|
Dysmyelogenic Leukodystrophy
Alexander disease is a very rare autosomal dominant leukodystrophy, which are neurological conditions caused by anomalies in the myelin which protects nerve fibers in the brain. The most common type is the infantile form that usually begins during the first 2 years of life. Symptoms include mental and physical developmental delays, followed by the loss of developmental milestones, an abnormal increase in head size and seizures. The juvenile form of Alexander disease has an onset between the ages of 2 and 13 years. These children may have excessive vomiting, difficulty swallowing and speaking, poor coordination, and loss of motor control. Adult-onset forms of Alexander disease are less common. The symptoms sometimes mimic those of Parkinson’s disease or multiple sclerosis, or may present primarily as a psychiatric disorder. According to the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, the destruction of white matter is accompanied by the formation of Rosenthal fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macroencephaly
Megalencephaly (or macrencephaly; abbreviated MEG) is a growth development disorder in which the brain is abnormally large. It is characterized by a brain with an average weight that is 2.5 standard deviations above the mean of the general population. Approximately 1 out of 50 children (2%) are said to have the characteristics of megalencephaly in the general population. A mutation in the PI3K-AKT pathway is believed to be the primary cause of brain proliferation and ultimately the root cause of megalencephaly. This mutation has produced a classification of brain overdevelopment that consists of two syndromes including megalencephaly-capillary malformation (MCAP) and megalencephaly-polydactyly-polymicrogyria-hydrocephalus (MPPH). Megalencephaly is usually diagnosed at birth and is confirmed with an MRI. There are several neuropsychiatric disorders linked with megalencephaly; however, studies have shown that autism is the most prevalent association with the malformation of MEG. Al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
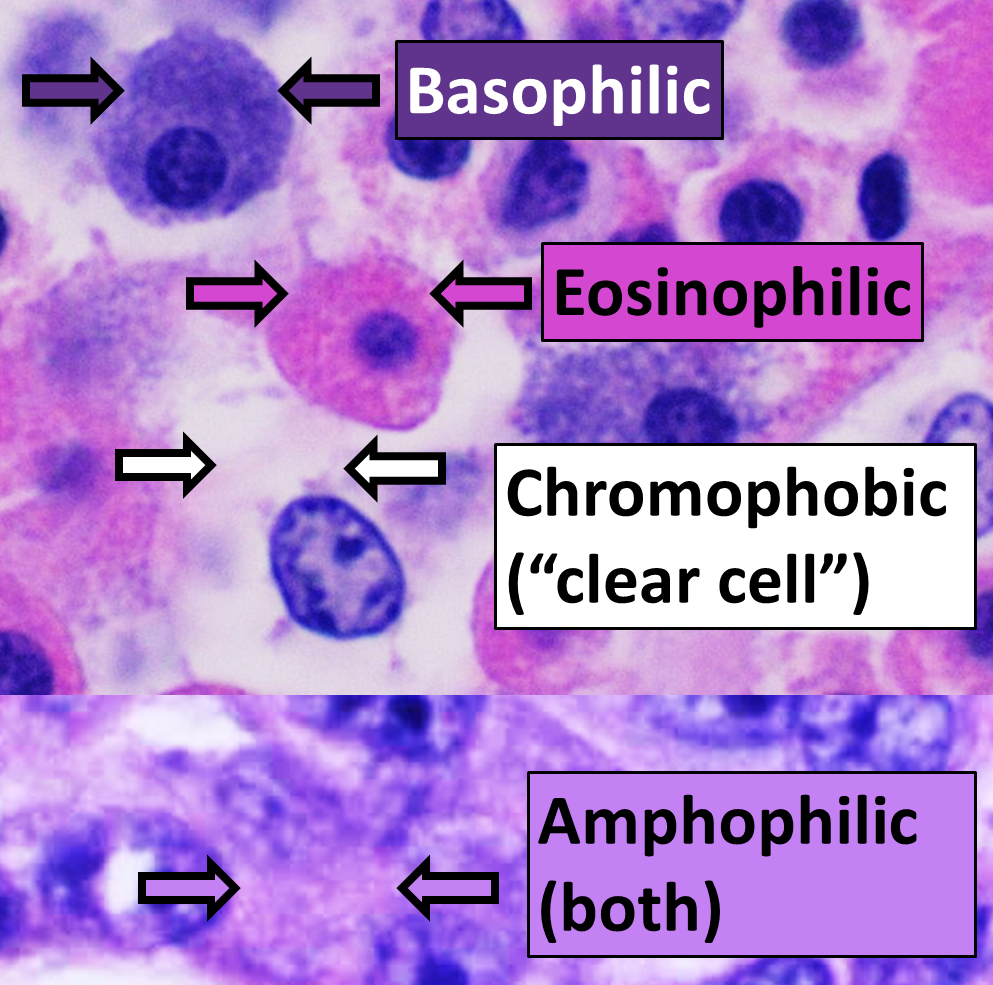
Eosinophilic
Eosinophilic (Greek suffix -phil-, meaning ''loves eosin'') is the staining of tissues, cells, or organelles after they have been washed with eosin, a dye. Eosin is an acidic dye for staining cell cytoplasm, collagen, and muscle fibers. ''Eosinophilic'' describes the appearance of cells and structures seen in histological sections that take up the staining dye eosin. Such eosinophilic structures are, in general, composed of protein. Eosin is usually combined with a stain called hematoxylin to produce a hematoxylin- and eosin-stained section (also called an H&E stain, HE or H+E section). It is the most widely used histological stain for a medical diagnosis. When a pathologist examines a biopsy of a suspected cancer, they will stain the biopsy with H&E. Some structures seen inside cells are described as being eosinophilic; for example, Lewy and Mallory bodies. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Matter
White matter refers to areas of the central nervous system (CNS) that are mainly made up of myelinated axons, also called tracts. Long thought to be passive tissue, white matter affects learning and brain functions, modulating the distribution of action potentials, acting as a relay and coordinating communication between different brain regions. White matter is named for its relatively light appearance resulting from the lipid content of myelin. However, the tissue of the freshly cut brain appears pinkish-white to the naked eye because myelin is composed largely of lipid tissue veined with capillaries. Its white color in prepared specimens is due to its usual preservation in formaldehyde. Structure White matter White matter is composed of bundles, which connect various grey matter areas (the locations of nerve cell bodies) of the brain to each other, and carry nerve impulses between neurons. Myelin acts as an insulator, which allows electrical signals to jump, rather than c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myelin Sheath
Myelin is a lipid-rich material that surrounds nerve cell axons (the nervous system's "wires") to insulate them and increase the rate at which electrical impulses (called action potentials) are passed along the axon. The myelinated axon can be likened to an electrical wire (the axon) with insulating material (myelin) around it. However, unlike the plastic covering on an electrical wire, myelin does not form a single long sheath over the entire length of the axon. Rather, myelin sheaths the nerve in segments: in general, each axon is encased with multiple long myelinated sections with short gaps in between called nodes of Ranvier. Myelin is formed in the central nervous system (CNS; brain, spinal cord and optic nerve) by glial cells called oligodendrocytes and in the peripheral nervous system (PNS) by glial cells called Schwann cells. In the CNS, axons carry electrical signals from one nerve cell body to another. In the PNS, axons carry signals to muscles and glands or from sensor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zygosity
Zygosity (the noun, zygote, is from the Greek "yoked," from "yoke") () is the degree to which both copies of a chromosome or gene have the same genetic sequence. In other words, it is the degree of similarity of the alleles in an organism. Most eukaryotes have two matching sets of chromosomes; that is, they are diploid. Diploid organisms have the same loci on each of their two sets of homologous chromosomes except that the sequences at these loci may differ between the two chromosomes in a matching pair and that a few chromosomes may be mismatched as part of a chromosomal sex-determination system. If both alleles of a diploid organism are the same, the organism is homozygous at that locus. If they are different, the organism is heterozygous at that locus. If one allele is missing, it is hemizygous, and, if both alleles are missing, it is nullizygous. The DNA sequence of a gene often varies from one individual to another. These gene variants are called alleles. While some gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dominance (genetics)
In genetics, dominance is the phenomenon of one variant (allele) of a gene on a chromosome masking or overriding the effect of a different variant of the same gene on the other copy of the chromosome. The first variant is termed dominant and the second recessive. This state of having two different variants of the same gene on each chromosome is originally caused by a mutation in one of the genes, either new (''de novo'') or inherited. The terms autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive are used to describe gene variants on non-sex chromosomes ( autosomes) and their associated traits, while those on sex chromosomes (allosomes) are termed X-linked dominant, X-linked recessive or Y-linked; these have an inheritance and presentation pattern that depends on the sex of both the parent and the child (see Sex linkage). Since there is only one copy of the Y chromosome, Y-linked traits cannot be dominant or recessive. Additionally, there are other forms of dominance such as incomplete d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromosome 17 (human)
Chromosome 17 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 17 spans more than 83 million base pairs (the building material of DNA) and represents between 2.5 and 3% of the total DNA in cells. Chromosome 17 contains the Homeobox B gene cluster. Genes Number of genes The following are some of the gene count estimates of human chromosome 17. Because researchers use different approaches to genome annotation their predictions of the number of genes on each chromosome varies (for technical details, see gene prediction). Among various projects, the collaborative consensus coding sequence project ( CCDS) takes an extremely conservative strategy. So CCDS's gene number prediction represents a lower bound on the total number of human protein-coding genes. Gene list The following is a partial list of genes on human chromosome 17. For complete list, see the link in the infobox on the right. The following are some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein
Glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) is a protein that is encoded by the ''GFAP'' gene in humans. It is a type III intermediate filament (IF) protein that is expressed by numerous cell types of the central nervous system (CNS), including astrocytes and ependymal cells during development. GFAP has also been found to be expressed in glomeruli and peritubular fibroblasts taken from rat kidneys, Leydig cells of the testis in both hamsters and humans, human keratinocytes, human osteocytes and chondrocytes and stellate cells of the pancreas and liver in rats. GFAP is closely related to the other three non-epithelial type III IF family members, vimentin, desmin and peripherin, which are all involved in the structure and function of the cell’s cytoskeleton. GFAP is thought to help to maintain astrocyte mechanical strength as well as the shape of cells, but its exact function remains poorly understood, despite the number of studies using it as a cell marker. The protein was named and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, mitosis, or meiosis or other types of damage to DNA (such as pyrimidine dimers caused by exposure to ultraviolet radiation), which then may undergo error-prone repair (especially microhomology-mediated end joining), cause an error during other forms of repair, or cause an error during replication (translesion synthesis). Mutations may also result from insertion or deletion of segments of DNA due to mobile genetic elements. Mutations may or may not produce detectable changes in the observable characteristics (phenotype) of an organism. Mutations play a part in both normal and abnormal biological processes including: evolution, cancer, and the development of the immune system, including junctional diversity. Mutation is the ultimate source o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Nervous System
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all parts of the bodies of bilaterally symmetric and triploblastic animals—that is, all multicellular animals except sponges and diploblasts. It is a structure composed of nervous tissue positioned along the rostral (nose end) to caudal (tail end) axis of the body and may have an enlarged section at the rostral end which is a brain. Only arthropods, cephalopods and vertebrates have a true brain (precursor structures exist in onychophorans, gastropods and lancelets). The rest of this article exclusively discusses the vertebrate central nervous system, which is radically distinct from all other animals. Overview In vertebrates, the brain and spinal cord are both enclosed in the meninges. The meninges provide a barrier to chemicals dissolv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |