|
DBM (computing)
In computing, a DBM is a library and file format providing fast, single-keyed access to data. A key-value database from the original Unix, ''dbm'' is an early example of a NoSQL system. History The original ''dbm'' library and file format was a simple database engine, originally written by Ken Thompson and released by AT&T in 1979. The name is a three-letter acronym for ''DataBase Manager'', and can also refer to the family of database engines with APIs and features derived from the original ''dbm''. The ''dbm'' library stores arbitrary data by use of a single key (a primary key) in fixed-size buckets and uses hashing techniques to enable fast retrieval of the data by key. The hashing scheme used is a form of extendible hashing, so that the hashing scheme expands as new buckets are added to the database, meaning that, when nearly empty, the database starts with one bucket, which is then split when it becomes full. The two resulting child buckets will themselves split when they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Library (computing)
In computing, a library is a collection of System resource, resources that can be leveraged during software development to implement a computer program. Commonly, a library consists of executable code such as compiled function (computer science), functions and Class (computer programming), classes, or a library can be a collection of source code. A resource library may contain data such as images and Text string, text. A library can be used by multiple, independent consumers (programs and other libraries). This differs from resources defined in a program which can usually only be used by that program. When a consumer uses a library resource, it gains the value of the library without having to implement it itself. Libraries encourage software reuse in a Modular programming, modular fashion. Libraries can use other libraries resulting in a hierarchy of libraries in a program. When writing code that uses a library, a programmer only needs to know how to use it not its internal d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Public Domain
The public domain (PD) consists of all the creative work to which no Exclusive exclusive intellectual property rights apply. Those rights may have expired, been forfeited, expressly Waiver, waived, or may be inapplicable. Because no one holds the exclusive rights, anyone can legally use or reference those works without permission. As examples, the works of William Shakespeare, Ludwig van Beethoven, Miguel de Cervantes, Zoroaster, Lao Zi, Confucius, Aristotle, L. Frank Baum, Leonardo da Vinci and Georges Méliès are in the public domain either by virtue of their having been created before copyright existed, or by their copyright term having expired. Some works are not covered by a country's copyright laws, and are therefore in the public domain; for example, in the United States, items excluded from copyright include the formulae of Classical mechanics, Newtonian physics and cooking recipes. Other works are actively dedicated by their authors to the public domain (see waiver) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cdb (software)
cdb, short for "constant database", refers to both a library and data format created by Daniel J. Bernstein. cdb acts as an on-disk associative array, mapping keys to values, and allows multiple values to be stored for a single key. A constant database allows only two operations: creation and reading. Both operations are designed to be very fast and highly reliable. Since the database does not change while it is in use, multiple processes can access a single database without locking. Additionally, since all modifications create a replacement database, it can take advantage of UNIX filesystem semantics to provide a guarantee of reliability. Record positions, key and value lengths, and hash values are 32-bit quantities and therefore must fit into 4 gigabytes. cdb is used by djbdns, fastforward, mess822, qmail and ucspi-tcp to provide highly efficient, reliable, and simple data access. Structure A database contains an entire data set (e.g. a single associative array) in a single ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
C (programming Language)
C (''pronounced'' '' – like the letter c'') is a general-purpose programming language. It was created in the 1970s by Dennis Ritchie and remains very widely used and influential. By design, C's features cleanly reflect the capabilities of the targeted Central processing unit, CPUs. It has found lasting use in operating systems code (especially in Kernel (operating system), kernels), device drivers, and protocol stacks, but its use in application software has been decreasing. C is commonly used on computer architectures that range from the largest supercomputers to the smallest microcontrollers and embedded systems. A successor to the programming language B (programming language), B, C was originally developed at Bell Labs by Ritchie between 1972 and 1973 to construct utilities running on Unix. It was applied to re-implementing the kernel of the Unix operating system. During the 1980s, C gradually gained popularity. It has become one of the most widely used programming langu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
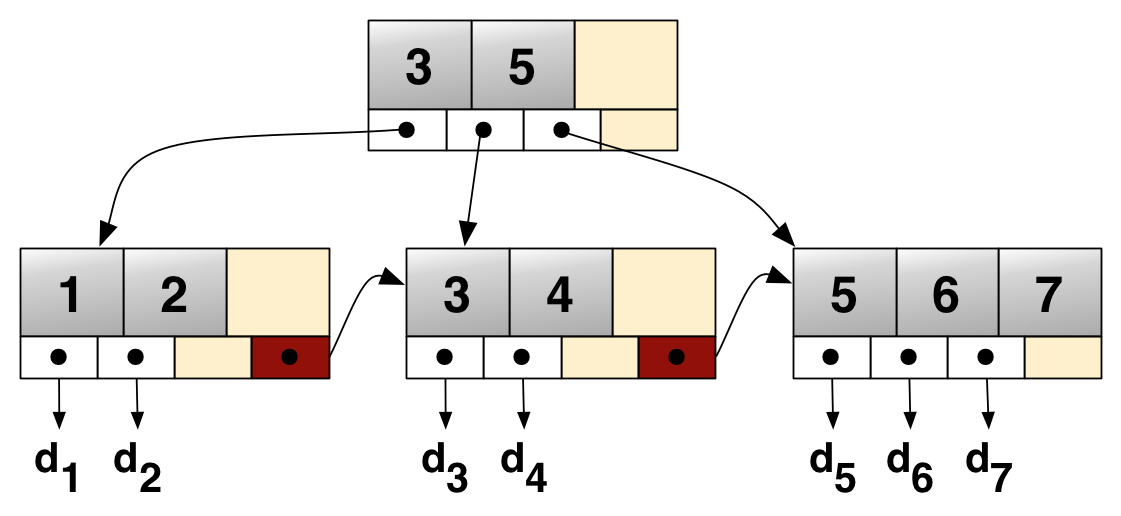
B+ Tree
A B+ tree is an m-ary tree with a variable but often large number of children per node. A B+ tree consists of a root, internal nodes and leaves. The root may be either a leaf or a node with two or more children. A B+ tree can be viewed as a B-tree in which each node contains only keys (not key–value pairs), and to which an additional level is added at the bottom with linked leaves. The primary value of a B+ tree is in storing data for efficient retrieval in a Block (data storage), block-oriented storage context—in particular, filesystems. This is primarily because unlike binary search trees, B+ trees have very high fanout (number of pointers to child nodes in a node, typically on the order of 100 or more), which reduces the number of I/O operations required to find an element in the tree. History There is no single paper introducing the B+ tree concept. Instead, the notion of maintaining all data in leaf nodes is repeatedly brought up as an interesting variant of the B- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Memory-mapped File
A memory-mapped file is a segment of virtual memory that has been assigned a direct byte-for-byte correlation with some portion of a file or file-like resource. This resource is typically a file that is physically present on disk, but can also be a device, shared memory object, or other resource that an operating system can reference through a file descriptor. Once present, this correlation between the file and the memory space permits applications to treat the mapped portion as if it were primary memory. History TOPS-20 PMAP An early () implementation of this was the PMAP system call on the DEC-20's TOPS-20 operating system, a feature used by Software House's System-1022 database system. SunOS 4 mmap SunOS 4 introduced Unix's mmap, which permitted programs "to map files into memory." Windows Growable Memory-Mapped Files (GMMF) Two decades after the release of TOPS-20's PMAP, Windows NT was given Growable Memory-Mapped Files (GMMF). Since " function requires a size to be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Copy-on-write
Copy-on-write (COW), also called implicit sharing or shadowing, is a resource-management technique used in programming to manage shared data efficiently. Instead of copying data right away when multiple programs use it, the same data is shared between programs until one tries to modify it. If no changes are made, no private copy is created, saving resources. A copy is only made when needed, ensuring each program has its own version when modifications occur. This technique is commonly applied to memory, files, and data structures. In virtual memory management Copy-on-write finds its main use in operating systems, sharing the physical memory of computers running multiple processes, in the implementation of the fork() system call. Typically, the new process does not modify any memory and immediately executes a new process, replacing the address space entirely. It would waste processor time and memory to copy all of the old process's memory during the fork only to immediately dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Lightning Memory-Mapped Database
Lightning Memory-Mapped Database (LMDB) is an embedded transactional database in the form of a key-value store. LMDB is written in C (programming language), C with #API and uses, API bindings for several programming languages. LMDB stores arbitrary key/data pairs as byte arrays, has a range-based search capability, supports multiple data items for a single key and has a special mode for appending records (MDB_APPEND) without checking for consistency.LMDB Reference Guide Retrieved on 2023-03-21 LMDB is not a relational database, it is strictly a key-value store like Berkeley DB and DBM (computing), DBM. LMDB may also be used #Concurrency, concurrently in a multi-threaded or multi-processing environment, with read performance scaling linearly by design. LMDB databases may have only one writer at a time, however unlike many similar key-value databases, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Berkeley Software Distribution
The Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD), also known as Berkeley Unix or BSD Unix, is a discontinued Unix operating system developed and distributed by the Computer Systems Research Group (CSRG) at the University of California, Berkeley, beginning in 1978. It began as an improved derivative of AT&T's original Unix that was developed at Bell Labs, based on the source code but over time diverging into its own code. BSD would become a pioneer in the advancement of Unix and computing. BSD's development was begun initially by Bill Joy, who added virtual memory capability to Unix running on a VAX-11 computer. In the 1980s, BSD was widely adopted by workstation vendors in the form of proprietary Unix distributions such as DEC Ultrix and Sun Microsystems SunOS due to its permissive licensing and familiarity to many technology company founders and engineers. It also became the most popular Unix at universities, where it was used for the study of operating systems. BSD was sponsored ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Oracle Corporation
Oracle Corporation is an American Multinational corporation, multinational computer technology company headquartered in Austin, Texas. Co-founded in 1977 in Santa Clara, California, by Larry Ellison, who remains executive chairman, Oracle was the List of the largest software companies, third-largest software company in the world in 2020 by revenue and market capitalization. The company's 2023 ranking in the Forbes Global 2000, ''Forbes'' Global 2000 was 80. The company sells Database, database software, particularly Oracle Database, and cloud computing. Oracle's core application software is a suite of enterprise software products, such as enterprise resource planning (ERP) software, human capital management (HCM) software, customer relationship management (CRM) software, enterprise performance management (EPM) software, Customer Experience Commerce (CX Commerce) and supply chain management (SCM) software. History Larry Ellison, Bob Miner, and Ed Oates co-founded Oracle in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Sleepycat Software
Sleepycat Software, Inc. was the software company primarily responsible for maintaining the Berkeley DB packages from 1996 to 2006. Company Berkeley DB is freely-licensed database software originally developed at the University of California, Berkeley for 4.4BSD Unix. Developers from that project founded Sleepycat in 1996 to provide commercial support after a request by Netscape to provide new features in the software. In February 2006, Sleepycat was acquired by Oracle Corporation, which continued developing Berkeley DB. The founders of the company were spouses Margo Seltzer and Keith Bostic, who are also original authors of Berkeley DB. Another original author, Michael Olson, was the President and CEO of Sleepycat. They attended University of California, Berkeley, where they developed the software that grew to become Berkeley DB. Sleepycat was originally based in Carlisle, Massachusetts and in 2000 moved to Lincoln, Massachusetts. Sleepycat distributed Berkeley DB under a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Berkeley DB
Berkeley DB (BDB) is an embedded database software library for key/value data, historically significant in open-source software. Berkeley DB is written in C with API bindings for many other programming languages. BDB stores arbitrary key/data pairs as byte arrays and supports multiple data items for a single key. Berkeley DB is not a relational database, although it has database features including database transactions, multiversion concurrency control and write-ahead logging. BDB runs on a wide variety of operating systems, including most Unix-like and Windows systems, and real-time operating systems. BDB was commercially supported and developed by Sleepycat Software from 1996 to 2006. Sleepycat Software was acquired by Oracle Corporation in February 2006, who continued to develop and sell the C Berkeley DB library. In 2013 Oracle re-licensed BDB under the AGPL license and released new versions until May 2020. Bloomberg L.P. continues to develop a fork of the 2013 versi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |