|
DKW F9
The DKW F9 was the prototype of a car Auto Union intended to launch as a successor to the DKW F8. The small DKWs were among top selling small cars in Germany in the 1930s, and regular model updates were part of the company's strategy for maintaining commercial success in this growing market sector. With its all steel body designed by Guenther Mickwausch the F9 would have represented a significantly greater step forward than the F8 had done: it appears that the F9 was already under development in 1937, two years before launch of its F8 predecessor. Several prototypes were built during the 1939-1942 period. A Cd factor of 0.42 was claimed for the new design and the look of the car was significantly smoother than the 1930s DKW designs. For the first time, a three cylinder engine was specified, implying useful performance advantages. In other respects, DKW traditions were respected. The engine was still a two stroke unit, and the driven wheels were still the front wheel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auto Union
Auto Union AG, was an amalgamation of four German automobile manufacturers, founded in 1932 and established in 1936 in Chemnitz, Saxony. It is the immediate predecessor of Audi as it is known today. As well as acting as an umbrella firm for its four constituent brands (Audi, Horch, DKW, Wanderer), Auto Union is widely known for its racing team (''Auto Union Rennabteilung'', based at Horch works in Zwickau/Saxony). The Silver Arrows of the two German teams (Mercedes-Benz and Auto Union) dominated not only GP car racing from 1934 onwards but set records that would take decades to beat, such as the fastest speed ever attained on a public road (at 432.7 km/h (268.9 mph), a record lasting until 2017. After being reduced to near ruin in the aftermath of World War II, Auto Union was re-founded in Ingolstadt, Bavaria, in 1949, ultimately evolving into the modern day Audi company following its takeover by Volkswagen in 1964 and later merger with NSU Motorenwerke in 1969. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
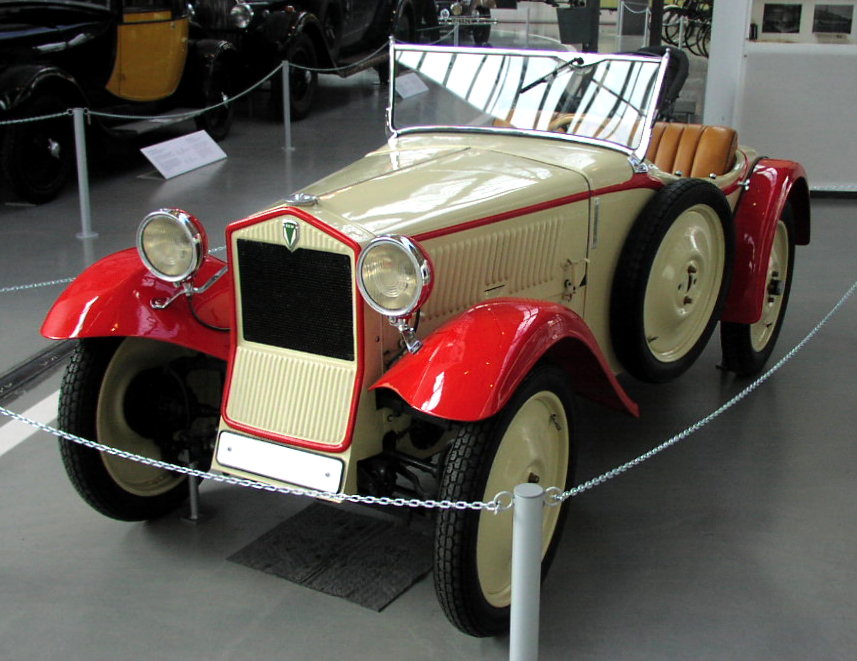
DKW F8
The DKW F8 is a compact front-wheel drive two-stroke engined saloon, introduced in 1939.Odin, L.C. ''World in Motion 1939 - The whole of the year's automobile production''. Belvedere Publishing, 2015. ASIN: B00ZLN91ZG. The F8 was slightly shorter than its predecessor despite having a marginally increased wheelbase. The base model, known as the Reichsklasse, was manufactured only till 1940 but the Meisterklasse sedan continued in production until 1942. In addition to the saloons, cabriolet versions were offered. The "F" in the car's name stood for "Front" which referred to its front wheel drive configuration. Although in retrospect it is almost always identified as the "F8" which distinguishes it from the "F7" which preceded it and from the "F9" which was intended to replace it, the manufacturer's publicity material from 1939 calls it simply the "DKW Front". After the war the car reappeared in 1949 as the IFA F8, from the Zwickau plant which now operated under Soviet control. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated between the Baltic and North seas to the north, and the Alps to the south; it covers an area of , with a population of almost 84 million within its 16 constituent states. Germany borders Denmark to the north, Poland and the Czech Republic to the east, Austria and Switzerland to the south, and France, Luxembourg, Belgium, and the Netherlands to the west. The nation's capital and most populous city is Berlin and its financial centre is Frankfurt; the largest urban area is the Ruhr. Various Germanic tribes have inhabited the northern parts of modern Germany since classical antiquity. A region named Germania was documented before AD 100. In 962, the Kingdom of Germany formed the bulk of the Holy Roman Empire. During the 16th ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Straight-3
A straight-three engine (also called an inline-triple or inline-three) is a three-cylinder piston engine where cylinders are arranged in a line along a common crankshaft. Less common than straight-four engines, straight-three engines have nonetheless been used in various motorcycles, cars and agricultural machinery. Design A crankshaft angle of 120 degrees is typically used by straight-three engines, since this results in an evenly spaced firing interval. Another benefit of this configuration is perfect primary balance and secondary balance, however an end-to-end rocking couple is induced because there is no symmetry in the piston velocities about the middle piston. A balance shaft is sometimes used to reduce the vibrations caused by the rocking couple. Other crankshaft angles have been used occasionally. The 1976-1981 Laverda Jota motorcycle used a 180 degree crankshaft, where the outer pistons rise and fall together and inner cylinder is offset from them by 180 degrees. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries. The major participants in the war threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Aircraft played a major role in the conflict, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and deploying the only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was by far the deadliest conflict in human history; it resulted in 70 to 85 million fatalities, mostly among civilians. Tens of millions died due to genocides (including the Holocaust), starvation, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zwickau
Zwickau (; is, with around 87,500 inhabitants (2020), the fourth-largest city of Saxony after Leipzig, Dresden and Chemnitz and it is the seat of the Zwickau District. The West Saxon city is situated in the valley of the Zwickau Mulde (German: ''Zwickauer Mulde''; progression: ), and lies in a string of cities sitting in the densely populated foreland of the Elster and Ore Mountains stretching from Plauen in the southwest via Zwickau, Chemnitz and Freiberg to Dresden in the northeast. From 1834 until 1952, Zwickau was the seat of the government of the south-western region of Saxony. The name of the city is of Sorbian origin and may refer to Svarog, the Slavic god of fire and of the sun. Zwickau is the seat of the West Saxon University of Zwickau (German: ''Westsächsische Hochschule Zwickau'') with campuses in Zwickau, Markneukirchen, Reichenbach im Vogtland and Schneeberg (Erzgebirge). The city is the birthplace of composer Robert Schumann. As cradle of Audi's forerunner ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IFA F9
The IFA F9, subsequently rebadged as the EMW 309, is a compact saloon manufactured under the auspices of the Russian and East German states between 1949 or 1950 and 1956. It was initially built at Zwickau at the plant previously owned by Auto Union. In 1953 production was transferred to the EMW, former BMW manufacturing plant at Eisenach under the name ''EMW 309'' until 1956 where its underpinnings subsequently found their way into the Wartburg 311. Origins Mechanically the F9 derived from the DKW F8 which had been available between 1939 and 1942. The body closely followed the design of the DKW F9, a prototype with which Auto Union would have replaced the F8 on the Zwickau production lines earlier, had the war not intervened. After the war, the first car assembled at Zwickau was the prewar DKW F8, but the more modern F9 started to appear in 1949 or 1950 (sources differ). Materials shortages probably delayed introduction in both German states, but the eastern car beat the wester ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Industrieverband Fahrzeugbau
''Industrieverband Fahrzeugbau'' ("Industrial Association for Vehicle Construction"), usually abbreviated as IFA, was a conglomerate and a union of companies for vehicle construction in the former East Germany. IFA produced bicycles, motorcycles, light commercial vehicles, automobiles, vans and heavy trucks. All East German vehicle manufacturers were part of the IFA, including Barkas, EMW (which made Wartburg cars), IWL, MZ, Multicar, Robur, Sachsenring (which made Trabant cars) and Simson. Car production IFA cars were based on pre-war ''DKW'' designs and made in the former Horch factory in Zwickau. The F8 had a two-cylinder engine, and the F9 had a three-cylinder unit. The F8 bodies were straight copies of the pre-war models, and rapidly looked old-fashioned, but some had more modern coachwork by Baur of Stuttgart, then in West Germany. The three cylinder cars (F9) had not got into production before war broke out in 1939, and so had more up to date bodies similar to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DKW F91
F91 may refer to : * F91 Dudelange, a football club, based in Dudelange in southern Luxembourg * ''Mobile Suit Gundam F91'', a 1991 animated film * HMS Brazen (F91), a 1981 British Royal Navy Type 22 frigate * HMS Murray (F91), a British Royal Navy Blackwood class second-rate anti-submarine frigate * Republic XF-91 Thunderceptor, a rocket-jet hybrid interceptor * Casio F-91W, a common and inexpensive digital watch, claimed by some to be associated with terrorism Terrorism, in its broadest sense, is the use of criminal violence to provoke a state of terror or fear, mostly with the intention to achieve political or religious aims. The term is used in this regard primarily to refer to intentional violen ... * The McCarthy 91 function, a recursively defined mathematical function and also: * Conduct disorders ICD-10 code {{Letter-NumberCombDisambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DKW Vehicles
DKW (''Dampf-Kraft-Wagen'', en, "steam-powered car", also ''Deutsche Kinder-Wagen'' en, "German children's car". ''Das-Kleine-Wunder'', en, "the little wonder" or ''Des-Knaben-Wunsch'', en, "the boy's wish"- from when the company built toy two-stroke engines) was a German car- and motorcycle-marque. DKW was one of the four companies that formed Auto Union in 1932 and thus became an ancestor of the modern-day Audi company. In 1916, Danish engineer Jørgen Skafte Rasmussen founded a factory in Zschopau, Saxony, Germany, to produce steam fittings. That year he attempted to produce a steam-driven car, called the DKW.Odin, L.C. ''World in Motion 1939 – The whole of the year's automobile production''. Belvedere Publishing, 2015. ASIN: B00ZLN91ZG. Although unsuccessful, he made a two-stroke toy engine in 1919, called ''Des Knaben Wunsch'' – "the boy's wish". He put a slightly modified version of this engine into a motorcycle and called it ''Das Kleine Wunder'' – "the litt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compact Cars
Compact as used in politics may refer broadly to a pact or treaty; in more specific cases it may refer to: * Interstate compact * Blood compact, an ancient ritual of the Philippines * Compact government, a type of colonial rule utilized in British North America * Compact of Free Association whereby the sovereign states of the Federated States of Micronesia, the Republic of the Marshall Islands and the Republic of Palau have entered into as associated states with the United States. * Mayflower Compact, the first governing document of Plymouth Colony * United Nations Global Compact * Global Compact for Migration, a UN non-binding intergovernmental agreement Mathematics * Compact element, those elements of a partially ordered set that cannot be subsumed by a supremum of any directed set that does not already contain them * Compact operator, a linear operator that takes bounded subsets to relatively compact subsets, in functional analysis * Compact space, a topological space such th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Front-wheel-drive Vehicles
Front-wheel drive (FWD) is a form of engine and transmission layout used in motor vehicles, where the engine drives the front wheels only. Most modern front-wheel drive vehicles feature a transverse engine, rather than the conventional longitudinal engine arrangement generally found in rear-wheel drive and four-wheel drive vehicles. Location of engine and transmission By far the most common layout for a front-wheel drive car is with the engine and transmission at the front of the car, mounted transversely. Other layouts of front-wheel drive that have been occasionally produced are a front-engine mounted longitudinally, a mid-engine layout and a rear-engine layout. History Prior to 1900 Experiments with front-wheel drive cars date to the early days of the automobile. The world's first self-propelled vehicle, Nicolas-Joseph Cugnot's 1769/1770 "fardier à vapeur", was a front-wheel driven three-wheeled steam-tractor. It then took at least a century, for the first e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |