|
Dadheech Brahmins
The Dadheech Brahmins, more usually called Dahima or Dayma, and also spelled Dadhich, which is their preferred spelling, are a subgroup of Brahmins in the Indian states of Rajasthan, Gujarat and Haryana. Origin The Dadheech Brahmin caste system in India, caste has a myth of origin which appears first to have been recorded in the late nineteenth or early twentieth centuries with the publication of the ''Dadhimathi Puranam'', a Sanskrit text comprising 966 verses. The publication was typical of its time, when many castes in India were forming organisations and promoting mythical origins as a response to the social and economic changes under the British Raj administration. Prior to this, the only records of Dadheech people were those of traditional geneaologist communities. The work attempts to fuse the creation of the caste itself, based on a genealogy of Hindu mythology, with the origin and deeds of Dadhimati as recounted both in well-known Hindu texts and regional story-telling. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brahmins
Brahmin (; sa, ब्राह्मण, brāhmaṇa) is a varna as well as a caste within Hindu society. The Brahmins are designated as the priestly class as they serve as priests (purohit, pandit, or pujari) and religious teachers (guru or acharya). The other three varnas are the Kshatriya, Vaishya and Shudra. The traditional occupation of Brahmins is that of priesthood at the Hindu temples or at socio-religious ceremonies, and rite of passage rituals such as solemnising a wedding with hymns and prayers.James Lochtefeld (2002), Brahmin, The Illustrated Encyclopedia of Hinduism, Vol. 1: A–M, Rosen Publishing, , page 125 Traditionally, the Brahmins are accorded the highest ritual status of the four social classes. Their livelihood is prescribed to be one of strict austerity and voluntary poverty ("A Brahmin should acquire what just suffices for the time, what he earns he should spend all that the same day"). In practice, Indian texts suggest that some Brahmins historically ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exogamy
Exogamy is the social norm of marrying outside one's social group. The group defines the scope and extent of exogamy, and the rules and enforcement mechanisms that ensure its continuity. One form of exogamy is dual exogamy, in which two groups continually intermarry with each other. In social science, exogamy is viewed as a combination of two related aspects: biological and cultural. Biological exogamy is marriage of nonblood-related beings, regulated by forms of incest law. Cultural exogamy is marrying outside a specific cultural group; the opposite being endogamy, marriage within a social group. Biology of exogamy Exogamy often results in two individuals that are not closely genetically related marrying each other; that is, outbreeding as opposed to inbreeding. In moderation, this benefits the offspring as it reduces the risk of the offspring inheriting two copies of a defective gene. Increasing the genetic diversity of the offspring improves the chances of offspring reprod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brahmin Communities Of Gujarat
Brahmin (; sa, ब्राह्मण, brāhmaṇa) is a varna as well as a caste within Hindu society. The Brahmins are designated as the priestly class as they serve as priests (purohit, pandit, or pujari) and religious teachers (guru or acharya). The other three varnas are the Kshatriya, Vaishya and Shudra. The traditional occupation of Brahmins is that of priesthood at the Hindu temples or at socio-religious ceremonies, and rite of passage rituals such as solemnising a wedding with hymns and prayers.James Lochtefeld (2002), Brahmin, The Illustrated Encyclopedia of Hinduism, Vol. 1: A–M, Rosen Publishing, , page 125 Traditionally, the Brahmins are accorded the highest ritual status of the four social classes. Their livelihood is prescribed to be one of strict austerity and voluntary poverty ("A Brahmin should acquire what just suffices for the time, what he earns he should spend all that the same day"). In practice, Indian texts suggest that some Brahmins historica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
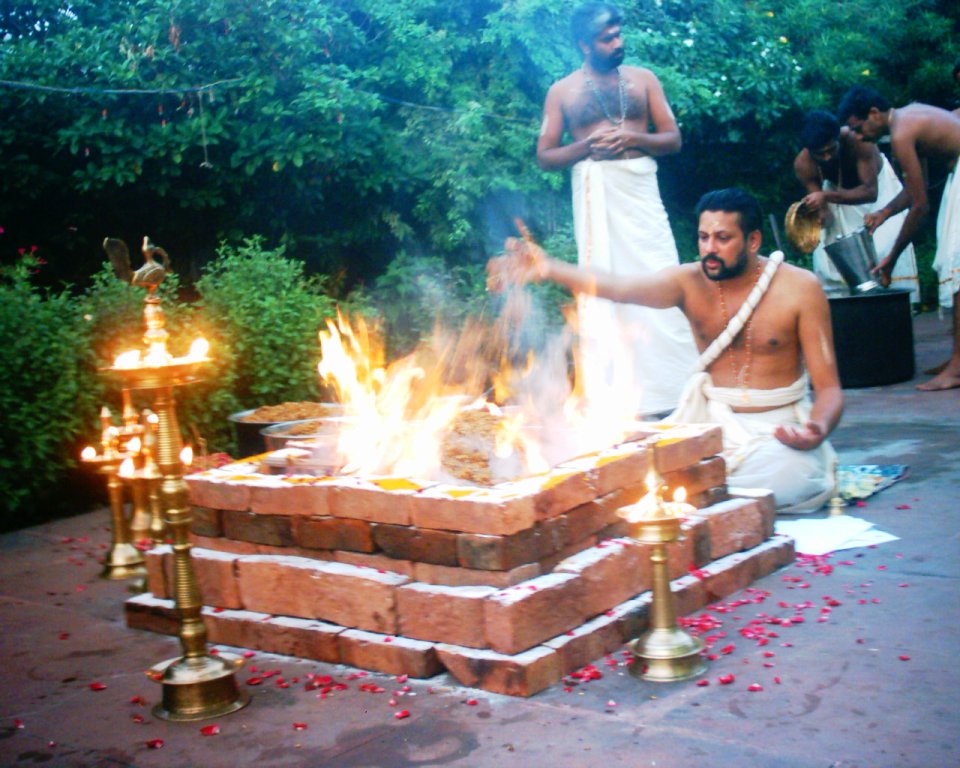
Homa (ritual)
In the Vedic Hinduism, a homa (Sanskrit: होम) also known as havan, is a fire ritual performed on special occasions by a Hindu priest usually for a homeowner (" grihastha": one possessing a home). The grihasth keeps different kinds of fire including one to cook food, heat his home, amongst other uses; therefore, a Yajna offering is made directly into the fire. A homa is sometimes called a "sacrifice ritual" because the fire destroys the offering, but a homa is more accurately a "votive ritual". The fire is the agent, and the offerings include those that are material and symbolic such as grains, ghee, milk, incense and seeds. It is rooted in the Vedic religion, and was adopted in ancient times by Buddhism and Jainism. The practice spread from India to Central Asia, East Asia and Southeast Asia. Homa rituals remain an important part of many Hindu ceremonies, and variations of homa continue to be practiced in current-day Buddhism, particularly in parts of Tibet and Japan. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kirtan
Kirtana ( sa, कीर्तन; ), also rendered as Kirtan, is a Sanskrit word that means "narrating, reciting, telling, describing" of an idea or story, specifically in Indian religions. It also refers to a genre of religious performance arts, connoting a musical form of narration or shared recitation, particularly of spiritual or religious ideas, native to the Indian subcontinent. With roots in the Vedic ''anukirtana'' tradition, a kirtan is a call-and-response style song or chant, set to music, wherein multiple singers recite or describe a legend, or express loving devotion to a deity, or discuss spiritual ideas. It may include dancing or direct expression of ''bhavas'' (emotive states) by the singer. Many kirtan performances are structured to engage the audience where they either repeat the chant,Sara Brown (2012), ''Every Word Is a Song, Every Step Is a Dance'', PhD Thesis, Florida State University (Advisor: Michael Bakan), pages 25-26, 87-88, 277 or reply to the call of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nathuram Mirdha
Nathuram Mirdha (20 October 1921 – 30 August 1996) was a parliamentarian, freedom fighter, social reformer and popular farmer leader of Marwar region in Rajasthan, India. He was born in Kuchera, Nagaur district, Rajasthan on 20 October 1921. His father's name was Thana Ram Mirdha. Education Nathuram Mirdha passed his matriculation from Darbar High School Jodhpur with first division with suplimentry. He earned an M.A. (Economics) and completed an LLB degree in 1944 from Lucknow University. Rise as farmer leader Nathuram Mirdha organised a massive farmer gathering at Jodhpur under the Chairmanship of Chhotu Ram. He joined the Institution of farmers "Kisan Sabha" founded by Baldev Ram Mirdha as Secretary in 1946. He was made the Revenue minister in the Jodhpur state. Nathuram Mirdha had an intimate association with Justice Kan Singh Parihar. Freedom fighter and political leader On 15 August 1947, with the independence of India, a popular Ministry was installed in Jodhpur. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jat People
The Jat people ((), ()) are a traditionally agricultural community in Northern India and Pakistan. Originally pastoralists in the lower Indus river-valley of Sindh, Jats migrated north into the Punjab region in late medieval times, and subsequently into the Delhi Territory, northeastern Rajputana, and the western Gangetic Plain in the 17th and 18th centuries. Quote: "Hiuen Tsang gave the following account of a numerous pastoral-nomadic population in seventh-century Sin-ti (Sind): 'By the side of the river.. f Sind along the flat marshy lowlands for some thousand li, there are several hundreds of thousands very great manyfamilies ..hichgive themselves exclusively to tending cattle and from this derive their livelihood. They have no masters, and whether men or women, have neither rich nor poor.' While they were left unnamed by the Chinese pilgrim, these same people of lower Sind were called Jats' or 'Jats of the wastes' by the Arab geographers. The Jats, as 'dromedary men.' we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patrilineality
Patrilineality, also known as the male line, the spear side or agnatic kinship, is a common kinship system in which an individual's family membership derives from and is recorded through their father's lineage. It generally involves the inheritance of property, rights, names, or titles by persons related through male kin. This is sometimes distinguished from cognate kinship, through the mother's lineage, also called the spindle side or the distaff side. A patriline ("father line") is a person's father, and additional ancestors, as traced only through males. Traditionally and historically people would identify the person's ethnicity with the father's heritage and ignore the maternal ancestry in the ethnic factor. In the Bible In the Bible, family and tribal membership appears to be transmitted through the father. For example, a person is considered to be a priest or Levite, if his father is a priest or Levite, and the members of all the Twelve Tribes are called Israelites because ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gotra
In Hindu culture, the term gotra (Sanskrit: गोत्र) is considered to be equivalent to lineage. It broadly refers to people who are descendants in an unbroken male line from a common male ancestor or patriline. Generally, the gotra forms an exogamous unit, with marriage within the same gotra being regarded as incest and prohibited by custom. The name of the gotra can be used as a surname, but it is different from a surname and is strictly maintained because of its importance in marriages among Hindus, especially among castes. Pāṇini defines ''gotra'' as ''apatyam pautraprabhrti gotram'' (IV. 1. 162), which means "the word ''gotra'' denotes the descendance (or descendants), ''apatya'', of a couple consisting of a ''pautra'', a son and a ''bharti'', a mother, i.e. a daughter-in-law." (Based on Monier Williams Dictionary definitions.) When a person says "I am Vipparla-gotra", he means that he traces his descent to the ancient sage Vipparla by an unbroken male descent. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_Bhumi_Puja%2C_yajna.jpg)