|
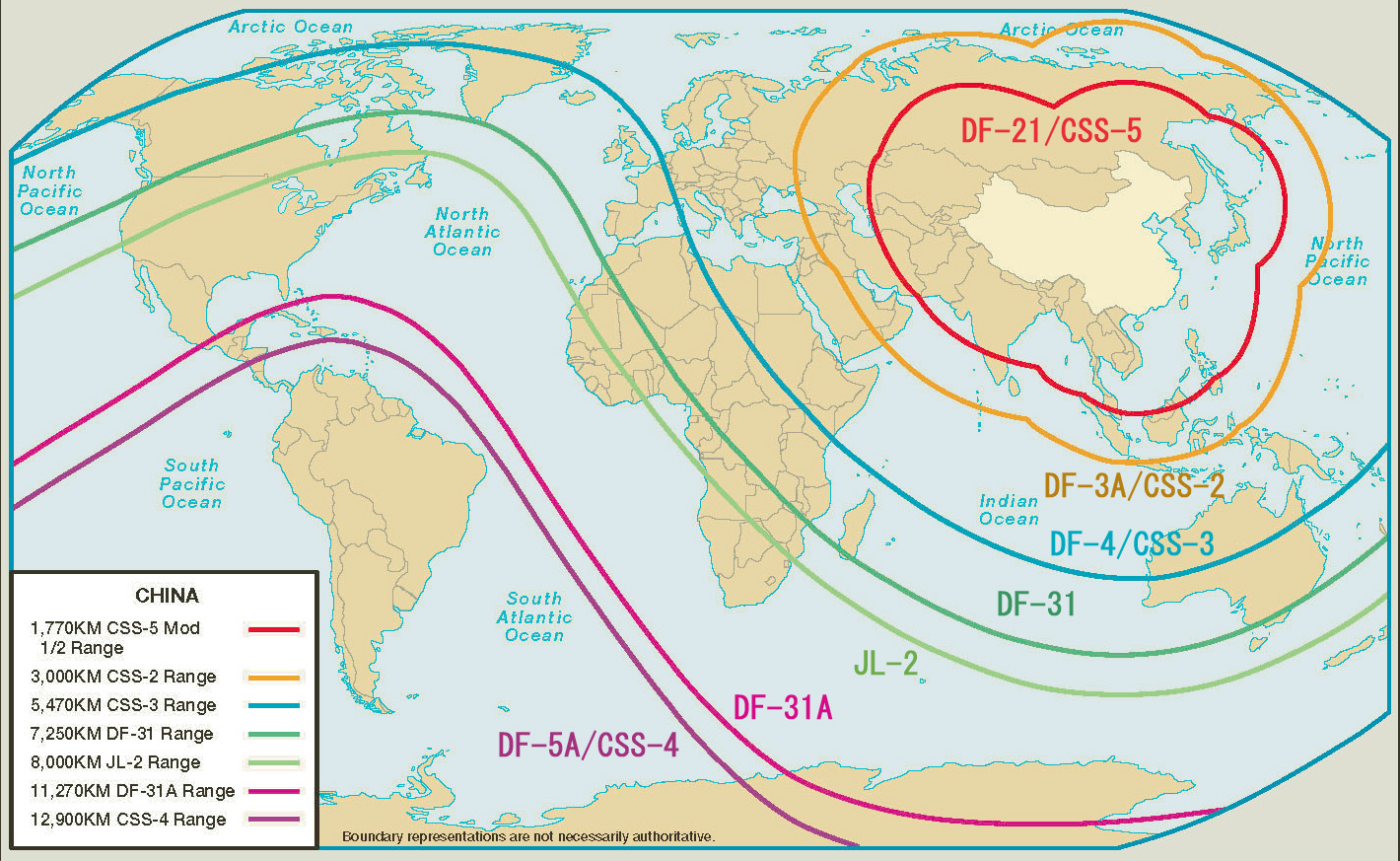
DF-21
The Dong-Feng 21 (DF-21; NATO reporting name CSS-5 - Dong-Feng () is a two-stage, solid-fuel rocket, single-warhead medium-range ballistic missile (MRBM) in the Dong Feng series developed by China Changfeng Mechanics and Electronics Technology Academy. Development started in the late 1960s and was completed around 1985–86, but it was not deployed until 1991. It was developed from the submarine-launched JL-1 missile, and is China's first solid-fuel land-based missile. The U.S. Department of Defense in 2008 estimated that China had 60-80 missiles and 60 launchers; approximately 10-11 missiles can be built annually. Originally developed as a strategic weapon, the DF-21's later variants were designed for both nuclear and conventional missions. It is thought able to carry a high explosive, submunition, or 300 kt nuclear warhead. The latest DF-21D was said to be the world's first anti-ship ballistic missile (ASBM). The DF-21 has also been developed into a space-capable anti-sate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dongfeng-21D
The Dong-Feng 21 (DF-21; NATO reporting name CSS-5 - Dong-Feng () is a two-stage, solid-fuel rocket, single-warhead medium-range ballistic missile (MRBM) in the Dong Feng series developed by China Changfeng Mechanics and Electronics Technology Academy. Development started in the late 1960s and was completed around 1985–86, but it was not deployed until 1991. It was developed from the submarine-launched JL-1 missile, and is China's first solid-fuel land-based missile. The U.S. Department of Defense in 2008 estimated that China had 60-80 missiles and 60 launchers; approximately 10-11 missiles can be built annually. Originally developed as a strategic weapon, the DF-21's later variants were designed for both nuclear and conventional missions. It is thought able to carry a high explosive, submunition, or 300 kt nuclear warhead. The latest DF-21D was said to be the world's first anti-ship ballistic missile (ASBM). The DF-21 has also been developed into a space-capable anti-sate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People's Liberation Army Rocket Force
The People's Liberation Army Rocket Force (PLARF; ), formerly the Second Artillery Corps (), is the strategic and tactical missile force of the People's Republic of China. The PLARF is the 4th branch of the People's Liberation Army (PLA) and controls China's arsenal of land-based ballistic missiles—both nuclear and conventional. The armed service branch was established on 1 July 1966 and made its first public appearance on 1 October 1984. The headquarters for operations is located at Qinghe, Beijing. The PLARF is under the direct command of the Chinese Communist Party The Chinese Communist Party (CCP), officially the Communist Party of China (CPC), is the founding and One-party state, sole ruling party of the China, People's Republic of China (PRC). Under the leadership of Mao Zedong, the CCP emerged victoriou ...'s Central Military Commission (CMC). In total, China is estimated to be in possession of 320 nuclear warheads as of 2020, with an unknown number of them activ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dongfeng (missile)
The ''Dongfeng'' () series, typically abbreviated as "DF missiles", are a family of short-range ballistic missile, short, medium-range ballistic missile, medium, intermediate-range ballistic missile, intermediate-range and intercontinental ballistic missile, intercontinental ballistic missiles operated by the People's Republic of China, Chinese People's Liberation Army Rocket Force (formerly the Second Artillery Corps). History After the signing of the Sino-Soviet Treaty of Friendship, Alliance and Mutual Assistance in 1950, the Soviet Union assisted China's military R&D with training, technical documentation, manufacturing equipment and licensed production of Soviet weapons. In the area of ballistic missiles, the Soviets transferred R-1 (missile), R-1 (SS-1), SS-2 Sibling, R-2 (SS-2) and R-11 Zemlya, R-11F technology to China.13,000 km). Currently, an estimated 24-36 DF-5A's are in service as China's primary ICBM force. If the DF-5A is launched from the eastern part of the Q ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Saudi Strategic Missile Force
The Royal Saudi Strategic Missile Force ( ar, قوة الصواريخ الإستراتيجية الملكية السعودية) or RSSMF is the fifth branch of the Saudi Arabian Armed Forces, responsible for commissioning long-range strategic missiles. The RSSMF formerly had its headquarters in an underground command facility in Riyadh– the capital of Saudi Arabia. The facility coordinated Saudi Arabia's advanced "Peace Shield" radar and air defense systems. In July 2013, the new RSSMF headquarters and academy buildings were officially opened by Prince Khalid bin Sultan bin Abdulaziz and current RSSMF commander Lieutenant general Jarallah Alaluwayt. History The RSSMF's role has grown rapidly since Saudi Arabia and other Arab States of the Persian Gulf announced in 2009 an initiative to obtain nuclear weapons as a countermeasure to the Iranian nuclear program. King Abdullah of Saudi Arabia and Prince Turki bin Faisal Al Saud, a former Saudi intelligence chief and ambassad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ASBM
An anti-ship ballistic missile (ASBM) is a military ballistic missile system designed to hit a warship at sea. Due to the often hypersonic flight speed of ballistic missiles an ASBM's kinetic energy alone may be sufficient to cripple or outright destroy a supercarrier with a single conventional warhead impact. Unlike a nuclear warhead, however, this would require a direct hit to be effective; therefore unlike a typical ballistic missile, which follows a ballistic flight path after the relatively brief initial phase of powered flight, an ASBM would require a precise and high-performance terminal guidance system with advanced sensors and in-flight calibrations in order successfully to hit a moving target. Soviet Union The 4K18 was a Soviet Union intermediate-range ballistic anti-ship missile (also known as R-27K, where "K" stands for Korabelnaya which means "ship-related") NATO SS-NX-13. Initial submarine testing began on 9 December 1972 on board the K-102, a Golf-class subm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-ship Ballistic Missile
An anti-ship ballistic missile (ASBM) is a military ballistic missile system Anti-ship missile, designed to hit a warship at sea. Due to the often hypersonic flight speed of ballistic missiles an ASBM's kinetic energy alone may be sufficient to cripple or outright destroy a supercarrier with a single conventional weapon, conventional warhead impact. Unlike a nuclear warhead, however, this would require a direct hit to be effective; therefore unlike a typical ballistic missile, which follows a ballistic trajectory, ballistic flight path after the relatively brief initial phase of powered flight, an ASBM would require a precise and high-performance terminal guidance system with advanced sensors and in-flight calibrations in order successfully to hit a moving target. Soviet Union The 4K18 was a Soviet, Soviet Union intermediate-range ballistic anti-ship missile (also known as R-27K, where "K" stands for Korabelnaya which means "ship-related") NATO SS-NX-13. Initial submarine tes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Missile
In military terminology, a missile is a guided airborne ranged weapon capable of self-propelled flight usually by a jet engine or rocket motor. Missiles are thus also called guided missiles or guided rockets (when a previously unguided rocket is made guided). Missiles have five system components: targeting, guidance system, flight system, engine and warhead. Missiles come in types adapted for different purposes: surface-to-surface and air-to-surface missiles (ballistic, cruise, anti-ship, anti-submarine, anti-tank, etc.), surface-to-air missiles (and anti-ballistic), air-to-air missiles, and anti-satellite weapons. Airborne explosive devices without propulsion are referred to as shells if fired by an artillery piece and bombs if dropped by an aircraft. Unguided jet- or rocket-propelled weapons are usually described as rocket artillery. Historically, the word ''missile'' referred to any projectile that is thrown, shot or propelled towards a target; this usage is still ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Active Radar Homing
Active radar homing (ARH) is a missile guidance method in which a missile contains a radar transceiver (in contrast to semi-active radar homing, which uses only a receiver) and the electronics necessary for it to find and track its target autonomously. The NATO brevity code for an air-to-air active radar homing missile launch is fox three. Advantages There are two major advantages to active radar homing: * As the missile is tracking the target it is going to be much closer to the target than the launching platform during the terminal phase, thus the missile's tracking can be much more accurate and better resistant to electronic countermeasures. Active radar homing missiles have some of the best kill probabilities, along with missiles employing track-via-missile guidance. * Because the missile is totally autonomous during the terminal phase, the launch platform does not need to have its radar enabled at all during this phase, and in the case of a mobile launching platform ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MRBM
A medium-range ballistic missile (MRBM) is a type of ballistic missile with medium range, this last classification depending on the standards of certain organizations. Within the U.S. Department of Defense, a medium-range missile is defined by having a maximum range of between . In modern terminology, MRBMs are part of the wider grouping of theatre ballistic missiles, which includes any ballistic missile with a range of less than . Specific MRBMs * DF-2 * DF-16 * DF-17 * DF-21 (China) , (Saudi Arabia) * SSBS S1 * Agni II * Agni-P * Ashoura * Emad * Fajr-3 (estimation) * Ghadr-110 * Khorramshahr (missile) * Sejjil * Shahab-3 * Badr-2000 * Jericho II * Hwasong-9 * Hwasong-10/RD-B Musudan * Pukkuksong-1 * Pukkuksong-2 * Pukkuksong-2 * Rodong-1 * Ababeel * Ghauri-I * Ghauri-II * Ghauri-III (Cancelled) * Shaheen-II * Shaheen-III [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medium-range Ballistic Missile
A medium-range ballistic missile (MRBM) is a type of ballistic missile with medium range, this last classification depending on the standards of certain organizations. Within the U.S. Department of Defense, a medium-range missile is defined by having a maximum range of between . In modern terminology, MRBMs are part of the wider grouping of theatre ballistic missiles, which includes any ballistic missile with a range of less than . Specific MRBMs * DF-2 * DF-16 * DF-17 * DF-21 (China) , (Saudi Arabia) * SSBS S1 * Agni II * Agni-P * Ashoura * Emad * Fajr-3 (estimation) * Ghadr-110 * Khorramshahr (missile) * Sejjil * Shahab-3 * Badr-2000 * Jericho II * Hwasong-9 * Hwasong-10/RD-B Musudan * Pukkuksong-1 * Pukkuksong-2 * Pukkuksong-2 * Rodong-1 * Ababeel * Ghauri-I * Ghauri-II * Ghauri-III (Cancelled) * Shaheen-II * Shaheen-III [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
JL-1
The Julang-1 (, also known as the JL-1; NATO reporting name CSS-N-3) was China's first generation nuclear submarine-launched ballistic missile (SLBM). According to a US Department of Defense report in 2011, the operational status of the JL-1 was "questionable". History Research and development began in 1967 and detailed design in the early 1970s, with a first land launch 30 April 1982 and a sea launch from a Project 629A (Golf) class submarine on 12 October 1982. The general designer of the missile was Huang Weilu, and Chen Deren (, 1922 – 21 December 2007) served as his deputy. The missile was assembled at Factory 307 (now Nanjing Dawn Group ��京晨光集团. The JL-1 was deployed on Xia class submarine in 1986. The Type 092 Xia class nuclear submarine has 12 launch tubes. The JL-1 was initially tested and deployed on the PLAN's modified Golf class SSB. The Golf has since been modified again for further testing of other missiles, such as the JL-2, which has test-launched ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
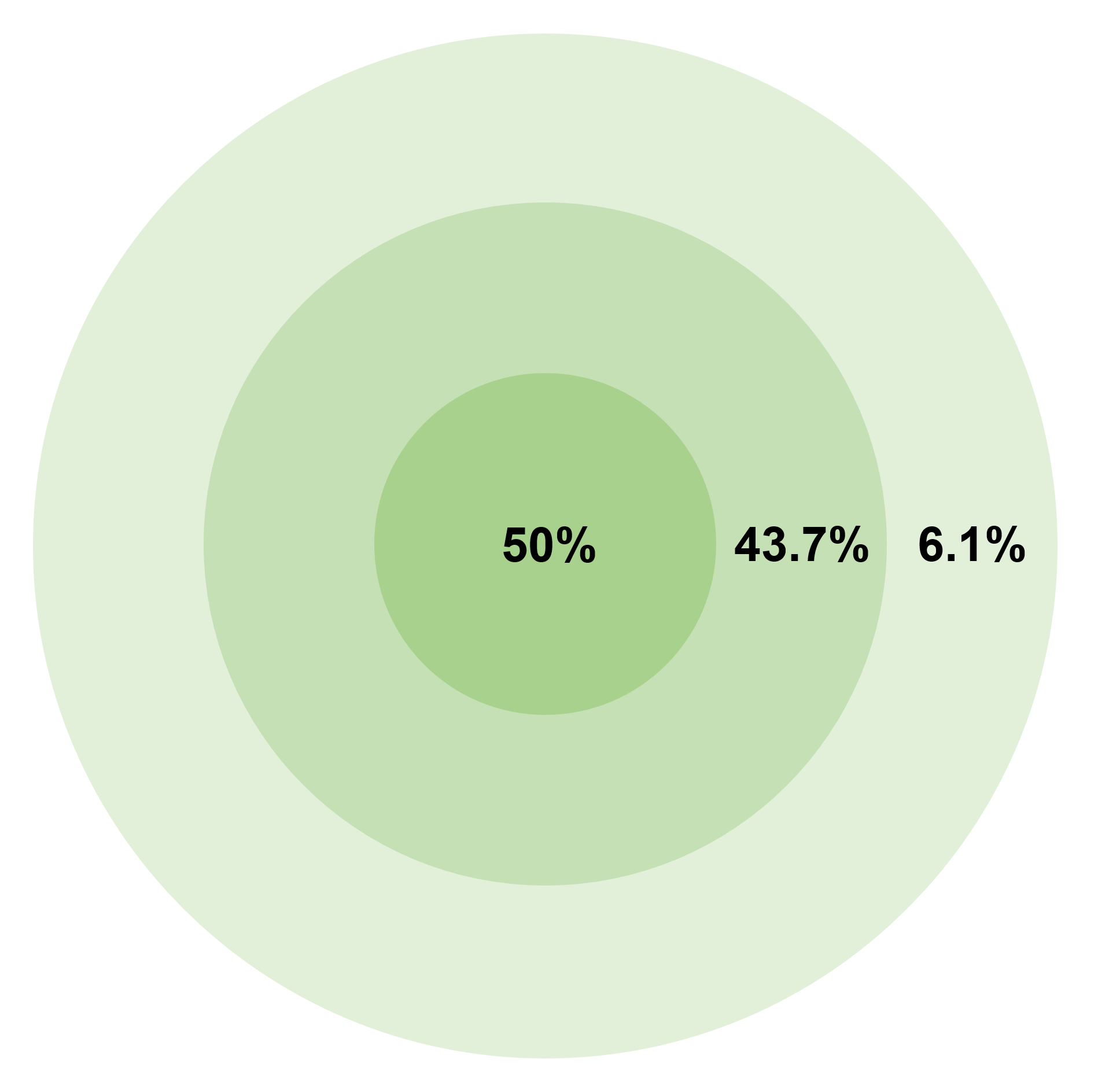
Circular Error Probable
In the military science of ballistics, circular error probable (CEP) (also circular error probability or circle of equal probability) is a measure of a weapon system's precision. It is defined as the radius of a circle, centered on the mean, whose perimeter is expected to include the landing points of 50% of the rounds; said otherwise, it is the median error radius. That is, if a given munitions design has a CEP of 100 m, when 100 munitions are targeted at the same point, 50 will fall within a circle with a radius of 100 m around their average impact point. (The distance between the target point and the average impact point is referred to as bias.) There are associated concepts, such as the DRMS (distance root mean square), which is the square root of the average squared distance error, and R95, which is the radius of the circle where 95% of the values would fall in. The concept of CEP also plays a role when measuring the accuracy of a position obtained by a navigati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |