|
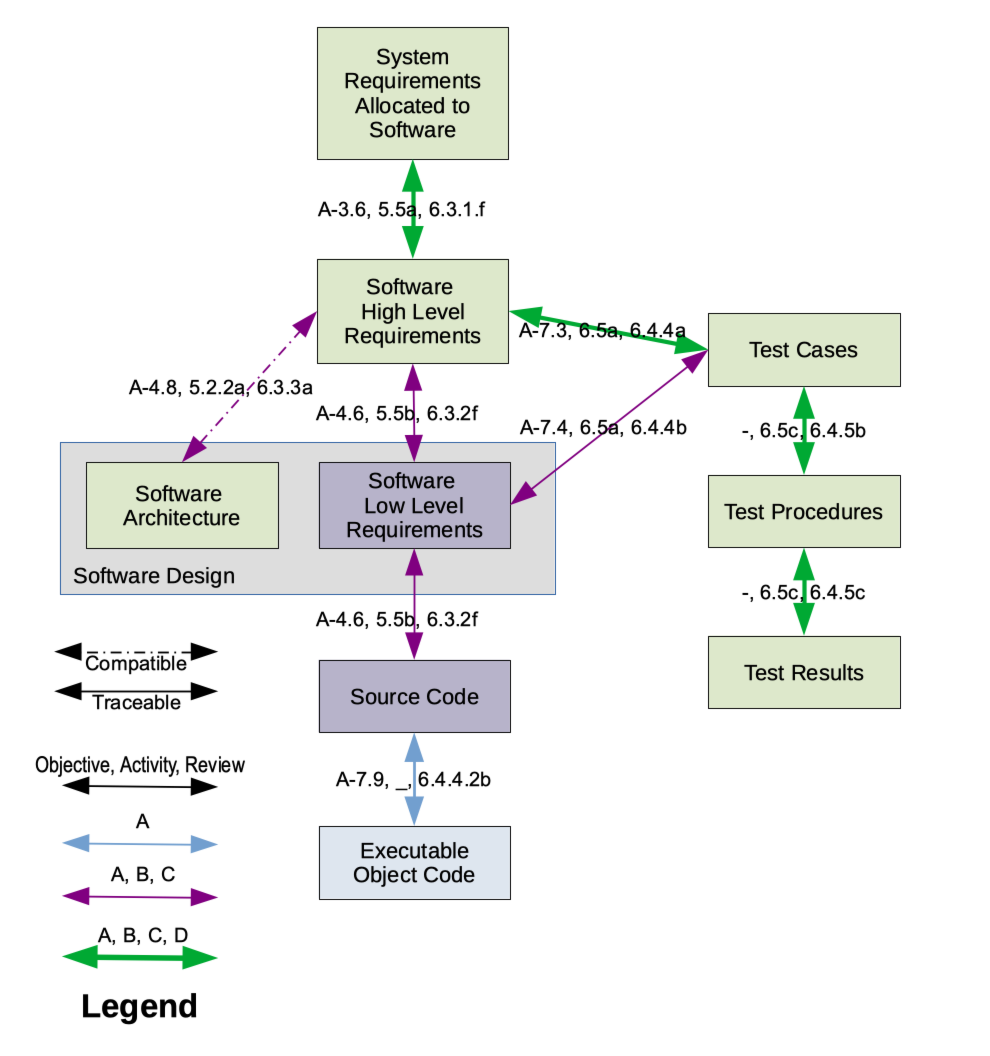
DO-178B
DO-178B, Software Considerations in Airborne Systems and Equipment Certification is a guideline dealing with the safety of safety-critical software used in certain airborne systems. It was jointly developed by the safety-critical working group RTCA SC-167 of the Radio Technical Commission for Aeronautics (RTCA) and WG-12 of the European Organisation for Civil Aviation Equipment (EUROCAE). RTCA published the document as RTCA/DO-178B, while EUROCAE published the document as ED-12B. Although technically a guideline, it was a ''de facto'' standard for developing avionics software systems until it was replaced in 2012 by DO-178C. The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) applies DO-178B as the document it uses for guidance to determine if the software will perform reliably in an airborne environment, when specified by the Technical Standard Order (TSO) for which certification is sought. In the United States, the introduction of TSOs into the airworthiness certification process, and b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DO-178C
DO-178C, Software Considerations in Airborne Systems and Equipment Certification is the primary document by which the certification authorities such as FAA, EASA and Transport Canada approve all commercial software-based aerospace systems. The document is published by RTCA, Incorporated, in a joint effort with EUROCAE, and replaces DO-178B. The new document is called DO-178C/ED-12C and was completed in November 2011 and approved by the RTCA in December 2011. It became available for sale and use in January 2012. Except for FAR 33/JAR E, the Federal Aviation Regulations do not directly reference software airworthiness. On 19 Jul 2013, the FAA approved AC 20-115C, designating DO-178C a recognized "acceptable means, but not the only means, for showing compliance with the applicable FAR airworthiness regulations for the software aspects of airborne systems and equipment certification." Background Since the release of DO-178B, there had been strong calls by DERs (FAA Designated Eng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Code Coverage
In computer science, test coverage is a percentage measure of the degree to which the source code of a program is executed when a particular test suite is run. A program with high test coverage has more of its source code executed during testing, which suggests it has a lower chance of containing undetected software bugs compared to a program with low test coverage. Many different metrics can be used to calculate test coverage. Some of the most basic are the percentage of program subroutines and the percentage of program statements called during execution of the test suite. Test coverage was among the first methods invented for systematic software testing. The first published reference was by Miller and Maloney in ''Communications of the ACM'', in 1963. Coverage criteria To measure what percentage of code has been executed by a test suite, one or more ''coverage criteria'' are used. These are usually defined as rules or requirements, which a test suite must satisfy. Basic cove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ARP4754
ARP4754, Aerospace Recommended Practice (ARP) ARP4754A (''Guidelines For Development Of Civil Aircraft and Systems''), is a guideline from SAE International, dealing with the development processes which support certification of Aircraft systems, addressing "the complete aircraft development cycle, from systems requirements through systems verification." Revision A was released in December 2010. It was recognized by the FAA in AC 20-174 published November 2011. EUROCAE jointly issues the document as ED–79. Objectives of the document The Aerospace Recommended Practice (ARP) is a guideline for development of civil aircraft and systems with an emphasis on safety aspects. Revision A is a substantial rewrite of the document which describes the safety process as a part of an Integrated Development Process. A significant new section is devoted to the process of determining Development Assurance Level (DAL) which determines the rigor of complex hardware and software development and ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hazard Analysis
A hazard analysis is used as the first step in a process used to assess risk. The result of a hazard analysis is the identification of different types of hazards. A hazard is a potential condition and exists or not (probability is 1 or 0). It may, in single existence or in combination with other hazards (sometimes called events) and conditions, become an actual Functional Failure or Accident (Mishap). The way this exactly happens in one particular sequence is called a scenario. This scenario has a probability (between 1 and 0) of occurrence. Often a system has many potential failure scenarios. It also is assigned a classification, based on the worst case severity of the end condition. Risk is the combination of probability and severity. Preliminary risk levels can be provided in the hazard analysis. The validation, more precise prediction (verification) and acceptance of risk is determined in the risk assessment (analysis). The main goal of both is to provide the best selection of m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ARP4761
ARP4761, Guidelines and Methods for Conducting the Safety Assessment Process on Civil Airborne Systems and Equipment is an Aerospace Recommended Practice from SAE International. In conjunction with ARP4754, ARP4761 is used to demonstrate compliance with 14 CFR 25.1309 in the U.S. Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) airworthiness regulations for transport category aircraft, and also harmonized international airworthiness regulations such as European Aviation Safety Agency (EASA) CS–25.1309. This Recommended Practice defines a process for using common modeling techniques to assess the safety of a system being put together. The first 30 pages of the document covers that process. The next 140 pages give an overview of the modeling techniques and how they should be applied. The last 160 pages give an example of the process in action. Some of the methods covered: * Functional Hazard Assessment (FHA) *Preliminary System Safety Assessment (PSSA) *System Safety Assessme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radio Technical Commission For Aeronautics
RTCA, Inc. (formerly known as Radio Technical Commission for Aeronautics) is a United States non-profit organization that develops technical guidance for use by government regulatory authorities and by industry. It was founded in 1935 and was re-incorporated in 1991 as a private not-for-profit corporation. It has over 20 active committees with multiple working groups under each committee and develops industry standards in cooperation with aviation regulators from around the world including the FAA. Requirements for membership are limited to organizations (e.g., private industry, government, academic, and research and development) that have an interest and skill in the aviation industry and are willing to provide those skills through the work of their employees who volunteer their time and energy to produce usable and complete engineering standards documents. Standards are developed and drafted by Special Committees (SC) and are approved by the Program Management Committee, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avionics Software
Avionics software is embedded software with legally mandated safety and reliability concerns used in avionics. The main difference between avionic software and conventional embedded software is that the development process is ''required by law'' and is ''optimized for safety.'' It is claimed that the process described below is only slightly slower and more costly (perhaps 15 percent) than the normal ''ad hoc'' processes used for commercial software. Since most software fails because of mistakes, eliminating the mistakes at the earliest possible step is also a relatively inexpensive and reliable way to produce software. In some projects however, mistakes in the specifications may not be detected until deployment. At that point, they can be very expensive to fix. The basic idea of any software development model is that each step of the design process has outputs called "deliverables." If the deliverables are tested for correctness and fixed, then normal human mistakes can not e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Safety-critical
A safety-critical system (SCS) or life-critical system is a system whose failure or malfunction may result in one (or more) of the following outcomes: * death or serious injury to people * loss or severe damage to equipment/property * environmental harm A safety-related system (or sometimes safety-involved system) comprises everything (hardware, software, and human aspects) needed to perform one or more safety functions, in which failure would cause a significant increase in the safety risk for the people or environment involved. Safety-related systems are those that do not have full responsibility for controlling hazards such as loss of life, severe injury or severe environmental degradation, environmental damage. The malfunction of a safety-involved system would only be that hazardous in conjunction with the failure of other systems or human error. Some safety organizations provide guidance on safety-related systems, for example the Health and Safety Executive (HSE) in the Un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
V Model
The V-model is a graphical representation of a systems development lifecycle. It is used to produce rigorous development lifecycle models and project management models. The V-model falls into three broad categories, the German ''V-Modell'', a general testing model and the US government standard. The V-model summarizes the main steps to be taken in conjunction with the corresponding deliverables within computerized system validation framework, or project life cycle development. It describes the activities to be performed and the results that have to be produced during product development. The left side of the "V" represents the decomposition of requirements, and creation of system specifications. The right side of the "V" represents integration of parts and their validation.Forsberg, K. and Mooz, H."The Relationship of Systems Engineering to the Project Cycle", First Annual Symposium of the National Council On Systems Engineering (NCOSE), October 1991 However, requirements need ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commercial Off-the-shelf
Commercial off-the-shelf or commercially available off-the-shelf (COTS) products are packaged or canned (ready-made) hardware or software, which are adapted aftermarket to the needs of the purchasing organization, rather than the commissioning of custom-made, or bespoke, solutions. A related term, Mil-COTS, refers to COTS products for use by the U.S. military. In the context of the U.S. government, the Federal Acquisition Regulation (FAR) has defined "COTS" as a formal term for commercial items, including services, available in the commercial marketplace that can be bought and used under government contract. For example, Microsoft is a COTS software provider. Goods and construction materials may qualify as COTS but bulk cargo does not. Services associated with the commercial items may also qualify as COTS, including installation services, training services, and cloud services. COTS purchases are alternatives to custom software or one-off developments – government-funded dev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Box Testing
Black-box testing is a method of software testing that examines the functionality of an application without peering into its internal structures or workings. This method of test can be applied virtually to every level of software testing: unit, integration, system and acceptance. It is sometimes referred to as specification-based testing. Test procedures Specific knowledge of the application's code, internal structure and programming knowledge in general is not required. The tester is aware of ''what'' the software is supposed to do but is not aware of ''how'' it does it. For instance, the tester is aware that a particular input returns a certain, invariable output but is not aware of ''how'' the software produces the output in the first place. Test cases Test cases are built around specifications and requirements, i.e., what the application is supposed to do. Test cases are generally derived from external descriptions of the software, including specifications, requirements ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quality Assurance
Quality assurance (QA) is the term used in both manufacturing and service industries to describe the systematic efforts taken to ensure that the product(s) delivered to customer(s) meet with the contractual and other agreed upon performance, design, reliability, and maintainability expectations of that customer. The core purpose of Quality Assurance is to prevent mistakes and defects in the development and production of both manufactured products, such as automobiles and shoes, and delivered services, such as automotive repair and athletic shoe design. Assuring quality and therefore avoiding problems and delays when delivering products or services to customers is what ISO 9000 defines as that "part of quality management focused on providing confidence that quality requirements will be fulfilled". This defect prevention aspect of quality assurance differs from the defect detection aspect of quality control and has been referred to as a ''shift left'' since it focuses on quality effor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |