|
Dyson's Eternal Intelligence
Dyson's eternal intelligence concept (the Dyson Scenario), proposed by Freeman Dyson in 1979, proposes a means by which an immortal society of intelligent beings in an open universe may escape the prospect of the heat death of the universe by extending subjective time to infinity even though expending only a finite amount of energy. Bremermann's limit can be invoked to deduce that the amount of time to perform a computation on 1 bit is inversely proportional to the change in energy in the system. As a result, the amount of computations that can be performed grows over time. The increase in energy available slows logarithmically, but never stops. Therefore, for any specific computation rate that requires a specific amount of energy, there will come a time when that energy is available to be used. The intelligent beings would begin by storing a finite amount of energy. They then use half (or any fraction) of this energy to power their thought. When the energy gradient created by u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freeman Dyson
Freeman John Dyson (15 December 1923 – 28 February 2020) was an English-American theoretical physicist and mathematician known for his works in quantum field theory, astrophysics, random matrices, mathematical formulation of quantum mechanics, condensed matter physics, nuclear physics, and engineering. He was Professor Emeritus in the Institute for Advanced Study in Princeton and a member of the Board of Sponsors of the Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists. Dyson originated several concepts that bear his name, such as Dyson's transform, a fundamental technique in additive number theory, which he developed as part of his proof of Mann's theorem; the Dyson tree, a hypothetical genetically engineered plant capable of growing in a comet; the Dyson series, a perturbative series where each term is represented by Feynman diagrams; the Dyson sphere, a thought experiment that attempts to explain how a spacefaring, space-faring civilization would meet its energy requirements with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immortality
Immortality is the concept of eternal life. Some modern species may possess biological immortality. Some scientists, futurists, and philosophers have theorized about the immortality of the human body, with some suggesting that human immortality may be achievable in the first few decades of the 21st century with the help of certain technologies such as mind uploading (digital immortality). Other advocates believe that life extension is a more achievable goal in the short term, with immortality awaiting further research breakthroughs. The absence of aging would provide humans with biological immortality, but not invulnerability to death by disease or injury. Whether the process of internal immortality is delivered within the upcoming years depends chiefly on research (and in neuron research in the case of internal immortality through an immortalized cell line) in the former view and perhaps is an awaited goal in the latter case. What form an unending human life would take, o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intelligence (trait)
Intelligence has been defined in many ways: the capacity for abstraction, logic, understanding, self-awareness, learning, emotional knowledge, reasoning, planning, creativity, critical thinking, and problem-solving. More generally, it can be described as the ability to perceive or infer information, and to retain it as knowledge to be applied towards adaptive behaviors within an environment or context. Intelligence is most often studied in humans but has also been observed in both non-human animals and in plant intelligence, plants despite controversy as to whether some of these forms of life exhibit intelligence. Intelligence in computers or other machines is called artificial intelligence. Etymology The word ''wikt:intelligence#English, intelligence'' derives from the Latin nouns ''wikt:intelligentia, intelligentia'' or ''wikt:intellectus, intellēctus'', which in turn stem from the verb ''wikt:intelligere, intelligere'', to comprehend or perceive. In the Middle Ages, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
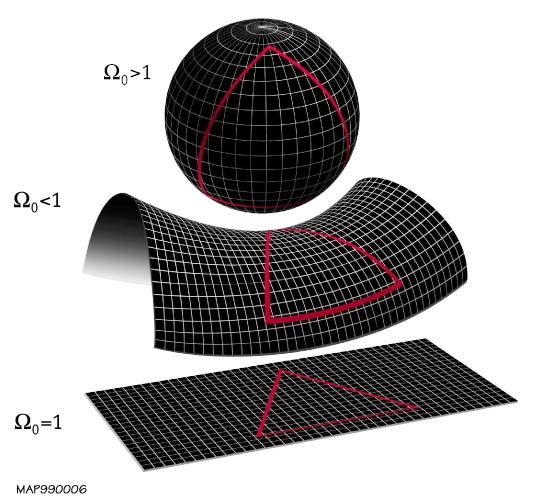
Open Universe
The shape of the universe, in physical cosmology, is the local and global geometry of the universe. The local features of the geometry of the universe are primarily described by its curvature, whereas the topology of the universe describes general global properties of its shape as a continuous object. The spatial curvature is defined by general relativity, which describes how spacetime is curved due to the effect of gravity. The spatial topology cannot be determined from its curvature, due to the fact that there exist locally indistinguishable spaces that may be endowed with different topological invariants. Cosmologists distinguish between the observable universe and the entire universe, the former being a ball-shaped portion of the latter that can, in principle, be accessible by astronomical observations. Assuming the cosmological principle, the observable universe is similar from all contemporary vantage points, which allows cosmologists to discuss properties of the entire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heat Death Of The Universe
The heat death of the universe (also known as the Big Chill or Big Freeze) is a hypothesis on the ultimate fate of the universe, which suggests the universe will evolve to a state of no thermodynamic free energy, and will therefore be unable to sustain processes that increase entropy. Heat death does not imply any particular absolute temperature; it only requires that temperature differences or other processes may no longer be exploited to perform work. In the language of physics, this is when the universe reaches thermodynamic equilibrium. The Heat Death theory has become the leading theory in the modern age with the fewest unpredictable factors. If the topology of the universe is open or flat, or if dark energy is a positive cosmological constant (both of which are consistent with current data), the universe will continue expanding forever, and a heat death is expected to occur, with the universe cooling to approach equilibrium at a very low temperature after a very long ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subjective Time
The study of time perception or chronoception is a field within psychology, cognitive linguistics and neuroscience that refers to the subjective experience, or sense, of time, which is measured by someone's own perception of the duration of the indefinite and unfolding of events. The perceived time interval between two successive events is referred to as perceived duration. Though directly experiencing or understanding another person's perception of time is not possible, perception can be objectively studied and inferred through a number of scientific experiments. Some temporal illusions help to expose the underlying neural mechanisms of time perception. Pioneering work, emphasizing species-specific differences, was conducted by Karl Ernst von Baer. Theories Time perception is typically categorized in three distinct ranges, because different ranges of duration are processed in different areas of the brain: * Sub-second timing or millisecond timing * Interval timing or seconds-t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bremermann's Limit
Bremermann's limit, named after Hans-Joachim Bremermann, is a limit on the maximum rate of computation that can be achieved in a self-contained system in the material universe. It is derived from Einstein's mass-energy equivalency and the Heisenberg uncertainty principle, and is '' c''2/'' h'' ≈ 1.36 × 1050 bits per second per kilogram. This value is important when designing cryptographic algorithms, as it can be used to determine the minimum size of encryption keys or hash values required to create an algorithm that could never be cracked by a brute-force search. For example, a computer with the mass of the entire Earth operating at Bremermann's limit could perform approximately 1075 mathematical computations per second. If one assumes that a cryptographic key can be tested with only one operation, then a typical 128-bit key could be cracked in under 10−36 seconds. However, a 256-bit key (which is already in use in some systems) would take about two minutes t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Logarithm
In mathematics, the logarithm is the inverse function to exponentiation. That means the logarithm of a number to the base is the exponent to which must be raised, to produce . For example, since , the ''logarithm base'' 10 of is , or . The logarithm of to ''base'' is denoted as , or without parentheses, , or even without the explicit base, , when no confusion is possible, or when the base does not matter such as in big O notation. The logarithm base is called the decimal or common logarithm and is commonly used in science and engineering. The natural logarithm has the number as its base; its use is widespread in mathematics and physics, because of its very simple derivative. The binary logarithm uses base and is frequently used in computer science. Logarithms were introduced by John Napier in 1614 as a means of simplifying calculations. They were rapidly adopted by navigators, scientists, engineers, surveyors and others to perform high-a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmological Constant
In cosmology, the cosmological constant (usually denoted by the Greek capital letter lambda: ), alternatively called Einstein's cosmological constant, is the constant coefficient of a term that Albert Einstein temporarily added to his field equations of general relativity. He later removed it. Much later it was revived and reinterpreted as the energy density of space, or vacuum energy, that arises in quantum mechanics. It is closely associated with the concept of dark energy. Einstein originally introduced the constant in 1917 to counterbalance the effect of gravity and achieve a static universe, a notion that was the accepted view at the time. Einstein's cosmological constant was abandoned after Edwin Hubble's confirmation that the universe was expanding. From the 1930s until the late 1990s, most physicists agreed with Einstein's choice of setting the cosmological constant to zero. That changed with the discovery in 1998 that the expansion of the universe is accelerating, im ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frank J
Frank or Franks may refer to: People * Frank (given name) * Frank (surname) * Franks (surname) * Franks, a medieval Germanic people * Frank, a term in the Muslim world for all western Europeans, particularly during the Crusades - see Farang Currency * Liechtenstein franc or frank, the currency of Liechtenstein since 1920 * Swiss franc or frank, the currency of Switzerland since 1850 * Westphalian frank, currency of the Kingdom of Westphalia between 1808 and 1813 * The currencies of the German-speaking cantons of Switzerland (1803–1814): ** Appenzell frank ** Argovia frank ** Basel frank ** Berne frank ** Fribourg frank ** Glarus frank ** Graubünden frank ** Luzern frank ** Schaffhausen frank ** Schwyz frank ** Solothurn frank ** St. Gallen frank ** Thurgau frank ** Unterwalden frank ** Uri frank ** Zürich frank Places * Frank, Alberta, Canada, an urban community, formerly a village * Franks, Illinois, United States, an unincorporated community * Franks, Missouri, United ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical Cosmology
Physical cosmology is a branch of cosmology concerned with the study of cosmological models. A cosmological model, or simply cosmology, provides a description of the largest-scale structures and dynamics of the universe and allows study of fundamental questions about its Cosmogony, origin, structure, Chronology of the universe, evolution, and ultimate fate.For an overview, see Cosmology as a science originated with the Copernican principle, which implies that astronomical object, celestial bodies obey identical physical laws to those on Earth, and Newtonian mechanics, which first allowed those physical laws to be understood. Physical cosmology, as it is now understood, began with the development in 1915 of Albert Einstein's general relativity, general theory of relativity, followed by major observational discoveries in the 1920s: first, Edwin Hubble discovered that the universe contains a huge number of external Galaxy, galaxies beyond the Milky Way; then, work by Vesto Sli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |