|
Double-ended Synchronization
For two connected exchanges in a communications network, a double-ended synchronization (also called double-ended control) is a synchronization control scheme in which the phase error signals used to control the clock at one telephone exchange are derived by comparison with the phase of the incoming digital signal A digital signal is a signal that represents data as a sequence of discrete values; at any given time it can only take on, at most, one of a finite number of values. This contrasts with an analog signal, which represents continuous values; ... and the phase of the internal clocks at both exchanges. References * Telecommunications techniques Synchronization {{telecomm-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communications Network
A telecommunications network is a group of nodes interconnected by telecommunications links that are used to exchange messages between the nodes. The links may use a variety of technologies based on the methodologies of circuit switching, message switching, or packet switching, to pass messages and signals. Multiple nodes may cooperate to pass the message from an originating node to the destination node, via multiple network hops. For this routing function, each node in the network is assigned a network address for identification and locating it on the network. The collection of addresses in the network is called the address space of the network. Examples of telecommunications networks include computer networks, the Internet, the public switched telephone network (PSTN), the global Telex network, the aeronautical ACARS network, and the wireless radio networks of cell phone telecommunication providers. Network structure this is the structure of network general, every telecommu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synchronization
Synchronization is the coordination of events to operate a system in unison. For example, the Conductor (music), conductor of an orchestra keeps the orchestra synchronized or ''in time''. Systems that operate with all parts in synchrony are said to be synchronous or ''in sync''—and those that are not are ''Asynchronous system, asynchronous''. Today, time synchronization can occur between systems around the world through satellite navigation signals and other time and frequency transfer techniques. Navigation and railways Time-keeping and synchronization of clocks is a critical problem in long-distance ocean navigation. Before radio navigation and Radionavigation-satellite service, satellite-based navigation, navigators required accurate time in conjunction with astronomical observations to determine History of longitude, how far east or west their vessel traveled. The invention of an accurate marine chronometer revolutionized marine navigation. By the end of the 19th cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phase (waves)
In physics and mathematics, the phase (symbol φ or ϕ) of a wave or other periodic function F of some real variable t (such as time) is an angle-like quantity representing the fraction of the cycle covered up to t. It is expressed in such a scale that it varies by one full turn as the variable t goes through each period (and F(t) goes through each complete cycle). It may be measured in any angular unit such as degrees or radians, thus increasing by 360° or 2\pi as the variable t completes a full period. This convention is especially appropriate for a sinusoidal function, since its value at any argument t then can be expressed as \varphi(t), the sine of the phase, multiplied by some factor (the amplitude of the sinusoid). (The cosine may be used instead of sine, depending on where one considers each period to start.) Usually, whole turns are ignored when expressing the phase; so that \varphi(t) is also a periodic function, with the same period as F, that repeatedly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Error
An error (from the Latin , meaning 'to wander'Oxford English Dictionary, s.v. “error (n.), Etymology,” September 2023, .) is an inaccurate or incorrect action, thought, or judgement. In statistics, "error" refers to the difference between the value which has been computed and the correct value. An error could result in failure or in a Deviation (statistics), deviation from the intended performance or behavior. Human behavior One reference differentiates between "error" and "mistake" as follows: In human behavior the norms or expectations for behavior or its consequences can be derived from the intention of the actor or from the expectations of other individuals or from a social grouping or from social norms. (See deviance (sociology), deviance.) Gaffes and faux pas can be labels for certain instances of this kind of error. More serious departures from social norms carry labels such as misbehavior and labels from the legal system, such as misdemeanor and crime. Departures f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
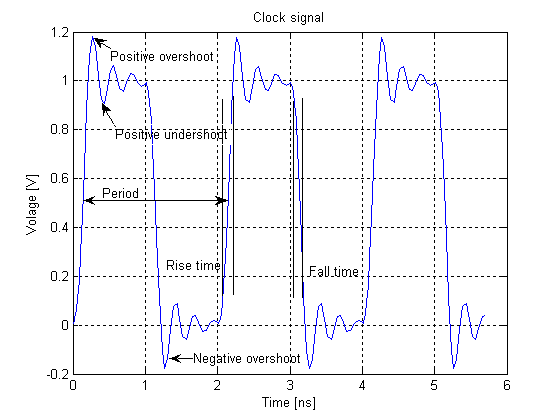
Clock Signal
In electronics and especially synchronous digital circuits, a clock signal (historically also known as ''logic beat'') is an electronic logic signal (voltage or current) which oscillates between a high and a low state at a constant frequency and is used like a metronome to synchronize actions of digital circuits. In a synchronous logic circuit, the most common type of digital circuit, the clock signal is applied to all storage devices, flip-flops and latches, and causes them all to change state simultaneously, preventing race conditions. A clock signal is produced by an electronic oscillator called a clock generator. The most common clock signal is in the form of a square wave with a 50% duty cycle. Circuits using the clock signal for synchronization may become active at either the rising edge, falling edge, or, in the case of double data rate, both in the rising and in the falling edges of the clock cycle. Digital circuits Most integrated circuits (ICs) of suffi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telephone Exchange
A telephone exchange, telephone switch, or central office is a central component of a telecommunications system in the public switched telephone network (PSTN) or in large enterprises. It facilitates the establishment of communication circuits, enabling telephone calls between subscribers. The term "central office" can also refer to a central location for fiber optic equipment for a fiber internet provider. In historical perspective, telecommunication terminology has evolved with time. The term ''telephone exchange'' is often used synonymously with ''central office'', a Bell System term. A central office is defined as the telephone switch controlling connections for one or more central office prefixes. However, it also often denotes the building used to house the inside plant equipment for multiple telephone exchange areas. In North America, the term ''wire center'' may be used to denote a central office location, indicating a facility that provides a telephone with a dial tone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Signal (electronics)
A digital signal is a signal that represents data as a sequence of discrete space, discrete values; at any given time it can only take on, at most, one of a finite number of values. This contrasts with an analog signal, which represents continuity (mathematics), continuous values; at any given time it represents a real number within a continuous range of values. Simple digital signals represent information in discrete bands of levels. All levels within a band of values represent the same information state. In most digital circuits, the signal can have two possible valid values; this is called a binary signal or logic signal. They are represented by two voltage bands: one near a reference value (typically termed as ''ground'' or zero volts), and the other a value near the supply voltage. These correspond to the two values ''zero'' and ''one'' (or ''false'' and ''true'') of the Boolean domain, so at any given time a binary signal represents one binary digit (bit). Because of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telecommunications Techniques
Telecommunication, often used in its plural form or abbreviated as telecom, is the transmission of information over a distance using electronic means, typically through cables, radio waves, or other communication technologies. These means of transmission may be divided into communication channels for multiplexing, allowing for a single medium to transmit several concurrent communication sessions. Long-distance technologies invented during the 20th and 21st centuries generally use electric power, and include the telegraph, telephone, television, and radio. Early telecommunication networks used metal wires as the medium for transmitting signals. These networks were used for telegraphy and telephony for many decades. In the first decade of the 20th century, a revolution in wireless communication began with breakthroughs including those made in radio communications by Guglielmo Marconi, who won the 1909 Nobel Prize in Physics. Other early pioneers in electrical and electronic t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |