|
Double Hammer
A double hammer is a forging implement used in metallurgy. It operates on puddle balls and blooms by hitting both sides at the same time. Double hammers are made of two blocks attached to rollers which facilitate opposing movement along a set of rails. Double hammers are normally operated by three people at a time: one holding the instrument in place and the other two moving the blocks back and forth. References {{reflist Metalworking tools ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forging
Forging is a manufacturing process involving the shaping of metal using localized compressive forces. The blows are delivered with a hammer (often a power hammer) or a die. Forging is often classified according to the temperature at which it is performed: cold forging (a type of cold working), warm forging, or hot forging (a type of hot working). For the latter two, the metal is heated, usually in a forge. Forged parts can range in weight from less than a kilogram to hundreds of metric tons.Degarmo, p. 389 Forging has been done by smiths for millennia; the traditional products were kitchenware, hardware, hand tools, edged weapons, cymbals, and jewellery. Since the Industrial Revolution, forged parts are widely used in mechanisms and machines wherever a component requires high strength; such forgings usually require further processing (such as machining) to achieve a finished part. Today, forging is a major worldwide industry. History Forging is one of the oldest known me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metallurgy
Metallurgy is a domain of materials science and engineering that studies the physical and chemical behavior of metallic elements, their inter-metallic compounds, and their mixtures, which are known as alloys. Metallurgy encompasses both the science and the technology of metals; that is, the way in which science is applied to the production of metals, and the engineering of metal components used in products for both consumers and manufacturers. Metallurgy is distinct from the craft of metalworking. Metalworking relies on metallurgy in a similar manner to how medicine relies on medical science for technical advancement. A specialist practitioner of metallurgy is known as a metallurgist. The science of metallurgy is further subdivided into two broad categories: chemical metallurgy and physical metallurgy. Chemical metallurgy is chiefly concerned with the reduction and oxidation of metals, and the chemical performance of metals. Subjects of study in chemical metallurgy include mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
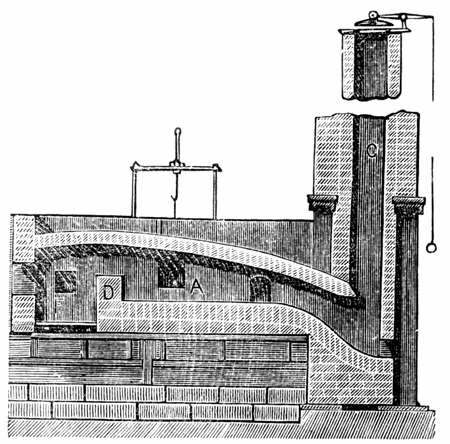
Puddling (metallurgy)
Puddling is the process of converting pig iron to bar (wrought) iron in a coal fired reverberatory furnace. It was developed in England during the 1780s. The molten pig iron was stirred in a reverberatory furnace, in an oxidizing environment, resulting in wrought iron. It was one of the most important processes of making the first appreciable volumes of valuable and useful bar iron (malleable wrought iron) without the use of charcoal. Eventually, the furnace would be used to make small quantities of specialty steels. Though it was not the first process to produce bar iron without charcoal, puddling was by far the most successful, and replaced the earlier potting and stamping processes, as well as the much older charcoal finery and bloomery processes. This enabled a great expansion of iron production to take place in Great Britain, and shortly afterwards, in North America. That expansion constitutes the beginnings of the Industrial Revolution so far as the iron industry is conc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bloomery
A bloomery is a type of metallurgical furnace once used widely for smelting iron from its oxides. The bloomery was the earliest form of smelter capable of smelting iron. Bloomeries produce a porous mass of iron and slag called a ''bloom''. The mix of slag and iron in the bloom, termed ''sponge iron'', is usually consolidated and further forged into wrought iron. Blast furnaces, which produce pig iron, have largely superseded bloomeries. Process A bloomery consists of a pit or chimney with heat-resistant walls made of earth, clay, or stone. Near the bottom, one or more pipes (made of clay or metal) enter through the side walls. These pipes, called ''tuyeres'', allow air to enter the furnace, either by natural draught or forced with bellows or a trompe. An opening at the bottom of the bloomery may be used to remove the bloom, or the bloomery can be tipped over and the bloom removed from the top. The first step taken before the bloomery can be used is the preparat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Wiley & Sons
John Wiley & Sons, Inc., commonly known as Wiley (), is an American multinational publishing company founded in 1807 that focuses on academic publishing and instructional materials. The company produces books, journals, and encyclopedias, in print and electronically, as well as online products and services, training materials, and educational materials for undergraduate, graduate, and continuing education students. History The company was established in 1807 when Charles Wiley opened a print shop in Manhattan. The company was the publisher of 19th century American literary figures like James Fenimore Cooper, Washington Irving, Herman Melville, and Edgar Allan Poe, as well as of legal, religious, and other non-fiction titles. The firm took its current name in 1865. Wiley later shifted its focus to scientific, technical, and engineering subject areas, abandoning its literary interests. Wiley's son John (born in Flatbush, New York, October 4, 1808; died in East Orange, New Je ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |