|
Driller's Depth
The original depth recorded while drilling an oil or gas well is known as the driller's depth. The problem Since there is not a single reference or measurement system for calculating the depth in sub-surface environments, two engineers talking about a single drilling might give different answers when asked to give a measurement of depth. The two main depth references used in the "downhole" (i.e. sub-surface) environment are driller's depths and logger's depths (also called wireline logger's depths). These measurement systems are recorded quite differently and logger's depths are generally considered the more accurate of the two: * Driller's depth measurement is tied to drilling operations and other closely associated activities such as logging while drilling), measurement while drilling, and coring. * Driller's depth is always recorded, and it constitutes the primary depth system, unless it is later superseded by a more accurate measurement such as the depth from an open- or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wireline Logging
Well logging, also known as borehole logging is the practice of making a detailed record (a ''well log'') of the geologic formations penetrated by a borehole. The log may be based either on visual inspection of samples brought to the surface (''geological'' logs) or on physical measurements made by instruments lowered into the hole (''geophysical'' logs). Some types of geophysical well logs can be done during any phase of a well's history: drilling, completing, producing, or abandoning. Well logging is performed in boreholes drilled for the oil and gas, groundwater, mineral and geothermal exploration, as well as part of environmental and geotechnical studies. Wireline logging The oil and gas industry uses wireline logging to obtain a continuous record of a formation's rock properties. Wireline logging can be defined as being "The acquisition and analysis of geophysical data performed as a function of well bore depth, together with the provision of related services." Note ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drill String
A drill string on a drilling rig is a column, or string, of drill pipe that transmits drilling fluid (via the mud pumps) and torque (via the kelly drive or top drive) to the Well drilling#Drill bits in mechanical drilling, drill bit. The term is loosely applied to the assembled collection of the smuggler pool, drill collars, tools and drill bit. The drill string is hollow so that drilling fluid can be pumped down through it and circulated back up the Annulus (oil well), annulus (the void between the drill string and the casing/open hole). Drill string components The drill string is typically made up of three sections: * Bottom hole assembly (BHA) * Transition pipe, which is often heavyweight drill pipe (HWDP) * Drill pipe Bottom hole assembly (BHA) The Bottom Hole Assembly (BHA) is made up of: a drill bit#Well drilling bits, drill bit, which is used to break up the rock Geologic formation, formations; drill collars, which are heavy, thick-walled tubes used to apply we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drill Collar
The shaft collar is a simple, yet important, machine component found in many power transmission applications, most notably motors and gearboxes. The collars are used as mechanical stops, locating components, and bearing faces. The simple design lends itself to easy installation. Set screw style The first mass-produced shaft collars were set screw collars and were used primarily on line shafting in early manufacturing mills. These early shaft collars were solid ring types, employing square-head set screws that protruded from the collar. Protruding screws proved to be a problem because they could catch on a worker's clothing while rotating on a shaft, pulling the worker into the machinery. Shaft collars saw few improvements until 1910 through 1911, when William G. Allen and Howard T. Hallowell, Sr, working independently, introduced commercially viable hex socket head set screws, and Hallowell patented a shaft collar with this safety-style set screw. His safety set collar was soon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drilling Rig
A drilling rig is an integrated system that drills wells, such as oil or water wells, or holes for piling and other construction purposes, into the earth's subsurface. Drilling rigs can be massive structures housing equipment used to drill water wells, oil wells, or natural gas extraction wells, or they can be small enough to be moved manually by one person and such are called augers. Drilling rigs can sample subsurface mineral deposits, test rock, soil and groundwater physical properties, and also can be used to install sub-surface fabrications, such as underground utilities, instrumentation, tunnels or wells. Drilling rigs can be mobile equipment mounted on trucks, tracks or trailers, or more permanent land or marine-based structures (such as oil platforms, commonly called 'offshore oil rigs' even if they don't contain a drilling rig). The term "rig" therefore generally refers to the complex equipment that is used to penetrate the surface of the Earth's crust. Small to medi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
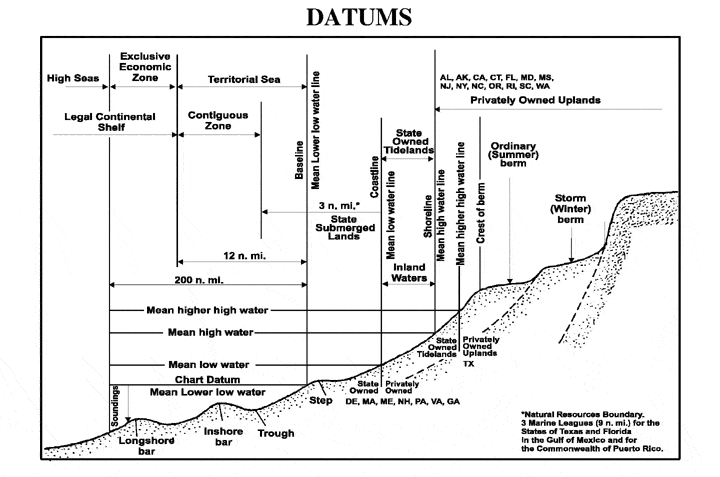
Chart Datum
A chart datum is the water level surface serving as origin of depths displayed on a nautical chart. A chart datum is generally derived from some tidal phase, in which case it is also known as a tidal datum. Common chart datums are ''lowest astronomical tide'' (LAT)Australian Bureau of MeteorologNational Tide Centre Glossary(retrieved 30 April 2013) and ''mean lower low water'' (MLLW). In non-tidal areas, e.g. the Baltic Sea, mean sea level (MSL) is used. A chart datum is a type of vertical datum and must not be confused with the horizontal datum for the chart. Definitions The following tidal phases are commonly used in the definition of chart datums. Lowest astronomical tide ''Lowest astronomical tide'' (LAT) is defined as the lowest tide level which can be predicted to occur under average meteorological conditions and under any combination of astronomical conditions. Many national charting agencies, including the United Kingdom Hydrographic Office and the Australian Hydrog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lowest Astronomical Tide
A chart datum is the water level surface serving as origin of depths displayed on a nautical chart. A chart datum is generally derived from some tidal phase, in which case it is also known as a tidal datum. Common chart datums are ''lowest astronomical tide'' (LAT)Australian Bureau of MeteorologNational Tide Centre Glossary(retrieved 30 April 2013) and ''mean lower low water'' (MLLW). In non-tidal areas, e.g. the Baltic Sea, mean sea level (MSL) is used. A chart datum is a type of vertical datum and must not be confused with the horizontal datum for the chart. Definitions The following tidal phases are commonly used in the definition of chart datums. Lowest astronomical tide ''Lowest astronomical tide'' (LAT) is defined as the lowest tide level which can be predicted to occur under average meteorological conditions and under any combination of astronomical conditions. Many national charting agencies, including the United Kingdom Hydrographic Office and the Australian Hydr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mean Sea Level
There are several kinds of mean in mathematics Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics ..., especially in statistics. Each mean serves to summarize a given group of data, often to better understand the overall value (magnitude (mathematics), magnitude and sign (mathematics), sign) of a given data set. For a data set, the ''arithmetic mean'', also known as "arithmetic average", is a measure of central tendency of a finite set of numbers: specifically, the sum of the values divided by the number of values. The arithmetic mean of a set of numbers ''x''1, ''x''2, ..., x''n'' is typically denoted using an overhead bar, \bar. If the data set were based on a series of observations obtained by sampling (statistics), sampling from a statistical population, the arithmetic mean is th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drill Pipe
Drill pipe, is hollow, thin-walled, steel or aluminium alloy piping that is used on drilling rigs. It is hollow to allow drilling fluid to be pumped down the hole through the bit and back up the annulus. It comes in a variety of sizes, strengths, and wall thicknesses, but is typically 27 to 32 feet in length (Range 2). Longer lengths, up to 45 feet, exist (Range 3). Background Drill stems must be designed to transfer drilling torque for combined lengths that often exceed several miles down into the Earth's crust, and also must be able to resist pressure differentials between inside and outside (or vice versa), and have sufficient strength to suspend the total weight of deeper components. For deep wells this requires tempered steel tubes that are expensive, and owners spend considerable efforts to reuse them after finishing a well. A used drill stem is inspected on site, or off location. Ultrasonic testing and modified instruments similar to the spherometer are used at inspection ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galling
Galling is a form of wear caused by adhesion between sliding surfaces. When a material galls, some of it is pulled with the contacting surface, especially if there is a large amount of force compressing the surfaces together. Galling is caused by a combination of friction and adhesion between the surfaces, followed by slipping and tearing of crystal structure beneath the surface. This will generally leave some material stuck or even friction welded to the adjacent surface, whereas the galled material may appear gouged with balled-up or torn lumps of material stuck to its surface. Galling is most commonly found in metal surfaces that are in sliding contact with each other. It is especially common where there is inadequate lubrication between the surfaces. However, certain metals will generally be more prone to galling, due to the atomic structure of their crystals. For example, aluminium is a metal that will gall very easily, whereas annealed (softened) steel is slightly mor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |