loops around Brinkburn Priory, founded in the 1130s for Augustinian Canons, and its associated mill. At Felton it is crossed by two bridges, one dating from the 15th century, and its replacement, built in 1927, both of which are listed structu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clydesdale (district)
Clydesdale (pronounced ; in Scottish Gaelic, ) was the name given to one of the nineteen districts of the Strathclyde region in Scotland from 1975 to 1996. The name is an archaic title for Lanarkshire, one of the traditional counties of Scotland. Clydesdale and Strathclyde take their names from a similar origin: strath, dale (place name element) (see dale as a landform) and the river Clyde. Initially named after its principal town Lanark,Clydesdale Undiscovered Scotland the Clydesdale district was formed by the and was roughly conterminous to Lanarkshire's 'upper ward' – its southern part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calderdale
Calderdale is a metropolitan borough of West Yorkshire, England, whose population in 2020 was 211,439. It takes its name from the River Calder, and dale, a word for valley. The name Calderdale usually refers to the borough through which the upper river flows, while the actual landform is known as the Calder Valley. Several small valleys contain tributaries of the River Calder. Calderdale covers part of the South Pennines, and the Calder Valley is the southernmost of the Yorkshire Dales, though it is not part of the Yorkshire Dales National Park. The borough was formed in 1974 by the merger of six local government districts, from east to west Brighouse, Elland, Halifax, Sowerby Bridge, Hebden Bridge and Todmorden. Mytholmroyd, together with Hebden Bridge, forms Hebden Royd. Halifax is the commercial, cultural and administrative centre of the borough. Calderdale is served by Calderdale Council, which is headquartered in Halifax, with some functions based in Todmorden ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annandale, Dumfries And Galloway
Annandale ( Gaelic: ''Srath Anann'') is a strath in Dumfries and Galloway, Scotland, named after the dale of the River Annan. It runs north–south through the Southern Uplands from Annanhead (north of Moffat) to Annan on the Solway Firth, and in its higher reaches it separates the Moffat hills on the east from the Lowther hills to the west. A long-distance walking route called Annandale Way running through Annandale (from the source of the River Annan to the sea) was opened in September 2009. History Annandale was also an historic district of Scotland, bordering Liddesdale to the east, Nithsdale to the west, Clydesdale and Tweeddale to the north and the Solway Firth to the south. The district which was in the Sheriffdom of Dumfries and later became part of the County of Dumfries, one of the counties of Scotland. The main reorganisation took place during the Local Government (Scotland) Act 1889, which established a uniform system of county councils and town councils in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Airedale
Airedale is a geographic area in Yorkshire, England, corresponding to the river valley or dale of the River Aire. The valley stretches from the river's origin in Aire Head Springs, Malham which is in the Yorkshire Dales, down past Skipton on to Keighley, Bingley and Shipley through to Leeds and Castleford and on to join the River Ouse at Airmyn. This valley is of great topographic significance as it provides low-altitude passes through the mid Pennines to the west coast known as the Aire Gap. History The upper Aire valley was formed 12,000 years ago by a retreating glacier. A moraine formed in the Cononley area and the lake stretched as far north as Gargrave. Colonisation by man developed later on, especially during the Iron Age. The peoples that occupied the Aire Valley (and much of north eastern England) were called Brigantes by the Romans. Transport improved in the 18th and 19th centuries with the building of the Aire and Calder Navigation and the Leeds and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dale (place Name Element)
A Dale (landform), dale is a valley. It was commonly used in northern England and Scotland to denote an open valley as a Dale (landform), dale, contrasted with a Gill (ravine), gill or narrow valley. List of places Places where dale is part of the name, but not the entire common name: United Kingdom England {{see also, List of Yorkshire Dales *Ainsdale, England *Airedale, England *Allendale, England *Birkdale, England *Darley Dale, England *Denby Dale, England *Derbyshire Dales, England *Eskdale, Cumbria, Eskdale, England *Glossopdale, England *Lathkill Dale, England *Langstrothdale, England *Nidderdale, England *Rochdale, England *Rossendale Valley, Rossendale, England *Skelmersdale, England * Slatepit Dale, England *Teesdale, England *Two Dales, England Scotland *Achrimsdale *Allandale, Falkirk, Allandale *Allasdale *Armadale, Skye *Armadale, Sutherland *Annandale (other), Annandale (other) *Arnisdale *Attadale, Scotland, Attadale *Bernisdale *Berriedale, Hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thalweg
In geography and fluvial geomorphology, a thalweg or talweg () is the line of lowest elevation within a valley or watercourse. Under international law, a thalweg is the middle of the primary navigable channel of a waterway that defines the boundary line between states. Also under international law, thalwegs can acquire special significance because disputed river borders are often deemed to run along the river's thalweg. Etymology The word '' thalweg'' is of 19th-century German origin. The German word (modern spelling ) is a compound noun that is built from the German elements (since Duden's orthography reform of 1901 written ) meaning ''valley'' (cognate with ''dale'' in English), and , meaning ''way.'' It literally means "valley way" and is used, with its modern spelling , in daily German to describe a path or road that follows the bottom of a valley, or in geography with the more technical meaning also adopted by English. Hydrology In hydrological and fluvial landforms, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)