|
Dying Earth Subgenre
Dying Earth is a subgenre of science fantasy or science fiction which takes place in the far future at either the end of life on Earth or the end of time, when the laws of the universe themselves fail. Themes of world-weariness, innocence (wounded or otherwise), idealism, entropy, (permanent) exhaustion/depletion of many or all resources (such as soil nutrients), and the hope of renewal dominate. Genre The Dying Earth genre differs from the apocalyptic subgenre in that it deals not with catastrophic destruction, but with entropic exhaustion of Earth. It is therefore described as more "melancholic". The genre was prefigured by the works of the Romantic movement. Jean-Baptiste Cousin de Grainville's ''Le Dernier Homme'' (1805) narrates the tale of Omegarus, the Last Man on Earth. It is a bleak vision of the future when Earth has become totally sterile. Lord Byron's poem "Darkness" (1816) shows Earth after the Sun has died. Mary Shelley's ''The Last Man'' (1826) details a fu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regeneration Artwork
Regeneration may refer to: Science and technology * Regeneration (biology), the ability to recreate lost or damaged cells, tissues, organs and limbs * Regeneration (ecology), the ability of ecosystems to regenerate biomass, using photosynthesis * Regeneration in humans, the ability of humans to recreate, or induce the regeneration of, lost tissue * Regenerative (design), a process for resilient and sustainable development * Regenerative agriculture, a sub-category of organic agriculture History and politics *Regeneration (Colombia), La Regeneración, a 19th-century period and political movement in Colombia *Regeneration (Portugal), a 19th-century period in the history of Portugal * The ReGeneration, a cultural generation concerned with environmentalism * Viðreisn (Regeneration), a political party in Iceland founded in 2016 Music * Regeneration (Stanley Cowell album), ''Regeneration'' (Stanley Cowell album) (1976) * Regeneration (Roy Orbison album), ''Regeneration'' (Roy Orbison ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mary Shelley
Mary Wollstonecraft Shelley (; ; 30 August 1797 – 1 February 1851) was an English novelist who wrote the Gothic fiction, Gothic novel ''Frankenstein, Frankenstein; or, The Modern Prometheus'' (1818), which is considered an History of science fiction#Shelley and Europe in the early 19th century, early example of science fiction. She also edited and promoted the works of her husband, the Romantic poet and philosopher Percy Bysshe Shelley. Her father was the political philosopher William Godwin and her mother was the philosopher and women's rights advocate Mary Wollstonecraft. Mary's mother died less than a fortnight after giving birth to her. She was raised by her father, who provided her with a rich if informal education, encouraging her to adhere to his own anarchist political theories. When she was four, her father married a neighbour, Mary Jane Clairmont, with whom Mary came to have a troubled relationship. In 1814, Mary began a romance with one of her father's politica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clark Ashton Smith
Clark Ashton Smith (January 13, 1893 – August 14, 1961) was an American writer and artist. He achieved early local recognition, largely through the enthusiasm of George Sterling, for traditional verse in the vein of Algernon Charles Swinburne, Swinburne. As a poet, Smith is grouped with the West Coast Romantics alongside Joaquin Miller, Sterling, and Nora May French and remembered as "The Last of the Great Romantics" and "The Bard of Auburn". Smith's work was praised by his contemporaries. H. P. Lovecraft stated that "in sheer daemonic strangeness and fertility of conception, Clark Ashton Smith is perhaps unexcelled", and Ray Bradbury said that Smith "filled my mind with incredible worlds, impossibly beautiful cities, and still more fantastic creatures". Smith was one of "the big three of ''Weird Tales'', with Robert E. Howard and H. P. Lovecraft", but some readers objected to his morbidness and violation of pulp traditions. The fantasy critic L. Sprague de Camp said of him th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Les Xipéhuz
''Les Xipéhuz'' (1888) is a novella by the writing duo J.-H. Rosny – although it is possible that Rosny aîné was the principal contributor. It describes the fight that threatens humanity, in the beginning of its history, against a new form of intelligent non-organic life, the Xipéhuz, some sort of sentient crystals. It is both his first story set in prehistoric times, and his first science fiction story, although the term did not yet exist. Plot The narrative consists of two parts. First is a descriptive third-person description of encounters between nomadic tribes and the Xipéhuz, resulting in many deaths from mysterious weapons and powers. This is followed by meetings of the clans and tribes, ritual sacrifices, and assembly of an army which is defeated by the Xipéhuz. The second part is the memoir of a wise war chief who observes the Xipéhuz from afar, then carefully approaches them to find out their habits and vulnerabilities. Despite nearly being killed on seve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
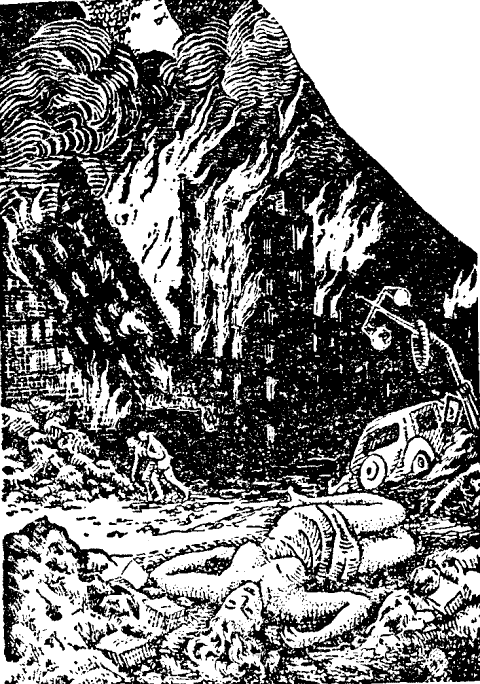
La Mort De La Terre
''The Death of the Earth'' (French: ''La Mort de la Terre'') is a 1910 Belgian novel by J.-H. Rosny aîné. Plot summary In the far future the Earth has become an immense, dry desert. Small communities of future humans, partially adapted to the harsher climate, survive united by the "Great Planetary" communications web. The means for human survival are rapidly diminishing beyond repair, the remaining supplies of water failing or becoming increasingly hard to find. Alongside of which a barely comprehensible form of life – "ferromagnetals" ("les ferromagnétaux") – have begun to develop and spread within and throughout the Earth itself. The narrative focuses mainly on group of humans led by Targ, who at the beginning of the story is the "watchman" ("veilleur") of the Great Planetary. See also * 1910 in science fiction External links * 1910 novels 1910 science fiction novels Belgian speculative fiction novels French-language novels Post-apocalyptic novels { ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dying Earth
''Dying Earth'' is a fantasy series by the American author Jack Vance, comprising four books originally published from 1950 to 1984. Some have been called picaresque. They vary from short story collections to a fix-up (novel created from older short stories), perhaps all the way to novel. Retrieved 2012-05-09. The first book in the series, ''The Dying Earth'', was ranked number 16 of 33 "All Time Best Fantasy Novels" by ''Locus (magazine), Locus'' in 1987, based on a poll of subscribers, although it was marketed as a collection and the Internet Speculative Fiction Database (ISFDB) calls it a "loosely connected series of stories". Setting The stories of the ''Dying Earth'' series are set in the distant future, at a point when the Dying Earth subgenre, sun is almost exhausted and magic has asserted itself as a dominant force. The Moon has disappeared and the Sun is in danger of burning out at any time, often flickering as if about to go out, before shining again. The various c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Night Land
''The Night Land'' is a horror/fantasy novel by English writer William Hope Hodgson, first published in 1912. As a work of fantasy it belongs to the Dying Earth subgenre. Hodgson also published a much shorter version of the novel, entitled '' The Dream of X'' (1912). Publication history ''The Night Land'' was revived in paperback by Ballantine Books, which republished the work in two parts as the 49th and 50th volumes of its Ballantine Adult Fantasy series in July 1972. H. P. Lovecraft's essay "Supernatural Horror in Literature" describes the novel as "one of the most potent pieces of macabre imagination ever written". Clark Ashton Smith wrote of it: When the book was written, the nature of the energy source that powers stars was not known: Lord Kelvin had published calculations based on the hypothesis that the energy came from the gravitational collapse of the gas cloud that had formed the sun and found that this mechanism gave the Sun a lifetime of only a few tens of mill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The House On The Borderland
''The House on the Borderland'' (1908) is a supernatural horror novel by British fantasist William Hope Hodgson. The novel is a hallucinatory account of a recluse's stay at a remote house, and his experiences of supernatural creatures and otherworldly dimensions. On encountering Hodgson's novels in 1934, American horror writer H. P. Lovecraft praised ''The House on the Borderland'' and other works by Hodgson at length. Terry Pratchett has called the novel "the Big Bang in my private universe as a science fiction and fantasy reader and, later, writer". Plot summary Two men on a two-week fishing vacation in remote western Ireland are surprised to discover a strange abyss. On a rock spur above this pit they find ruins and buried in them a journal, which they read. The author of the journal introduces himself as an old man who has lived for years in an ancient house accompanied only by his sister, who serves as housekeeper, and his dog, Pepper. He has no contact with the local ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Hope Hodgson
William Hope Hodgson (15 November 1877 – 19 April 1918) was an English author. He produced a large body of work, consisting of essays, short fiction, and novels, spanning several overlapping genres including horror, fantastic fiction, and science fiction.Alder, Emily. "Passing the Barrier or Life: Spiritualism, Psychical Research and Boundaries in William Hope Hodgson's "The Night Land"". in Ramone, Jenni and Twitchen, Gemma, eds. ''Boundaries''. Newcastle: Cambridge Scholars Publishing, 2007. (pp. 120-139). Stableford, Brian, "Hodgson, William Hope", in Pringle, David ed., ''St. James Guide to Horror, Ghost & Gothic Writers''. London: St. James Press, 1998. (pp. 273-275). Hodgson used his experiences at sea to lend authentic detail to his short horror stories, many of which are set on the ocean, including his series of linked tales forming the "Sargasso Sea Stories". His novels, such as '' The House on the Borderland'' (1908) and ''The Night Land'' (1912), feature more cosm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Time Machine
''The Time Machine'' is a science fiction novella by H. G. Wells, published in 1895. The work is generally credited with the popularization of the concept of time travel by using a vehicle or device to travel purposely and selectively forward or backward through time. The term "time machine", coined by Wells, is now almost universally used to refer to such a vehicle or device. Utilizing a frame story set in then-present Victorian England, Wells' text focuses on a recount of the otherwise anonymous Time Traveller's journey into the far future. A work of future history and speculative evolution, ''Time Machine'' is interpreted in modern times as a commentary on the increasing inequality and class divisions of Wells' era, which he projects as giving rise to two separate human species: the fair, childlike Eloi, and the savage, simian Morlocks, distant descendants of the contemporary upper and lower classes respectively. It is believed that Wells' depiction of the Eloi as a rac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Novella
A novella is a narrative prose fiction whose length is shorter than most novels, but longer than most short stories. The English word ''novella'' derives from the Italian ''novella'' meaning a short story related to true (or apparently so) facts. Definition The Italian term is a feminine of ''novello'', which means ''new'', similarly to the English word ''news''. Merriam-Webster defines a novella as "a work of fiction intermediate in length and complexity between a short story and a novel". No official definition exists regarding the number of pages or words necessary for a story to be considered a novella, a short story or a novel. The Science Fiction and Fantasy Writers Association defines a novella's word count to be between 17,500 and 40,000 words. History The novella as a literary genre began developing in the Italian literature of the early Renaissance, principally Giovanni Boccaccio, author of ''The Decameron'' (1353). ''The Decameron'' featured 100 tales (named nov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camille Flammarion
Nicolas Camille Flammarion FRAS (; 26 February 1842 – 3 June 1925) was a French astronomer and author. He was a prolific author of more than fifty titles, including popular science works about astronomy, several notable early science fiction novels, and works on psychical research and related topics. He also published the magazine '' L'Astronomie'', starting in 1882. He maintained a private observatory at Juvisy-sur-Orge, France. Biography Camille Flammarion was born in Montigny-le-Roi, Haute-Marne, France. He was the brother of Ernest Flammarion (1846–1936), the founder of the Groupe Flammarion publishing house. In 1858 he became a computer at the Paris Observatory. He was a founder and the first president of the '' Société astronomique de France'', which originally had its own independent journal, ''BSAF'' (''Bulletin de la Société astronomique de France''), which was first published in 1887. In January 1895, after 13 volumes of '' L'Astronomie'' and 8 of ''BSAF'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |