|
D2700
D2700, also known as Dmanisi skull 3, is one of five skulls discovered in Dmanisi, Georgia in 2001 and classified as early ''Homo erectus''. It is an almost complete skull and is in an exceptionally good condition. It was dated stratigraphically as about 1.8 million years old. Since the publication of the Dmanisi skull 5 in 2013, all of the five Dmanisi skulls (Skull 3 included) have contributed to the ongoing debate on human taxonomy, with some experts proposing the re-categorization of ''Homo ergaster'', and possibly even ''Homo habilis'', as morphologically diverse subspecies of ''H. erectus''. Discovery D2700 and D2735 were found in 2001, just a decade after the first discovery of an early hominin mandible D211 at Dmanisi on September 24, 1991. In 1999, partial crania D2280 and D2282 were discovered. Cranium D2282 is likely the accompanying skull to mandible D211 and to be the remains of a young adult around 18–20 years old. Skull D2280 is inferred to have been an ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homo Erectus Georgicus
The Dmanisi hominins, Dmanisi people, or Dmanisi man were a population of Early Pleistocene hominins whose fossils have been recovered at Dmanisi, Georgia. The fossils and stone tools recovered at Dmanisi range in age from 1.85–1.77 million years old, making the Dmanisi hominins the earliest well-dated hominin fossils in Eurasia and the best preserved fossils of early ''Homo'' from a single site so early in time, though earlier fossils and artifacts have been found in Asia. Though their precise classification is controversial and disputed, the Dmanisi fossils are highly significant within research on early hominin migrations out of Africa. The Dmanisi hominins are known from over a hundred postcranial fossils and five famous well-preserved skulls, referred to as Dmanisi Skulls 1–5. The taxonomic status of the Dmanisi hominins is somewhat unclear due to their small brain size, primitive skeletal architecture, and the range of variation exhibited between the skulls. Their ini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dmanisi Hominid Skulls
The Dmanisi hominins, Dmanisi people, or Dmanisi man were a population of Early Pleistocene hominins whose fossils have been recovered at Dmanisi, Georgia. The fossils and stone tools recovered at Dmanisi range in age from 1.85–1.77 million years old, making the Dmanisi hominins the earliest well-dated hominin fossils in Eurasia and the best preserved fossils of early ''Homo'' from a single site so early in time, though earlier fossils and artifacts have been found in Asia. Though their precise classification is controversial and disputed, the Dmanisi fossils are highly significant within research on early hominin migrations out of Africa. The Dmanisi hominins are known from over a hundred postcranial fossils and five famous well-preserved skulls, referred to as Dmanisi Skulls 1–5. The taxonomic status of the Dmanisi hominins is somewhat unclear due to their small brain size, primitive skeletal architecture, and the range of variation exhibited between the skulls. Their init ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dmanisi Skulls
The Dmanisi hominins, Dmanisi people, or Dmanisi man were a population of Early Pleistocene Hominini, hominins whose fossils have been recovered at Dmanisi historic site, Dmanisi, Georgia. The fossils and stone tools recovered at Dmanisi range in age from 1.85–1.77 million years old, making the Dmanisi hominins the earliest well-dated hominin fossils in Eurasia and the best preserved fossils of early ''Homo'' from a single site so early in time, though earlier fossils and artifacts have been found in Asia. Though their precise classification is controversial and disputed, the Dmanisi fossils are highly significant within research on Early expansions of hominins out of Africa, early hominin migrations out of Africa. The Dmanisi hominins are known from over a hundred postcranial fossils and five famous well-preserved skulls, referred to as Dmanisi Skulls 1–5. The taxonomic status of the Dmanisi hominins is somewhat unclear due to their small brain size, primitive skeletal archi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homo Georgicus
The Dmanisi hominins, Dmanisi people, or Dmanisi man were a population of Early Pleistocene hominins whose fossils have been recovered at Dmanisi, Georgia. The fossils and stone tools recovered at Dmanisi range in age from 1.85–1.77 million years old, making the Dmanisi hominins the earliest well-dated hominin fossils in Eurasia and the best preserved fossils of early ''Homo'' from a single site so early in time, though earlier fossils and artifacts have been found in Asia. Though their precise classification is controversial and disputed, the Dmanisi fossils are highly significant within research on early hominin migrations out of Africa. The Dmanisi hominins are known from over a hundred postcranial fossils and five famous well-preserved skulls, referred to as Dmanisi Skulls 1–5. The taxonomic status of the Dmanisi hominins is somewhat unclear due to their small brain size, primitive skeletal architecture, and the range of variation exhibited between the skulls. Their init ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dmanisi Skull 4
The Dmanisi hominins, Dmanisi people, or Dmanisi man were a population of Early Pleistocene Hominini, hominins whose fossils have been recovered at Dmanisi historic site, Dmanisi, Georgia. The fossils and stone tools recovered at Dmanisi range in age from 1.85–1.77 million years old, making the Dmanisi hominins the earliest well-dated hominin fossils in Eurasia and the best preserved fossils of early ''Homo'' from a single site so early in time, though earlier fossils and artifacts have been found in Asia. Though their precise classification is controversial and disputed, the Dmanisi fossils are highly significant within research on Early expansions of hominins out of Africa, early hominin migrations out of Africa. The Dmanisi hominins are known from over a hundred postcranial fossils and five famous well-preserved skulls, referred to as Dmanisi Skulls 1–5. The taxonomic status of the Dmanisi hominins is somewhat unclear due to their small brain size, primitive skeletal archi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dmanisi Skull
The Dmanisi skull, also known as Skull 5 or D4500, is one of five skulls discovered in Dmanisi, Georgia and classified as early '' Homo erectus''. Described in a publication in October 2013, it is estimated to be about 1.8 million years old and is the most complete skull of a Pleistocene ''Homo'' species, and the first complete adult hominin skull of that degree of antiquity. According to researchers, the discovery "provides the first evidence that early ''Homo'' comprised adult individuals with small brains but body mass, stature and limb proportions reaching the lower range limit of modern variation." The skull has been the cause of a paleontological controversy that is still ongoing as of 2017: many hominin fossils thought to be from different species such as ''Homo rudolfensis'' or '' Homo habilis'' may not have been separate species at all. Rather, they may have been a single evolving lineage. Discovery of the skull In 1991, Georgian scientist David Lordkipanidze found ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Human Evolution Fossils
The following tables give an overview of notable finds of Hominini, hominin fossils and Skeleton, remains relating to human evolution, beginning with the formation of the tribe Hominini (the divergence of the Chimpanzee–human last common ancestor, human and chimpanzee lineages) in the late Miocene, roughly 7 to 8 million years ago. As there are thousands of fossils, mostly fragmentary, often consisting of single bones or isolated teeth with complete skulls and skeletons rare, this overview is not complete, but show some of the most important findings. The fossils are arranged by approximate age as determined by radiometric dating and/or incremental dating and the species name represents current consensus; if there is no clear scientific consensus the other possible classifications are indicated. The early fossils shown are not considered ancestors to ''Homo sapiens'' but are closely related to ancestors and are therefore important to the study of the lineage. After 1.5 million ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dmanisi Skull 5
The Dmanisi skull, also known as Skull 5 or D4500, is Dmanisi skulls, one of five skulls discovered in Dmanisi, Georgia (country), Georgia and classified as early ''Homo erectus''. Described in a publication in October 2013, it is estimated to be about 1.8 million years old and is the most complete skull of a Pleistocene ''Homo'' species, and the first complete adult hominin skull of that degree of antiquity. According to researchers, the discovery "provides the first evidence that early ''Homo'' comprised adult individuals with small brains but body mass, stature and limb proportions reaching the lower range limit of modern variation." The skull has been the cause of a paleontological controversy that is still ongoing as of 2017: many hominin fossils thought to be from different species such as ''Homo rudolfensis'' or ''Homo habilis'' may not have been separate species at all. Rather, they may have been a single evolving Lineage (evolution), lineage. Discovery of the skull I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homo Ergaster
''Homo ergaster'' is an extinct species or subspecies of archaic humans who lived in Africa in the Early Pleistocene. Whether ''H. ergaster'' constitutes a species of its own or should be subsumed into ''Homo erectus, H. erectus'' is an ongoing and unresolved dispute within paleoanthropology, palaeoanthropology. Proponents of synonymisation typically designate ''H. ergaster'' as "African ''Homo erectus''" or "''Homo erectus ergaster''". The name ''Homo ergaster'' roughly translates to ":wikt:ergaster, working man", a reference to the more advanced tools used by the species in comparison to those of their ancestors. The fossil range of ''H. ergaster'' mainly covers the period of 1.7 to 1.4 million years ago, though a broader time range is possible. Though fossils are known from across East and Southern Africa, most ''H. ergaster'' fossils have been found along the shores of Lake Turkana in Kenya. There are later African fossils, some younger than 1 million years ago, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homo Erectus
''Homo erectus'' (; meaning "upright man") is an extinct species of archaic human from the Pleistocene, with its earliest occurrence about 2 million years ago. Several human species, such as '' H. heidelbergensis'' and '' H. antecessor'' — with the former generally considered to have been the ancestor to Neanderthals, Denisovans, and modern humans — appear to have evolved from ''H. erectus''. Its specimens are among the first recognizable members of the genus ''Homo''. ''H. erectus'' was the first human ancestor to spread throughout Eurasia, with a continental range extending from the Iberian Peninsula to Java. Asian populations of ''H. erectus'' may be ancestral to '' H. floresiensis'' and possibly to '' H. luzonensis''. The last known population of ''H. erectus'' is '' H. e. soloensis'' from Java, around 117,000–108,000 years ago. ''H. erectus'' had a more modern gait and body proportions, and was the first human species to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
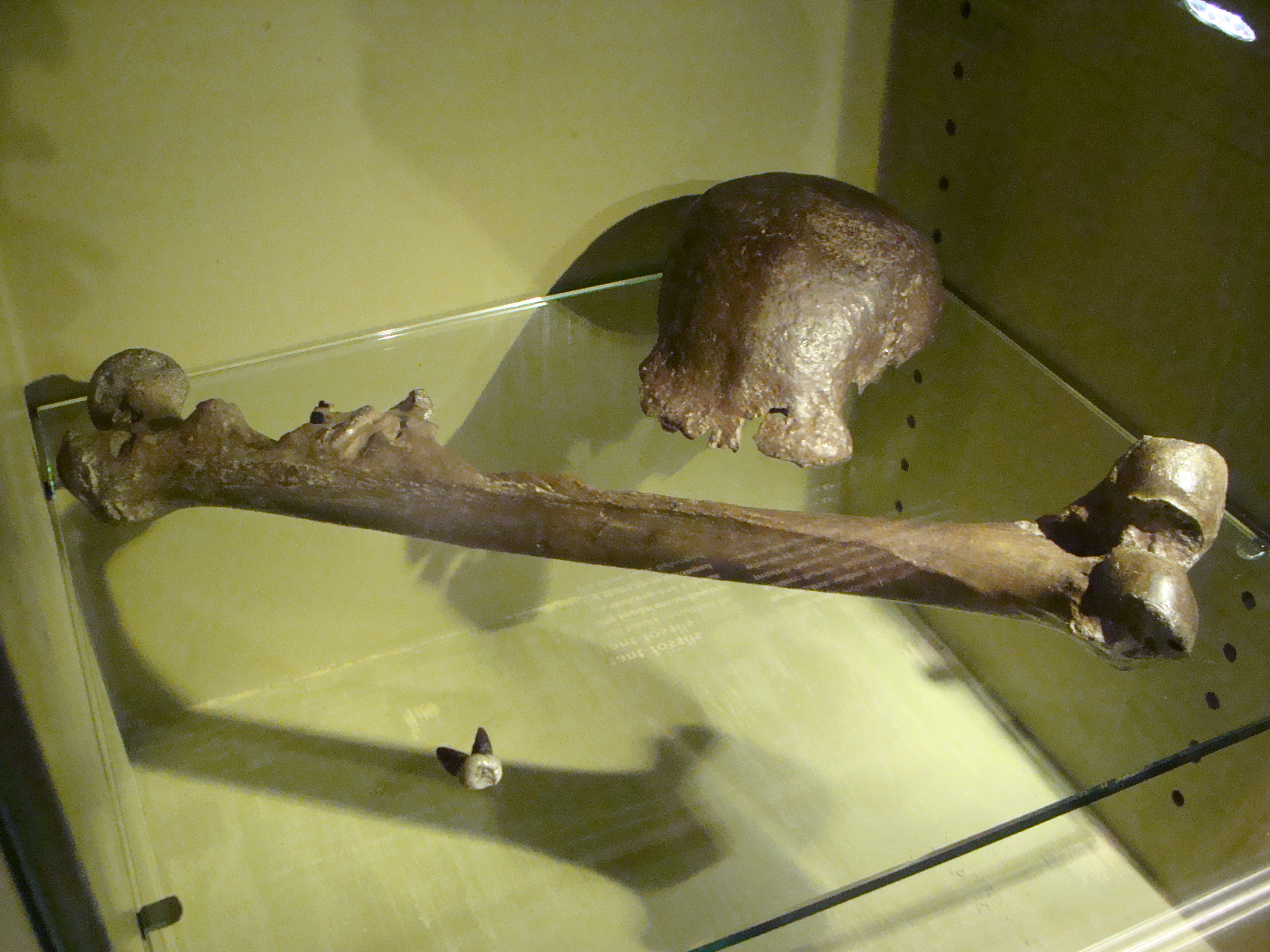
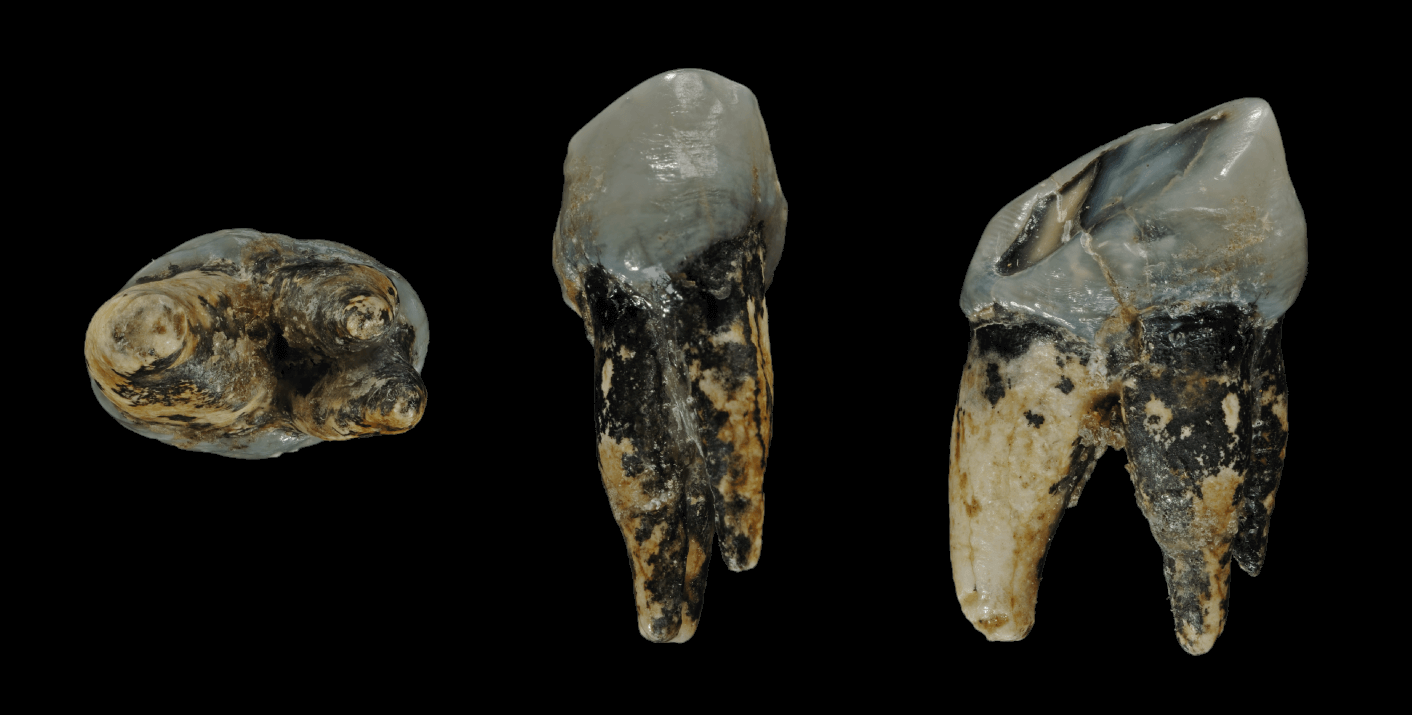
Dmanisi Fossils D2700 %2B D2735
Dmanisi ( ka, დმანისი, tr, , az, Başkeçid) is a town and archaeological site in the Kvemo Kartli region of Georgia approximately 93 km southwest of the nation’s capital Tbilisi in the river valley of Mashavera. The hominin site is dated to 1.8 million years ago.1.85-1.78 Ma 95% CI. Garcia, T., Féraud, G., Falguères, C., de Lumley, H., Perrenoud, C., & Lordkipanidze, D. (2010). "Earliest human remains in Eurasia: New 40Ar/39Ar dating of the Dmanisi hominid-bearing levels, Georgia". Quaternary Geochronology, 5(4), 443–451. doi:10.1016/j.quageo.2009.09.012 It was the earliest known evidence of hominins outside Africa before stone tools dated to 2.1 million years were discovered in 2018 in Shangchen, China. A series of skulls which had diverse physical traits, discovered at Dmanisi in the early 2010s, led to the hypothesis that many separate species in the genus ''Homo'' were in fact a single lineage. Also known as Skull 5, D4500 is the fifth skull to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dmanisi
Dmanisi ( ka, დმანისი, tr, , az, Başkeçid) is a town and archaeological site in the Kvemo Kartli region of Georgia approximately 93 km southwest of the nation’s capital Tbilisi in the river valley of Mashavera. The hominin site is dated to 1.8 million years ago.1.85-1.78 Ma 95% CI. Garcia, T., Féraud, G., Falguères, C., de Lumley, H., Perrenoud, C., & Lordkipanidze, D. (2010). "Earliest human remains in Eurasia: New 40Ar/39Ar dating of the Dmanisi hominid-bearing levels, Georgia". Quaternary Geochronology, 5(4), 443–451. doi:10.1016/j.quageo.2009.09.012 It was the earliest known evidence of hominins outside Africa before stone tools dated to 2.1 million years were discovered in 2018 in Shangchen, China. A series of skulls which had diverse physical traits, discovered at Dmanisi in the early 2010s, led to the hypothesis that many separate species in the genus ''Homo'' were in fact a single lineage. Also known as Skull 5, D4500 is the fifth skull to be d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |