|
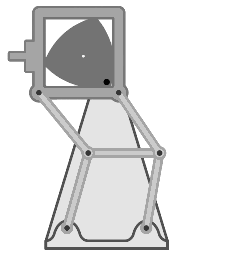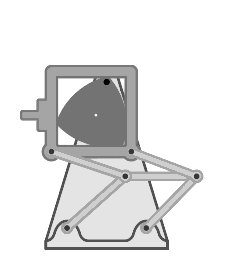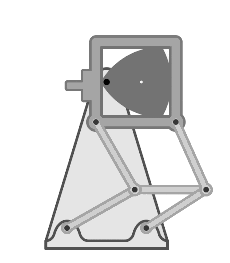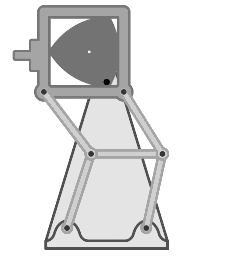
Dwell Mechanism
A dwell mechanism (either a linkage or cam-follower type) is an intermittent motion mechanism that alternates forward and return motion with holding position(s). Dwells in cam mechanisms Single dwell cam mechanisms A single dwell cam mechanism has a motion function which follows a dwell-rise-fall sequence that repeats. It is sometimes desired to use a rise function such that the acceleration of the follower is non-zero at its end of the rise. To maintain continuity, the fall function often begins such that the follower has the same non-zero acceleration as it had at the end of the rise function. The follower then stays stationary during the dwell function, with its velocity, acceleration, and jerk zero. There are a number of functions that can provide these motion requirements. A double-harmonic function is a common example used for single dwell. Double dwell cam mechanisms A double dwell cam mechanism has a motion function which follows a rise-dwell-fall-dwell motion fu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Four-bar Linkage
In the study of mechanisms, a four-bar linkage, also called a four-bar, is the simplest closed- chain movable linkage. It consists of four bodies, called ''bars'' or ''links'', connected in a loop by four joints. Generally, the joints are configured so the links move in parallel planes, and the assembly is called a ''planar four-bar linkage''. Spherical and spatial four-bar linkages also exist and are used in practice. Planar four-bar linkage Planar four-bar linkages are constructed from four links connected in a loop by four one- degree-of-freedom joints. A joint may be either a revolute joint – also known as a pin joint or hinged joint – denoted by R, or a prismatic joint – also known as a sliding pair – denoted by P. A link that are fixed in place relative to the viewer is called a ''ground link.'' A link connecting to the ground by a revolute joint that can perform a complete revolution is called a '' crank link.'' A link connecting to the ground by a revolute join ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linkage (mechanical)
A mechanical linkage is an assembly of systems connected to manage forces and movement. The movement of a body, or link, is studied using geometry so the link is considered to be rigid. The connections between links are modeled as providing ideal movement, pure rotation or sliding for example, and are called joints. A linkage modeled as a network of rigid links and ideal joints is called a kinematic chain. Linkages may be constructed from open chains, closed chains, or a combination of open and closed chains. Each link in a chain is connected by a joint to one or more other links. Thus, a kinematic chain can be modeled as a graph in which the links are paths and the joints are vertices, which is called a linkage graph. The movement of an ideal joint is generally associated with a subgroup of the group of Euclidean displacements. The number of parameters in the subgroup is called the degrees of freedom (DOF) of the joint. Mechanical linkages are usually designed to tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intermittent Mechanism
{{short description, Device by which motion picture film is advanced An intermittent mechanism or intermittent movement is a device or movement which regularly advances an object, web, or plastic film and then holds it in place. This process is commonly used in industry and manufacturing. This motion is critical to the use of film in a movie camera or movie projector. This is in contrast to a continuous mechanism, whereby the film is constantly in motion and the image is held steady by optical or electronic methods. The reason the intermittent mechanism "works" for the viewer is because of a phenomenon called persistence of vision. History Intermittent mechanisms were first used in sewing machines, in order for the fabric to be fed through correctly - ensuring it is stationary as each stitch is made, while moving the required distance between stitches. Methods used The intermittent mechanism must be employed in concert with a rotating shutter which blocks light transmitt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hoecken Linkage
In kinematics, the Hoecken linkage (named for Karl Hoecken) is a four-bar linkage that converts rotational motion to approximate straight-line motion. The Hoecken linkage is a cognate linkage of the Chebyshev linkage and Chebyshev's Lambda Mechanism. The linkage was first published in 1926. A generalization of the Hoecken linkage is Wittgenstein's rod. See also *Chebyshev linkage and Chebyshev lambda linkage, linkages that produce a very similar locus without the need of a sliding joint. *Straight line mechanism *Four-bar linkage In the study of mechanisms, a four-bar linkage, also called a four-bar, is the simplest closed- chain movable linkage. It consists of four bodies, called ''bars'' or ''links'', connected in a loop by four joints. Generally, the joints are configu ... References External links Straight line mechanisms Linkages (mechanical) {{technology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hippopede
In geometry, a hippopede () is a plane curve determined by an equation of the form :(x^2+y^2)^2=cx^2+dy^2, where it is assumed that and since the remaining cases either reduce to a single point or can be put into the given form with a rotation. Hippopedes are bicircular, rational, algebraic curves of degree 4 and symmetric with respect to both the and axes. Special cases When ''d'' > 0 the curve has an oval form and is often known as an oval of Booth, and when the curve resembles a sideways figure eight, or lemniscate, and is often known as a lemniscate of Booth, after 19th-century mathematician James Booth who studied them. Hippopedes were also investigated by Proclus (for whom they are sometimes called Hippopedes of Proclus) and Eudoxus. For , the hippopede corresponds to the lemniscate of Bernoulli. Definition as spiric sections Hippopedes can be defined as the curve formed by the intersection of a torus and a plane, where the plane is parallel to the axis of the to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feed Dogs
A feed dog is a movable plate which pulls fabric through a sewing machine in discrete steps between stitches. Action A set of feed dogs typically resembles two or three short, thin metal bars, crosscut with diagonal teeth, which move both front to back and up and down in slots in a sewing machine's needle plate: front to back to advance fabric gripped between the dogs and the presser foot toward the needle, and up and down to recess at the end of their stroke, release the fabric, and remain recessed while returning before emerging again to begin a new one. Name A mechanical dog is named to suggest the jaw or teeth of a dog, the animal, clamped on to an object, refusing to let go. This arrangement is called "drop feed" in reference to the way the dogs drop below the needle plate when returning for the next stroke. Allen B. Wilson invented it during the time period 1850 to 1854,The date of 1850 is given by James Paton in his "Sewing Machines" article in the Encyclopædia Brit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camshaft
A camshaft is a shaft that contains a row of pointed cams, in order to convert rotational motion to reciprocating motion. Camshafts are used in piston engines (to operate the intake and exhaust valves), mechanically controlled ignition systems and early electric motor speed controllers. Camshafts in piston engines are usually made from steel or cast iron, and the shape of the cams greatly affects the engine's characteristics. History Trip hammers are one of the early uses of a form of cam to convert rotating motion, e.g. from a waterwheel, into the reciprocating motion of a hammer used in forging or to pound grain. Evidence for these exists back to the Han Dynasty in China, and they were widespread by the medieval period. The camshaft was described in 1206 by engineer Al-Jazari. He employed it as part of his automata, water-raising machines, and water clocks such as the castle clock. Once the rotative version of the steam engine was developed in the late 18th century, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geneva Drive
The Geneva drive or Maltese cross is a gear mechanism that translates a continuous rotation movement into intermittent rotary motion. The ''rotating drive'' wheel is usually equipped with a pin that reaches into a slot located in the other wheel (''driven wheel'' that advances it by one step at a time. The drive wheel also has an elevated circular blocking disc that "locks" the rotating driven wheel in position between steps. History The name, Geneva drive, is derived from the devices earliest application in mechanical watches, which were popularized in Geneva, being the classical origin of watchmaking industry. The mechanism is frequently used in mechanical watches, since it can be made small and is able to withstand substantial mechanical stress. The ''Geneva drive'' is also called a "Maltese cross mechanism" due to the visual resemblance when the rotating wheel has four spokes. In the most common arrangement of the Geneva drive, the client wheel has four slots and thu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intermittent Mechanism
{{short description, Device by which motion picture film is advanced An intermittent mechanism or intermittent movement is a device or movement which regularly advances an object, web, or plastic film and then holds it in place. This process is commonly used in industry and manufacturing. This motion is critical to the use of film in a movie camera or movie projector. This is in contrast to a continuous mechanism, whereby the film is constantly in motion and the image is held steady by optical or electronic methods. The reason the intermittent mechanism "works" for the viewer is because of a phenomenon called persistence of vision. History Intermittent mechanisms were first used in sewing machines, in order for the fabric to be fed through correctly - ensuring it is stationary as each stitch is made, while moving the required distance between stitches. Methods used The intermittent mechanism must be employed in concert with a rotating shutter which blocks light transmitt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)