|
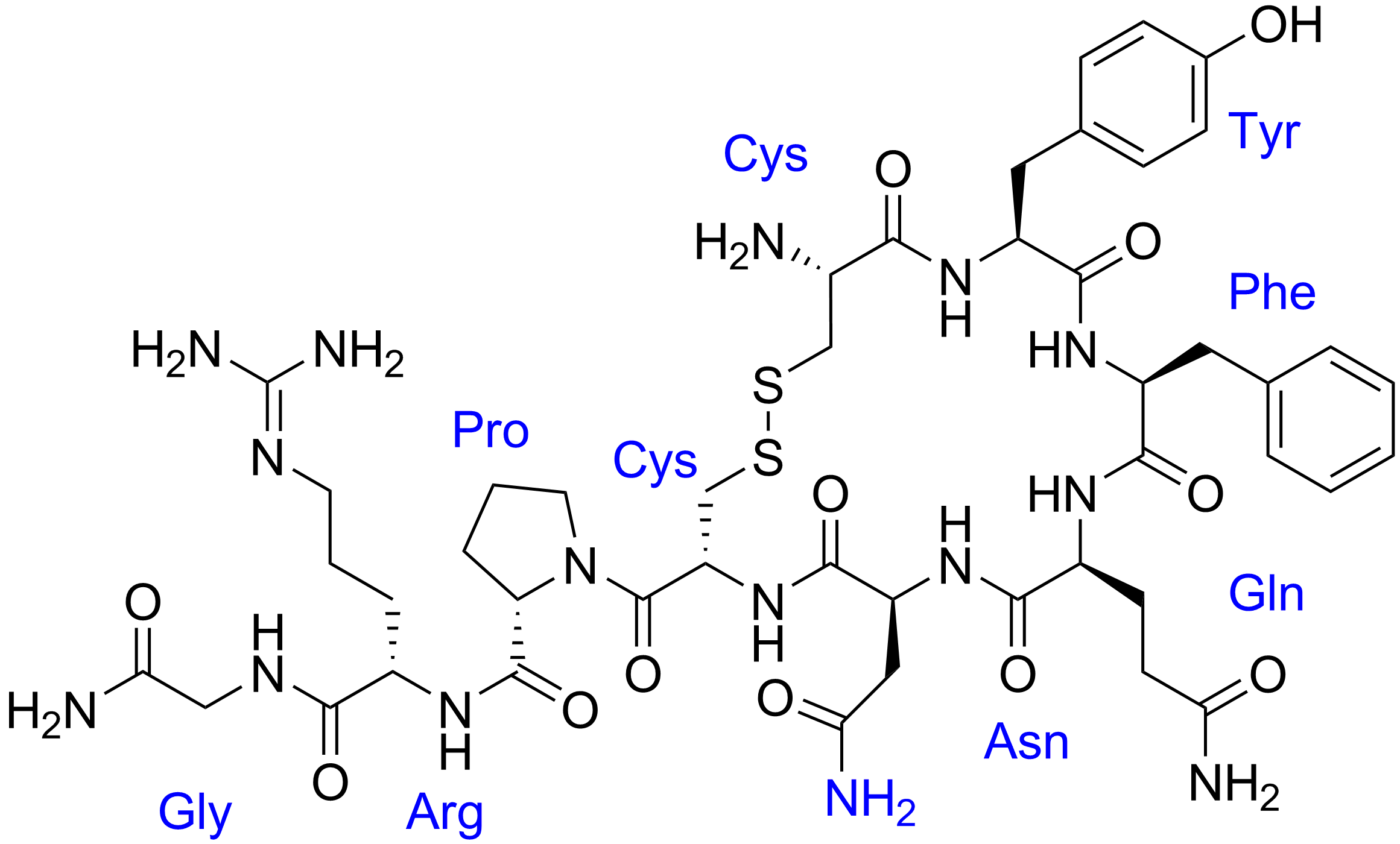
DDAVP
Desmopressin, sold under the trade name DDAVP among others, is a medication used to treat diabetes insipidus, nocturnal enuresis, bedwetting, hemophilia A, von Willebrand disease, and uremia, high blood urea levels. In hemophilia A and von Willebrand disease, it should only be used for mild to moderate cases. It may be given nasal administration, in the nose, intravenous therapy, by injection into a vein, oral administration, by mouth, or sublingual administration, under the tongue. Common side effects include headaches, diarrhea, and hyponatremia, low blood sodium. The low blood sodium that results may cause seizures. It should not be used in people with significant kidney problems or low blood sodium. It appears to be safe to use during pregnancy. It is a chemical synthesis, synthetic analogue of vasopressin, the hormone that plays roles in the control of the body’s osmotic balance, blood pressure regulation, kidney function, and reduction of urine production. Desmopressin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nocturnal Enuresis
Nocturnal enuresis, also informally called bedwetting, is urinary incontinence, involuntary urination while sleep, asleep after the age at which bladder control usually begins. Bedwetting in children and adults can result in emotional stress. Complications can include urinary tract infections. Most bedwetting is a Specific developmental disorder, developmental delay—not an emotional problem or physical illness. Only a small percentage (5 to 10%) of bedwetting cases have a specific medical cause. Bedwetting is commonly associated with a Family history (medicine), family history of the condition. Nocturnal enuresis is considered ''primary'' when a child has not yet had a prolonged period of being dry. ''Secondary'' nocturnal enuresis is when a child or adult begins wetting again after having stayed dry. Treatments range from Behaviour therapy, behavioral therapy, such as bedwetting alarms, to medication, such as Hormone replacement therapy, hormone replacement, and even surgery ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diabetes Insipidus
Diabetes insipidus (DI), recently renamed to Arginine Vasopressin Deficiency (AVP-D) and Arginine Vasopressin Resistance (AVP-R), is a condition characterized by large amounts of dilute urine and increased thirst. The amount of urine produced can be nearly 20 liters per day. Reduction of fluid has little effect on the concentration of the urine. Complications may include dehydration or seizures. There are four types of DI, each with a different set of causes. Central DI (CDI) is due to a lack of the hormone vasopressin (antidiuretic hormone). This can be due to injury to the hypothalamus or pituitary gland or genetics. Nephrogenic DI (NDI) occurs when the kidneys do not respond properly to vasopressin. Dipsogenic DI is a result of excessive fluid intake due to damage to the hypothalamic thirst mechanism. It occurs more often in those with certain psychiatric disorders or on certain medications. Gestational DI occurs only during pregnancy. Diagnosis is often based on urine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intravenous Therapy
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutrients for those who cannot, or will not—due to reduced mental states or otherwise—consume food or water by mouth. It may also be used to administer medications or other medical therapy such as blood products or electrolytes to correct electrolyte imbalances. Attempts at providing intravenous therapy have been recorded as early as the 1400s, but the practice did not become widespread until the 1900s after the development of techniques for safe, effective use. The intravenous route is the fastest way to deliver medications and fluid replacement throughout the body as they are introduced directly into the circulatory system and thus quickly distributed. For this reason, the intravenous route of administration is also used for the consump ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring develops ( gestates) inside a woman's uterus (womb). A multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins. Pregnancy usually occurs by sexual intercourse, but can also occur through assisted reproductive technology procedures. A pregnancy may end in a live birth, a miscarriage, an induced abortion, or a stillbirth. Childbirth typically occurs around 40 weeks from the start of the last menstrual period (LMP), a span known as the gestational age. This is just over nine months. Counting by fertilization age, the length is about 38 weeks. Pregnancy is "the presence of an implanted human embryo or fetus in the uterus"; implantation occurs on average 8–9 days after fertilization. An '' embryo'' is the term for the developing offspring during the first seven weeks following implantation (i.e. ten weeks' gestational age), after which the term ''fetus'' is used until birth. Signs an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nausea
Nausea is a diffuse sensation of unease and discomfort, sometimes perceived as an urge to vomit. While not painful, it can be a debilitating symptom if prolonged and has been described as placing discomfort on the chest, abdomen, or back of the throat. Over 30 definitions of nausea were proposed in a 2011 book on the topic. Nausea is a non-specific symptom, which means that it has many possible causes. Some common causes of nausea are gastroenteritis and other gastrointestinal disorders, food poisoning, motion sickness, dizziness, migraine, fainting, low blood sugar, anxiety, and lack of sleep. Nausea is a side effect of many medications including chemotherapy, or morning sickness in early pregnancy. Nausea may also be caused by disgust and depression. Medications taken to prevent and treat nausea and vomiting are called antiemetics. The most commonly prescribed antiemetics in the US are promethazine, metoclopramide, and the newer ondansetron. The word nausea is from Lat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flushing (physiology)
Flushing is to become markedly red in the face and often other areas of the skin, from various physiological conditions. Flushing is generally distinguished, despite a close physiological relation between them, from blushing, which is milder, generally restricted to the face, cheeks or ears, and generally assumed to reflect emotional stress, such as embarrassment, anger, or romantic stimulation. Flushing is also a cardinal symptom of carcinoid syndrome—the syndrome that results from hormones (often serotonin or histamine) being secreted into systemic circulation. Causes * abrupt cessation of physical exertion (resulting in heart output in excess of current muscular need for blood flow) * abdominal cutaneous nerve entrapment syndrome (ACNES), usually in patients who have had abdominal surgery * alcohol flush reaction * antiestrogens such as tamoxifen * atropine poisoning * body contact with warm or hot water (hot tub, bath, shower) * butorphanol reaction with some narcotic an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus
Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus, also known as renal diabetes insipidus, is a form of diabetes insipidus primarily due to pathology of the kidney. This is in contrast to central or neurogenic diabetes insipidus, which is caused by insufficient levels of antidiuretic hormone (also called vasopressin). Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus is caused by an improper response of the kidney to antidiuretic hormone, leading to a decrease in the ability of the kidney to concentrate the urine by removing free water. Signs and symptoms The clinical manifestation is similar to neurogenic diabetes insipidus, presenting with polydipsia (excessive thirst) and polyuria (excretion of a large amount of dilute urine). Dehydration is common, and incontinence can occur secondary to chronic bladder distension. On investigation, there will be an increased plasma osmolarity and decreased urine osmolarity. As pituitary function is normal, antidiuretic hormone levels are likely to be abnormal or raised. Polyur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antidiuretic Hormone
Human vasopressin, also called antidiuretic hormone (ADH), arginine vasopressin (AVP) or argipressin, is a hormone synthesized from the AVP gene as a peptide prohormone in neurons in the hypothalamus, and is converted to AVP. It then travels down the axon terminating in the posterior pituitary, and is released from vesicles into the circulation in response to extracellular fluid hypertonicity (hyperosmolality). AVP has two primary functions. First, it increases the amount of solute-free water reabsorbed back into the circulation from the filtrate in the kidney tubules of the nephrons. Second, AVP constricts arterioles, which increases peripheral vascular resistance and raises arterial blood pressure. A third function is possible. Some AVP may be released directly into the brain from the hypothalamus, and may play an important role in social behavior, sexual motivation and pair bonding, and maternal responses to stress. Vasopressin induces differentiation of stem cells in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurogenic Diabetes Insipidus
Central diabetes insipidus, also called neurogenic diabetes insipidus, is a type of diabetes insipidus due to a lack of vasopressin (ADH) production in the brain. Vasopressin acts to increase the volume of blood (intravascularly), and decrease the volume of urine produced. Therefore, a lack of it causes increased urine production and volume depletion. It is also known as neurohypophyseal diabetes insipidus, referring to the posterior pituitary (neurohypophysis), which is supplied by the hypothalamus in the brain. This condition has only polyuria in common with diabetes. Although not mutually exclusive, with most typical cases, the name diabetes insipidus is a misleading misnomer. A better name might be "hypothalamic-neurohypophyseal ADH deficiency". Signs and symptoms Increased thirst, polyuria and dehydration with metabolic encephalopathy. Causes Unknown In at least 25% of cases (the most commonly occurring classification), neurogenic diabetes insipidus is of unknown cause, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Factor VIII
Factor VIII (FVIII) is an essential blood-clotting protein, also known as anti-hemophilic factor (AHF). In humans, factor VIII is encoded by the ''F8'' gene. Defects in this gene result in hemophilia A, a recessive X-linked coagulation disorder. Factor VIII is produced in liver sinusoidal cells and endothelial cells outside the liver throughout the body. This protein circulates in the bloodstream in an inactive form, bound to another molecule called von Willebrand factor, until an injury that damages blood vessels occurs. In response to injury, coagulation factor VIII is activated and separates from von Willebrand factor. The active protein (sometimes written as coagulation factor VIIIa) interacts with another coagulation factor called factor IX. This interaction sets off a chain of additional chemical reactions that form a blood clot. Factor VIII participates in blood coagulation; it is a cofactor for factor IXa, which, in the presence of Ca2+ and phospholipids, forms a complex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Generic Medication
A generic drug is a pharmaceutical drug that contains the same chemical substance as a drug that was originally protected by chemical patents. Generic drugs are allowed for sale after the patents on the original drugs expire. Because the active chemical substance is the same, the medical profile of generics is equivalent in performance. A generic drug has the same active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) as the original, but it may differ in some characteristics such as the manufacturing process, formulation, excipients, color, taste, and packaging. Although they may not be associated with a particular company, generic drugs are usually subject to government regulations in the countries in which they are dispensed. They are labeled with the name of the manufacturer and a generic non-proprietary name such as the United States Adopted Name (USAN) or International Nonproprietary Name (INN) of the drug. A generic drug must contain the same active ingredients as the original brand-name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WHO Model List Of Essential Medicines
The WHO Model List of Essential Medicines (aka Essential Medicines List or EML), published by the World Health Organization (WHO), contains the medications considered to be most effective and safe to meet the most important needs in a health system. The list is frequently used by countries to help develop their own local lists of essential medicines. , more than 155 countries have created national lists of essential medicines based on the World Health Organization's model list. This includes both developed and developing countries. The list is divided into core items and complementary items. The core items are deemed to be the most cost-effective options for key health problems and are usable with little additional health care resources. The complementary items either require additional infrastructure such as specially trained health care providers or diagnostic equipment or have a lower cost–benefit ratio. About 25% of items are in the complementary list. Some medicatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |