|
DNA History Of Egypt
The genetic history of Egypt's demographics reflects its geographical location at the crossroads of several major biocultural areas: North Africa, the Sahara, the Middle East, the Mediterranean and sub-Saharan Africa. Ancient DNA Contamination from handling and intrusion from microbes can create issues in the recovery of ancient DNA, but new extraction methods from multiple different types of tissue have reduced contamination analysis rates Barry Kemp (Egyptologist) has noted that DNA studies can only provide firm conclusions about the population of ancient Egypt if the sample results are of a significant number of individuals and represent a broad geographical and chronological range. DNA studies have been criticised for a range of methodological problems and providing misleading, interpretations on racial classifications. 2012 Ramesses III In 2012, the 20th dynasty mummies of Ramesses III and another mummy "Unknown Man E" believed to be Ramesses III's son Pentawer were a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic History
Archaeogenetics is the study of ancient DNA using various molecular genetic methods and DNA resources. This form of genetic analysis can be applied to human, animal, and plant specimens. Ancient DNA can be extracted from various fossilized specimens including bones, eggshells, and artificially preserved tissues in human and animal specimens. In plants, Ancient DNA can be extracted from seeds and tissue. Archaeogenetics provides us with genetic evidence of ancient population group migrations, domestication events, and plant and animal evolution. The ancient DNA cross referenced with the DNA of relative modern genetic populations allows researchers to run comparison studies that provide a more complete analysis when ancient DNA is compromised. Archaeogenetics receives its name from the Greek word ''arkhaios'', meaning "ancient", and the term ''genetics'', meaning "the study of heredity". The term archaeogenetics was conceived by archaeologist Colin Renfrew. In February 2021, scienti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abusir
Abusir ( ar, ابو صير ; Egyptian ''pr wsjr'' cop, ⲃⲟⲩⲥⲓⲣⲓ ' "the House or Temple of Osiris"; grc, Βούσιρις) is the name given to an Egyptian archaeological locality – specifically, an extensive necropolis of the Old Kingdom period, together with later additions – in the vicinity of the modern capital Cairo. The name is also that of a neighbouring village in the Nile Valley, whence the site takes its name. Abusir is located several kilometres north of Saqqara and, like it, served as one of the main elite cemeteries for the ancient Egyptian capital city of Memphis. Several other villages in northern and southern Egypt are named Abusir or Busiri. Abusir is one relatively small segment of the extensive "pyramid field" that extends from north of Giza to below Saqqara. The locality of Abusir took its turn as the focus of the prestigious western burial rites operating out of the then-capital of Memphis during the Old Kingdom 5th Dynasty. As an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
12th Dynasty
The Twelfth Dynasty of ancient Egypt (Dynasty XII) is considered to be the apex of the Middle Kingdom by Egyptologists. It often is combined with the Eleventh, Thirteenth, and Fourteenth dynasties under the group title, Middle Kingdom. Some scholars only consider the 11th and 12th dynasties to be part of the Middle Kingdom. History The chronology of the Twelfth Dynasty is the most stable of any period before the New Kingdom. The Turin Royal Canon gives 213 years (1991–1778 BC). Manetho stated that it was based in Thebes, but from contemporary records it is clear that the first king of this dynasty, Amenemhat I, moved its capital to a new city named "Amenemhat-itj-tawy" ("Amenemhat the Seizer of the Two Lands"), more simply called, Itjtawy. The location of Itjtawy has not been discovered yet, but is thought to be near the Fayyum, probably near the royal graveyards at el-Lisht. The order of its rulers of the Twelfth Dynasty is well known from several sources: two lists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ernest Mackay
Ernest is a given name derived from Germanic word ''ernst'', meaning "serious". Notable people and fictional characters with the name include: People * Archduke Ernest of Austria (1553–1595), son of Maximilian II, Holy Roman Emperor * Ernest, Margrave of Austria (1027–1075) *Ernest, Duke of Bavaria (1373–1438) * Ernest, Duke of Opava (c. 1415–1464) *Ernest, Margrave of Baden-Durlach (1482–1553) *Ernest, Landgrave of Hesse-Rheinfels (1623–1693) *Ernest Augustus, Elector of Brunswick-Lüneburg (1629–1698) *Ernest, Count of Stolberg-Ilsenburg (1650–1710) * Ernest Augustus, King of Hanover (1771–1851), son of King George III of Great Britain *Ernest II, Duke of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha (1818–1893), sovereign duke of the Duchy of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha *Ernest Augustus, Crown Prince of Hanover (1845–1923) *Ernest, Landgrave of Hesse-Philippsthal (1846–1925) *Ernest Augustus, Prince of Hanover (1914–1987) *Prince Ernst August of Hanover (born 1954) * Prince Erns ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flinders Petrie
Sir William Matthew Flinders Petrie ( – ), commonly known as simply Flinders Petrie, was a British Egyptologist and a pioneer of systematic methodology in archaeology and the preservation of artefacts. He held the first chair of Egyptology in the United Kingdom, and excavated many of the most important archaeological sites in Egypt in conjunction with his wife, Hilda Urlin. Some consider his most famous discovery to be that of the Merneptah Stele, an opinion with which Petrie himself concurred. Undoubtedly at least as important is his 1905 discovery and correct identification of the character of the Proto-Sinaitic script, the ancestor of almost all alphabetic scripts. Petrie developed the system of dating layers based on pottery and ceramic findings. He remains controversial for his pro-eugenics views; he was a dedicated believer in the superiority of the Northern peoples over the Latinate and Southern peoples. Early life Petrie was born on 3 June 1853 in Charlto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Egypt
Prehistoric Egypt and Predynastic Egypt span the period from the earliest human settlement to the beginning of the Early Dynastic Period around 3100 BC, starting with the first Pharaoh, Narmer for some Egyptologists, Hor-Aha for others, with the name Menes also possibly used for one of these kings. At the end of prehistory, "Predynastic Egypt" is traditionally defined as the period from the final part of the Neolithic period beginning c. 6000 BC to the end of the Naqada III period c. 3000 BC. The dates of the Predynastic period were first defined before widespread archaeological excavation of Egypt took place, and recent finds indicating very gradual Predynastic development have led to controversy over when exactly the Predynastic period ended. Thus, various terms such as " Protodynastic period", "Zero Dynasty" or "Dynasty 0" are used to name the part of the period which might be characterized as Predynastic by some and Early Dynastic by others. The Predynastic period is ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Near East
The ''Near East''; he, המזרח הקרוב; arc, ܕܢܚܐ ܩܪܒ; fa, خاور نزدیک, Xāvar-e nazdik; tr, Yakın Doğu is a geographical term which roughly encompasses a transcontinental region in Western Asia, that was once the historical Fertile Crescent, and later the Levant region. It also comprises Turkey (both Anatolia and East Thrace) and Egypt (mostly located in North Africa, with the Sinai Peninsula being in Asia). Despite having varying definitions within different academic circles, the term was originally applied to the maximum extent of the Ottoman Empire. According to the National Geographic Society, the terms ''Near East'' and ''Middle East'' denote the same territories and are "generally accepted as comprising the countries of the Arabian Peninsula, Cyprus, Egypt, Iraq, Iran, Israel, Jordan, Lebanon, Palestinian territories, Syria, and Turkey". In 1997, the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations defined the region similarly, bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classical Anatolia
Classical Anatolia is Anatolia during Classical Antiquity. Early in that period, Anatolia was divided into several Iron Age kingdoms, most notably Lydia in the west, Phrygia in the center and Urartu in the east. Anatolia fell under Achaemenid Persian rule c. 550 BC. In the aftermath of the Greco-Persian Wars, all of Anatolia remained under Persian control except for the Aegean coast, which was incorporated in the Delian League in the 470s BC. Alexander the Great finally wrested control of the whole region from Persia in the 330s BC. After Alexander's death, his conquests were split amongst several of his trusted generals, but were under constant threat of invasion from both the Gauls and other powerful rulers in Pergamon, Pontus, and Egypt. The Seleucid Empire, the largest of Alexander's territories, and which included Anatolia, became involved in a disastrous war with Rome culminating in the battles of Thermopylae and Magnesia. The resulting Treaty of Apamea in (188 BC) saw t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Afroasiatic Languages
The Afroasiatic languages (or Afro-Asiatic), also known as Hamito-Semitic, or Semito-Hamitic, and sometimes also as Afrasian, Erythraean or Lisramic, are a language family of about 300 languages that are spoken predominantly in the geographic subregions of Western Asia, North Africa, the Horn of Africa, and parts of the Sahara/ Sahel. With the exception of its Semitic branch, all branches of the Afroasiatic family are exclusively native to the African continent. Afroasiatic languages have over 500 million native speakers, which is the fourth-largest number of native speakers of any language family (after Indo-European, Sino-Tibetan, and Niger–Congo). The phylum has six branches: Berber, Chadic, Cushitic, Egyptian, Semitic, and Omotic. The most widely spoken modern Afroasiatic language or dialect continuum by far is Arabic, a ''de facto'' group of distinct language varieties within the Semitic branch. The languages that evolved from Proto-Arabic have around 313 m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
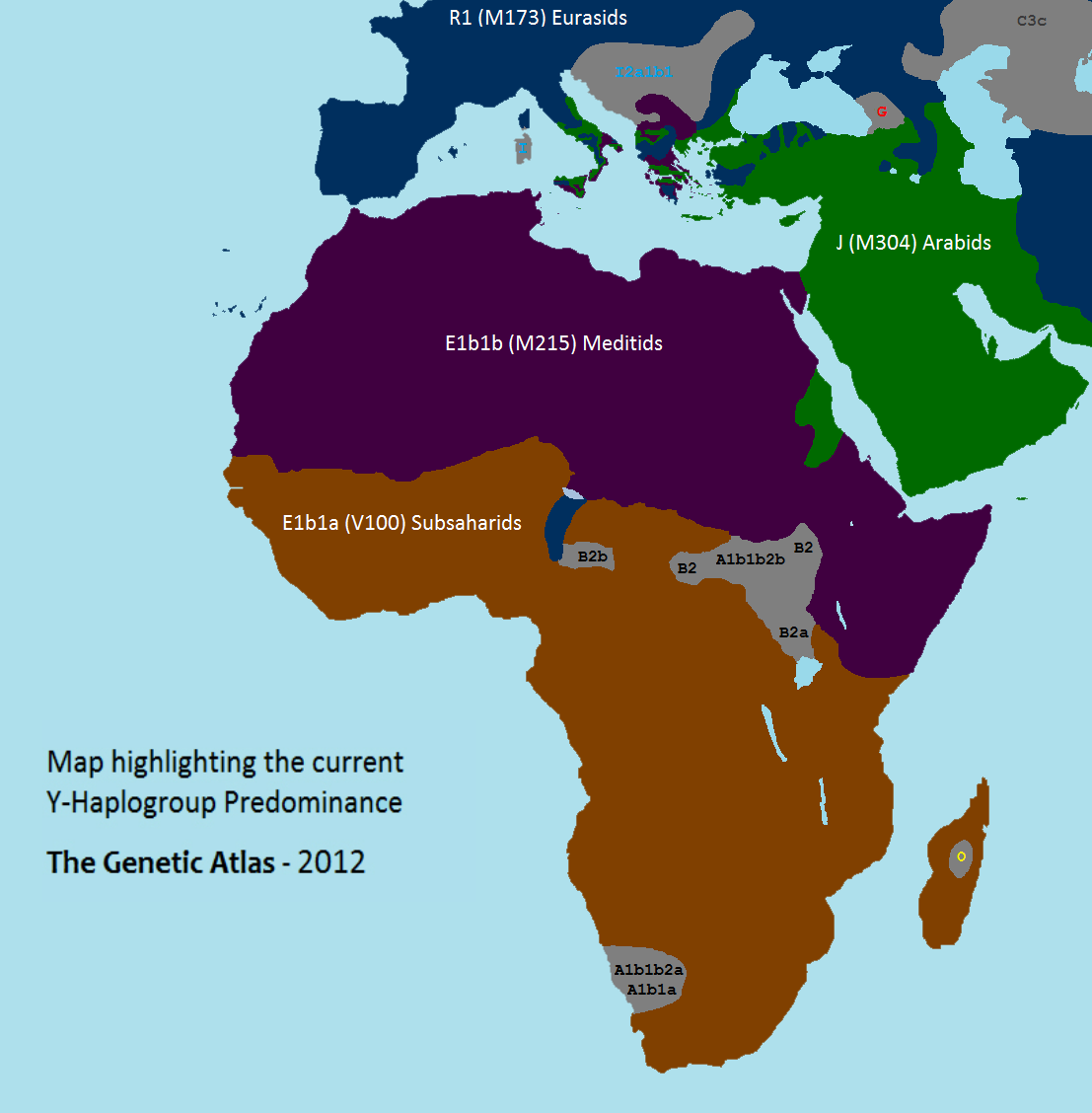
Haplogroup E (Y-DNA)
Haplogroup E-M96 is a human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup. It is one of the two main branches of the older and ancestral haplogroup DE, the other main branch being haplogroup D. The E-M96 clade is divided into two main subclades: the more common E-P147, and the less common E-M75. Origins Underhill (2001) proposed that haplogroup E may have arisen in East Africa. Some authors as Chandrasekar (2007), accept the earlier position of Hammer (1997) that Haplogroup E may have originated in West Asia, given that: * E is a clade of Haplogroup DE, with the other major clade, haplogroup D, being exclusively distributed in Asia. * DE is a clade within M168 with the other two major clades, C and F, considered to have already a Eurasian origin. However, several discoveries made since the Hammer articles are thought to make an Asian origin less likely: # Underhill and Kivisild (2007) demonstrated that C and F have a common ancestor meaning that DE has only one sibling which is non-Africa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haplogroup J (Y-DNA)
Haplogroup J-M304, also known as J, ISOGGbr> ''Y-DNA Haplogroup J and its Subclades - 2016'' (2 February 2016). is a human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup. It is believed to have evolved in Western Asia. The clade spread from there during the Neolithic, primarily into North Africa, the Horn of Africa, the Socotra Archipelago, the Caucasus, Europe, Western Asia, Central Asia, South Asia, and Southeast Asia. Haplogroup J-M304 is divided into two main subclades (branches), J-M267 and J-M172. Origins Haplogroup J-M304 is believed to have split from the haplogroup I-M170 roughly 43,000 years ago in Western Asia, as both lineages are haplogroup IJ subclades. Haplogroup IJ and haplogroup K derive from haplogroup IJK, and only at this level of classification does haplogroup IJK join with Haplogroup G-M201 and Haplogroup H as immediate descendants of Haplogroup F-M89. J-M304 is defined by the M304 genetic marker, or the equivalent 12f2.1 marker. The main current subgroups J-M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Asia
Western Asia, West Asia, or Southwest Asia, is the westernmost subregion of the larger geographical region of Asia, as defined by some academics, UN bodies and other institutions. It is almost entirely a part of the Middle East, and includes Anatolia, the Arabian Peninsula, Iran, Mesopotamia, the Armenian Highlands, the Levant, the island of Cyprus, the Sinai Peninsula, and partly the Caucasus Region ( Transcaucasia). The region is considered to be separated from Africa by the Isthmus of Suez in Egypt, and separated from Europe by the waterways of the Turkish Straits and the watershed of the Greater Caucasus. Central Asia lies to its northeast, while South Asia lies to its east. Twelve seas surround the region (clockwise): the Aegean Sea, the Sea of Marmara, the Black Sea, the Caspian Sea, the Persian Gulf, the Gulf of Oman, the Arabian Sea, the Gulf of Aden, the Red Sea, the Gulf of Aqaba, the Gulf of Suez, and the Mediterranean Sea. Western Asia covers an area of , with a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_and_migration_routes.png)


.jpg)