|
Drina Mariae
The Drina ( sr-Cyrl, Дрина, ) is a long Balkans river, which forms a large portion of the border between Bosnia and Herzegovina and Serbia. It is the longest tributary of the Sava River and the longest karst river in the Dinaric Alps which belongs to the Danube river watershed. Its name is derived from the Roman name of the river ( la, Drinus) which in turn is derived from Greek (Ancient Greek: ). The Drina originates from the confluence of the rivers Tara and Piva, in the glen between the slopes of the Maglić, Hum and Pivska Planina mountains, in the area of Šćepan Polje (in Montenegro) and Hum (Bosnia and Herzegovina) villages. Hydrological characteristics The Drina is a very fast and cold alpine river, with a very high 175:346 meandering ratio, and relatively clean water, which has particularly intensive green coloration, a usual characteristic of most alpine rivers running through a karstic and flysch terrain made of limestone, underlying the area in which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
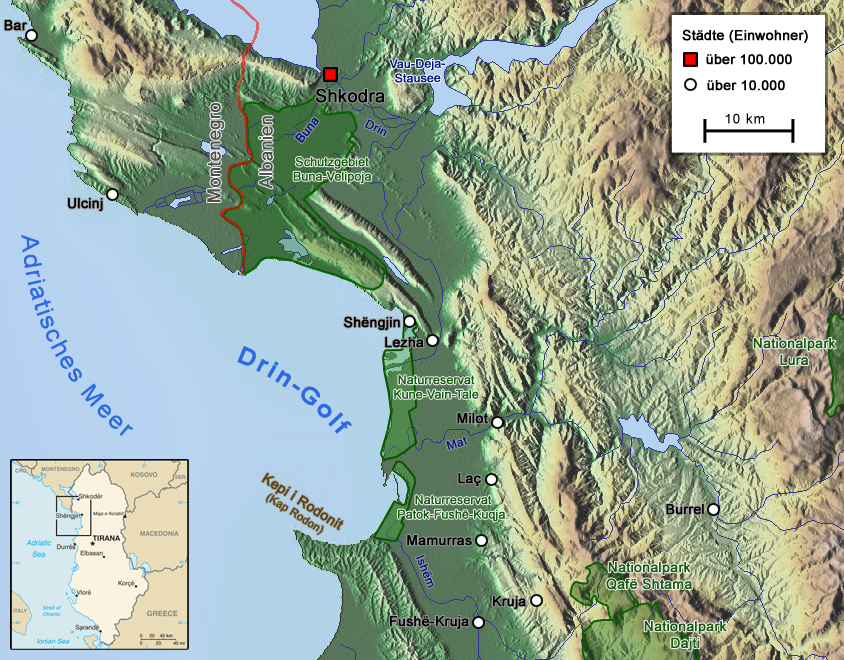
Drin River
The Drin (; sq, Drin or ; mk, Дрим, Drim ) is a river in Southern and Southeastern Europe with two distributaries one discharging into the Adriatic Sea and the other one into the Buna River. Its catchment area extends across Albania, Kosovo, Serbia, Greece, Montenegro and North Macedonia. The river and its tributaries form the Gulf of Drin, an ocean basin that encompasses the northern Albanian Adriatic Sea Coast. At long, the Drin is the longest river of Albania of which passes across Albania and the remainder through Kosovo and North Macedonia. It starts at the confluence of its two headwaters, namely the Black Drin and White Drin. It originates in the mountainous northern mountain range, flows westwards through the Albanian Alps and Dukagjin Highlands, and eventually drains into the Adriatic Sea, between Shëngjin and Durrës. Numerous lakes and reservoirs are formed by the river or flow into it such as the Fierza Lake and Koman Lake. Located in the Balkan P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic period (), and the Classical period (). Ancient Greek was the language of Homer and of fifth-century Athenian historians, playwrights, and philosophers. It has contributed many words to English vocabulary and has been a standard subject of study in educational institutions of the Western world since the Renaissance. This article primarily contains information about the Epic and Classical periods of the language. From the Hellenistic period (), Ancient Greek was followed by Koine Greek, which is regarded as a separate historical stage, although its earliest form closely resembles Attic Greek and its latest form approaches Medieval Greek. There were several regional dialects of Ancient Greek, of which Attic Greek developed into Koine. Dia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drainage Basin
A drainage basin is an area of land where all flowing surface water converges to a single point, such as a river mouth, or flows into another body of water, such as a lake or ocean. A basin is separated from adjacent basins by a perimeter, the '' drainage divide'', made up of a succession of elevated features, such as ridges and hills. A basin may consist of smaller basins that merge at river confluences, forming a hierarchical pattern. Other terms for a drainage basin are catchment area, catchment basin, drainage area, river basin, water basin, and impluvium. In North America, they are commonly called a watershed, though in other English-speaking places, "watershed" is used only in its original sense, that of a drainage divide. In a closed drainage basin, or endorheic basin, the water converges to a single point inside the basin, known as a sink, which may be a permanent lake, a dry lake, or a point where surface water is lost underground. Drainage basins are similar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Romania, Russia, Turkey, and Ukraine. The Black Sea is supplied by major rivers, principally the Danube, Dnieper, and Don. Consequently, while six countries have a coastline on the sea, its drainage basin includes parts of 24 countries in Europe. The Black Sea covers (not including the Sea of Azov), has a maximum depth of , and a volume of . Most of its coasts ascend rapidly. These rises are the Pontic Mountains to the south, bar the southwest-facing peninsulas, the Caucasus Mountains to the east, and the Crimean Mountains to the mid-north. In the west, the coast is generally small floodplains below foothills such as the Strandzha; Cape Emine, a dwindling of the east end of the Balkan Mountains; and the Dobruja Plateau considerably farth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albania
Albania ( ; sq, Shqipëri or ), or , also or . officially the Republic of Albania ( sq, Republika e Shqipërisë), is a country in Southeastern Europe. It is located on the Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea and shares land borders with Montenegro to the northwest, Kosovo to the northeast, North Macedonia to the east and Greece to the south. Tirana is its capital and largest city, followed by Durrës, Vlorë, and Shkodër. Albania displays varied climatic, geological, hydrological, and morphological conditions, defined in an area of . It possesses significant diversity with the landscape ranging from the snow-capped mountains in the Albanian Alps as well as the Korab, Skanderbeg, Pindus and Ceraunian Mountains to the hot and sunny coasts of the Albanian Adriatic and Ionian Sea along the Mediterranean Sea. Albania has been inhabited by different civilisations over time, such as the Illyrians, Thracians, Greeks, Romans, Byzantines, Venetians, and Ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ljubovija
Ljubovija ( sr-cyr, Љубовија, ) is a small town and municipality located in the Mačva District of western Serbia. As of 2011, the population of the municipality is 14,469 inhabitants. Settlements Aside from the town of Ljubovija, the municipality includes the following settlements: * Berlovine * Vrhpolje * Gornja Ljuboviđa * Gornja Orovica * Gornja Trešnjica * Gornje Košlje * Gračanica * Grčić * Donja Ljuboviđa * Donja Orovica * Drlače * Duboko * Leović * Lonjin * Orovička Planina * Podnemić * Postenje * Rujevac * Savković * Selenac * Sokolac * Tornik * Uzovnica * Caparić * Crnča * Čitluk Demographics According to the 2011 census results, the municipality of Ljubovija has 14,469 inhabitants. Ethnic groups The ethnic composition of the municipality: Economy The following table gives a preview of total number of employed people per their core activity (as of 2017): Notable people * Dragana Stanković, basketball player, Olympic bronze med ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bajina Bašta
Bajina Bašta ( sr-cyr, Бајина Башта, ) is a town and municipality located in the Zlatibor District of western Serbia. The town lies in the valley of the Drina river at the eastern edge of Tara National Park. The population of the town, according to 2011 census, is 9,148 inhabitants, while the municipality has 25,724 inhabitants. History In 1834 Bajina Bašta was established on the remains of the old Turkish community of Pljeskovo which was situated on the right bank of the Drina River between the Rača and Pilica Rivers, under the east foothills of Tara Mountain. By the end of the 19th century, in accordance with the Serbian-Turkish agreement, the local Muslims had to move from this region directly across the Drina River into Bosnia, where they built settlements in the villages of Skelani and Dobrak. The name ''Bajina Bašta'' comes from the vast orchards and vegetable gardens, that used to be located on the left bank of the Pilica River, which belonged to Turki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tijesno
Tisno is a town and municipality in Šibenik-Knin County, Croatia. Etymology Tisno was named after the Croatian ikavian word ''tisno'' which means strait, which describes its location at the narrow strait separating the island of Murter from the mainland. The municipality extends both to several other villages on the island as well as several nearby villages inland. Settlements In the 2011 census, there were a total of 3,094 inhabitants, in the following settlements: * Betina, population 697 * Dazlina, population 45 * Dubrava kod Tisna, population 179 * Jezera, population 886 * Tisno, population 1,287 In the 2011 census, 96.67% of the population were Croats. History Tisno was first mentioned in 1474 during the Turkish invasion and during the war against the Venetians when numerous refugees fled to Tisno to seek shelter. Tisno has a memorial-site dedicated to the several hundred Croatian civilians killed and dropped into a local pit in the aftermath of World War II by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms when these minerals precipitate out of water containing dissolved calcium. This can take place through both biological and nonbiological processes, though biological processes, such as the accumulation of corals and shells in the sea, have likely been more important for the last 540 million years. Limestone often contains fossils which provide scientists with information on ancient environments and on the evolution of life. About 20% to 25% of sedimentary rock is carbonate rock, and most of this is limestone. The remaining carbonate rock is mostly dolomite, a closely related rock, which contains a high percentage of the mineral dolomite, . ''Magnesian limestone'' is an obsolete and poorly-defined term used variously for dolomite, for limes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flysch
Flysch () is a sequence of sedimentary rock layers that progress from deep-water and turbidity flow deposits to shallow-water shales and sandstones. It is deposited when a deep basin forms rapidly on the continental side of a mountain building episode. Examples are found near the North American Cordillera, the Alps, the Pyrenees and the Carpathians. Sedimentological properties Flysch consists of repeated sedimentary cycles with upwards fining of the sediments. There are sometimes coarse conglomerates or breccias at the bottom of each cycle, which gradually evolve upwards into sandstone and shale/mudstone. Flysch typically consists of a sequence of shales rhythmically interbedded with thin, hard, graywacke-like sandstones. Typically the shales do not contain many fossils, while the coarser sandstones often have fractions of micas and glauconite. Tectonics In a continental collision, a subducting tectonic plate pushes on the plate above it, making the rock fold, often to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |