|
Dream Memories Of Tao’an
Dream Memories of Tao'an (陶庵梦忆, Táo ān mèng yì) is a collection of autobiographical essays written by Ming dynasty scholar and prolific writer Zhang Dai. It is considered one of Zhang Dai's most famous works and a summit of xiaopin style essays in the late Ming dynasty. Background Zhang Dai was born into an esteemed and cultured family. He led a comfortable and refined life in his early years. Following the Jiashen Incident that overthrown the Ming dynasty, Zhang Dai served as an aide to Prince of Lu and participated in efforts to restore the Ming dynasty. After the fall of the Southern Ming, Zhang Dai's family fortune was depleted. He retreated to the mountains and spent his later years enduring poverty and hardship. Dream Memories of Tao'an was written during this period, although it wasn't published until 1775, forty years into the Qianlong reign. Title and content The book takes its name from the concept of dreams. Zhang Dai confessed in the preface tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ming Dynasty
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol Empire, Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last orthodox dynasty of China ruled by the Han Chinese, Han people, the majority ethnic group in China. Although the primary capital of Beijing fell in 1644 to a rebellion led by Li Zicheng (who established the short-lived Shun dynasty), numerous rump state, rump regimes ruled by remnants of the House of Zhu, Ming imperial family—collectively called the Southern Ming—survived until 1662. The Ming dynasty's founder, the Hongwu Emperor (r. 1368–1398), attempted to create a society of self-sufficient rural communities ordered in a rigid, immobile system that would guarantee and support a permanent class of soldiers for his dynasty: the empire's standing army exceeded one million troops and the naval history of China, navy's dockyards in Nanjin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xiaopin (literary Genre)
In Chinese literature, xiaopin (小品, Wade-Giles: ''hsiao-p'in'') is a form of short essay, usually non-fictional, and usually being exclusively composed in prose.Mair 2001. "Introduction: The Origins and Impact of Literati Culture", paragraph 21. The form is comparable to that of ''Tsurezuregusa'' by the Japanese monk Yoshida Kenkō. The genre flourished in the late Ming and early Qing dynasties.Mair 2001. "Introduction: The Origins and Impact of Literati Culture", paragraph 19. Notable practitioners The following authors are considered among the most notable historical practitioners of the genre:Mair 2001. "Introduction: The Origins and Impact of Literati Culture", paragraph 22. * Gui Youguang (1506-1571) * Lu Shusheng (1509-1605) * Xu Wei (1521-1593) * Li Zhi (1527-1602) * Tu Long (1542-1605) * Chen Jiru (1558-1639) * Yuan Zongdao (1569-1600) * Yuan Hongdao (1568-1610) * Yuan Zhongdao (1570-1624) * Zhong Xing (1574-1624) * Li Liufang (1575-1629) * Wang Siren (1575-1646) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jiashen Incident
The Jiashen Incident (), also known as the Battle of Beijing, took place between February and April 1644 in the areas surrounding Beijing, and was fought between forces of the Ming dynasty and the Shun dynasty. It eventually resulted in the collapse of the Ming dynasty. Remnants of the imperial House of Zhu, whose regime is known as the Southern Ming dynasty in historiography, would continue to rule parts of southern China until 1662. Li Zicheng led his rebel army to attack the Ming capital Beijing from two directions (north and south). The eunuch official Du Zhizhi (杜之秩) ordered the Ming forces defending Beijing to open the city gates and let Li Zicheng's army in. After the fall of Beijing, the last Ming ruler, the Chongzhen Emperor, committed suicide by hanging himself on a tree near the Forbidden City. No actual battle was fought in Beijing itself as the rebels marched into the capital unopposed, and even after occupying Beijing, the rebels did not face any resistance. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhu Yihai
Zhu Yihai (; 1618–1662), courtesy name Juchuan (巨川), art name Hengshan (恆山) and Changshizi (常石子), was a regent of the Southern Ming from 1645 to 1653. Early life Zhu Yihai was born in 1618, during the 46th year of the reign of the Wanli Emperor of the Ming dynasty. A son of Zhu Shouyong, he was a ninth-generation descendant (the same generation as the Taichang Emperor) of Zhu Tan, Prince Huang of Lu, tenth son of the Hongwu Emperor. The mansion of the Prince of Lu was located at Yanzhou. The Qing forces had attacked Yanzhou and destroyed the mansion. At that time, the peerage of Prince of Lu was succeeded by Zhu Yihai's eldest brother, Zhu Yipai. After the Qing invaded, Zhu Yipai committed suicide along with two of his brothers, Zhu Yixing (朱以洐) and Zhu Yijiang (朱以江). After his brother's suicide, Zhu Yihai was enfeoffed as the 11th Prince of Lu by the Chongzhen Emperor. After four days he succeeded his peerage, Li Zicheng attacked Beijing and he fl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transition From Ming To Qing
The transition from Ming to Qing, alternatively known as Ming–Qing transition or the Manchu conquest of China, from 1618 to 1683, saw the transition between two major dynasties in Chinese history. It was a decades-long conflict between the emerging Qing dynasty, the incumbent Ming dynasty, and several smaller factions (like the Shun dynasty and Xi dynasty). It ended with the consolidation of Qing rule, and the fall of the Ming and several other factions. Overview The transition from the Ming to Qing was a decades-long period of conflict between: # the Qing dynasty, established by the Manchu clan Aisin Gioro in contemporary Northeast China; # the Ming dynasty, the incumbent dynasty led by the Zhu clan; # and various other rebel powers in China, such as the short-lived Xi dynasty led by Zhang Xianzhong and the short-lived Shun dynasty led by Li Zicheng. Leading up to the Qing, in 1618, the Later Jin khan Nurhaci commissioned a document entitled the Seven Grievances, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Ming
The Southern Ming (), also known as the Later Ming (), officially the Great Ming (), was an imperial dynasty of China and a series of rump states of the Ming dynasty that came into existence following the Jiashen Incident of 1644. Shun forces led by Li Zicheng captured Beijing and the Chongzhen Emperor committed suicide. The Ming general Wu Sangui then opened the gates of the Shanhai Pass in the eastern section of the Great Wall to the Qing banners, in hope of using them to annihilate the Shun forces. Ming loyalists fled to Nanjing, where they enthroned Zhu Yousong as the Hongguang Emperor, marking the start of the Southern Ming. The Nanjing regime lasted until 1645, when Qing forces captured Nanjing. Zhu fled before the city fell, but was captured and executed shortly thereafter. Later figures continued to hold court in various southern Chinese cities, although the Qing considered them to be pretenders. The Nanjing regime lacked the resources to pay and supply its soldiers, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qianlong Emperor
The Qianlong Emperor (25 September 17117 February 1799), also known by his temple name Emperor Gaozong of Qing, born Hongli, was the fifth Emperor of the Qing dynasty and the fourth Qing emperor to rule over China proper, reigning from 1735 to 1796. The fourth son of the Yongzheng Emperor, he reigned officially from 11 October 1735 to 8 February 1796. In 1796, he abdicated in favour of his son, the Jiaqing Emperor, out of filial piety towards his grandfather, the Kangxi Emperor, who ruled for 61 years, so that he not officially usurp him as the longest-reigning emperor. Despite his retirement, however, the Qianlong Emperor retained ultimate power as the Emperor Emeritus until his death in 1799, making him one of the longest-reigning monarchs in history, and dying at the age of 87, one of the longest-lived. As a capable and cultured ruler inheriting a thriving empire, during his long reign, the Qing Empire reached its most splendid and prosperous era, boasting a large popul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kang-i Sun Chang
Kang-i Sun Chang (born Sun K'ang-i, ; 21 February 1944), is a Chinese-born American sinologist. She is a scholar of classical Chinese literature. She is the inaugural Malcolm G. Chace Professor, and former chair of the Department of East Asian Languages and Literatures at Yale University. Early life and education Sun K'ang-i was born on 21 February 1944 in Beijing. Her father Sun Yü-kuang (孫裕光) was from Tianjin, and her mother Ch'en Yü-chen (陳玉真) was born in Kaohsiung, Taiwan. The couple met when they were both studying in Japan, and they later moved to Beijing, where Sun taught at Peking University. In 1946, Peking University was unable to pay its employees due to hyperinflation. Influenced by his close friend (張我軍), later a leading literary figure and the father of archaeologist Kwang-chih Chang, Sun Yü-kuang decided to follow Chang and move to Taiwan; Kang-i was two years old at the time. In 1950, Sun was arrested by the Kuomintang (Nationalists) during ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Connoisseur
A connoisseur ( French traditional, pre-1835, spelling of , from Middle-French , then meaning 'to be acquainted with' or 'to know somebody/something') is a person who has a great deal of knowledge about the fine arts; who is a keen appreciator of cuisines, fine wines, and other gourmet products; or who is an expert judge in matters of taste. In many areas, the term now has an air of pretension, and may be used in a partly ironic sense. In the art trade, however, expert connoisseurship remains a crucial skill for the identification and attribution to individual artists of works by the style and technique, where documentary evidence of provenance is lacking. The situation in the wine trade is similar, for example in assessing the potential for ageing in a young wine through wine tasting. Connoisseurship in art "The ability to tell almost instinctively who painted a picture is defined ... as connoisseurship". Connoisseurs evaluate works of art on the basis of their experie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Lake
West Lake (; ) is a freshwater lake in Hangzhou, China. It is divided into five sections by three causeways. There are numerous temples, pagodas, gardens, and natural/artificial islands within the lake. Gushan (孤山) is the largest natural island and three artificial islands: Xiaoyingzhou (小瀛洲), Huixin Pavilion (湖心亭), and Ruan Gongdun (阮公墩) stand at the middle of the lake. Leifeng Pagoda (雷峰塔) and Baochu Pagoda (保俶塔) are separated by the lake. Mirroring each other, the basic pattern of "one mountain, two towers, three islands, three banks, and five lakes" is formed. West Lake is located at No. 1 Longjing Road, Xihu District, Hangzhou City, Zhejiang Province, in the west of Hangzhou City. The total area of the scenic spot is 49 square kilometers, the catchment area is 21.22 square kilometers, and the lake area is 6.38 square kilometers. West Lake has influenced poets and painters throughout Chinese history for its natural beauty and historic r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
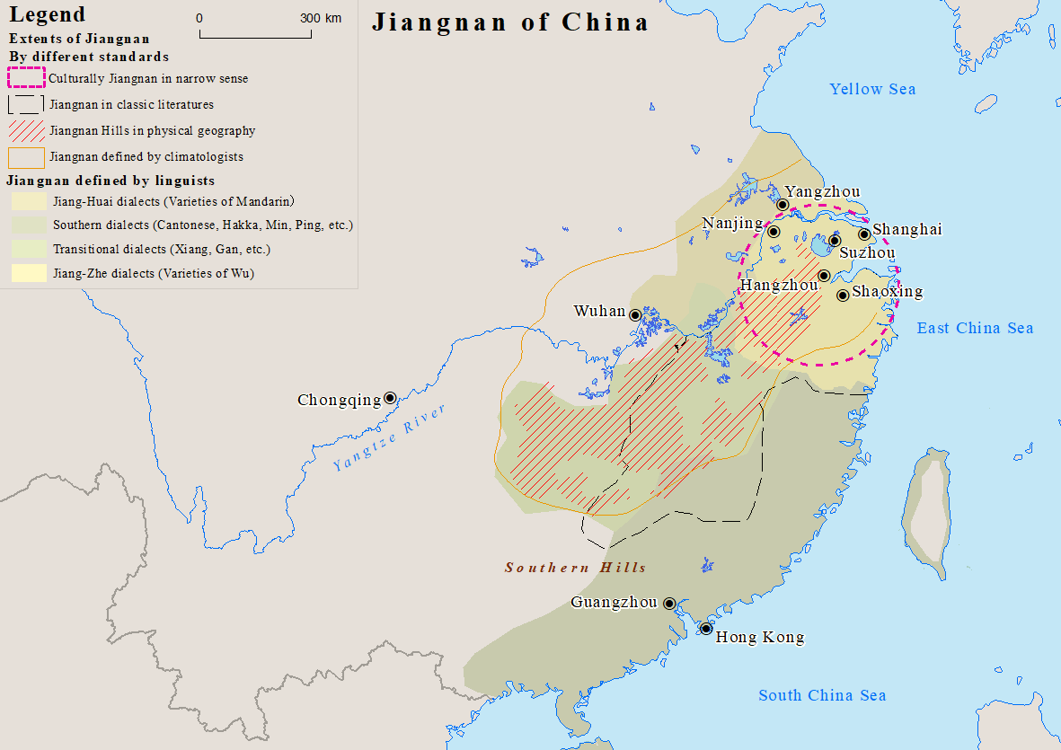
Jiangnan
Jiangnan or Jiang Nan (; formerly romanized Kiang-nan, literally "South of the River" meaning "South of the Yangtze") is a geographic area in China referring to lands immediately to the south of the lower reaches of the Yangtze River, including the southern part of its delta. The region encompasses the city of Shanghai, the southern part of Jiangsu Province, the southeastern part of Anhui Province, the northern part of Jiangxi Province and the northern part of Zhejiang Province. The most important cities in the area include Anqing, Changzhou, Hangzhou, Nanjing, Ningbo, Shaoxing, Suzhou, Wuxi, Wenzhou, and Zhenjiang. Jiangnan has long been regarded as one of the most prosperous regions in China due to its wealth in trade and very high human development. Most people of the region speak Wu Chinese dialects as their native languages. Etymology The word Jiangnan is based on the Chinese name for the Yangtze, ''Cháng Jiāng'', and ''nán'' meaning "south." In the 19th century, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.png)