|
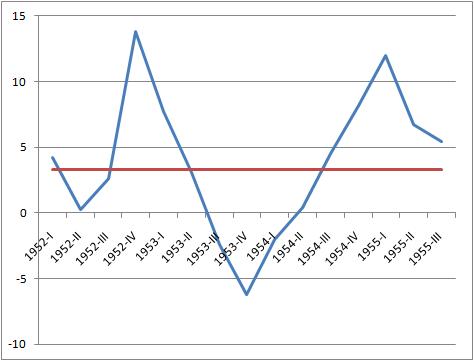
Double-dip Recession
Recession shapes or recovery shapes are used by economists to describe different types of recessions and their subsequent recoveries. There is no specific academic theory or classification system for recession shapes; rather the terminology is used as an informal shorthand to characterize recessions and their recoveries. The most commonly used terms are V-shaped (with variations of square-root shaped, and Nike-swoosh shaped), U-shaped, W-shaped (also known as a double-dip recession), and L-shaped recessions, with the COVID-19 pandemic leading to the K-shaped recession (also known as a two-stage recession). The names derive from the shape the economic data – particularly GDP – takes during the recession and recovery. V-shaped In a V-shaped recession, the economy suffers a sharp but brief period of economic decline with a clearly defined trough, followed by a strong recovery. V-shapes are the normal shape for a recession, as the strength of the economic recovery is typicall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recession
In economics, a recession is a business cycle contraction when there is a general decline in economic activity. Recessions generally occur when there is a widespread drop in spending (an adverse demand shock). This may be triggered by various events, such as a financial crisis, an external trade shock, an adverse supply shock, the bursting of an economic bubble, or a large-scale Anthropogenic hazard, anthropogenic or natural disaster (e.g. a pandemic). In the United States, a recession is defined as "a significant decline in economic activity spread across the market, lasting more than a few months, normally visible in real GDP, real income, employment, industrial production, and wholesale-retail sales." The European Union has adopted a similar definition. In the United Kingdom, a recession is defined as negative economic growth for two consecutive quarters. Governments usually respond to recessions by adopting expansionary macroeconomic policies, such as monetary policy, incr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Bureau Of Economic Research
The National Bureau of Economic Research (NBER) is an American private nonprofit research organization "committed to undertaking and disseminating unbiased economic research among public policymakers, business professionals, and the academic community". The NBER is well known for providing start and end dates for recessions in the United States. Many chairpersons of the Council of Economic Advisers were previously NBER Research Associates, including the former NBER president and Harvard Professor, Martin Feldstein. The NBER's president and CEO is James M. Poterba of MIT. History The NBER was founded in 1920. Its first staff economist, director of research, and one of its founders was American economist Wesley Clair Mitchell. He was succeeded by Malcolm C. Rorty in 1922. The Russian American economist Simon Kuznets, a student of Mitchell, was working at the NBER when the U.S. government recruited him to oversee the production of the first official estimates of national in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
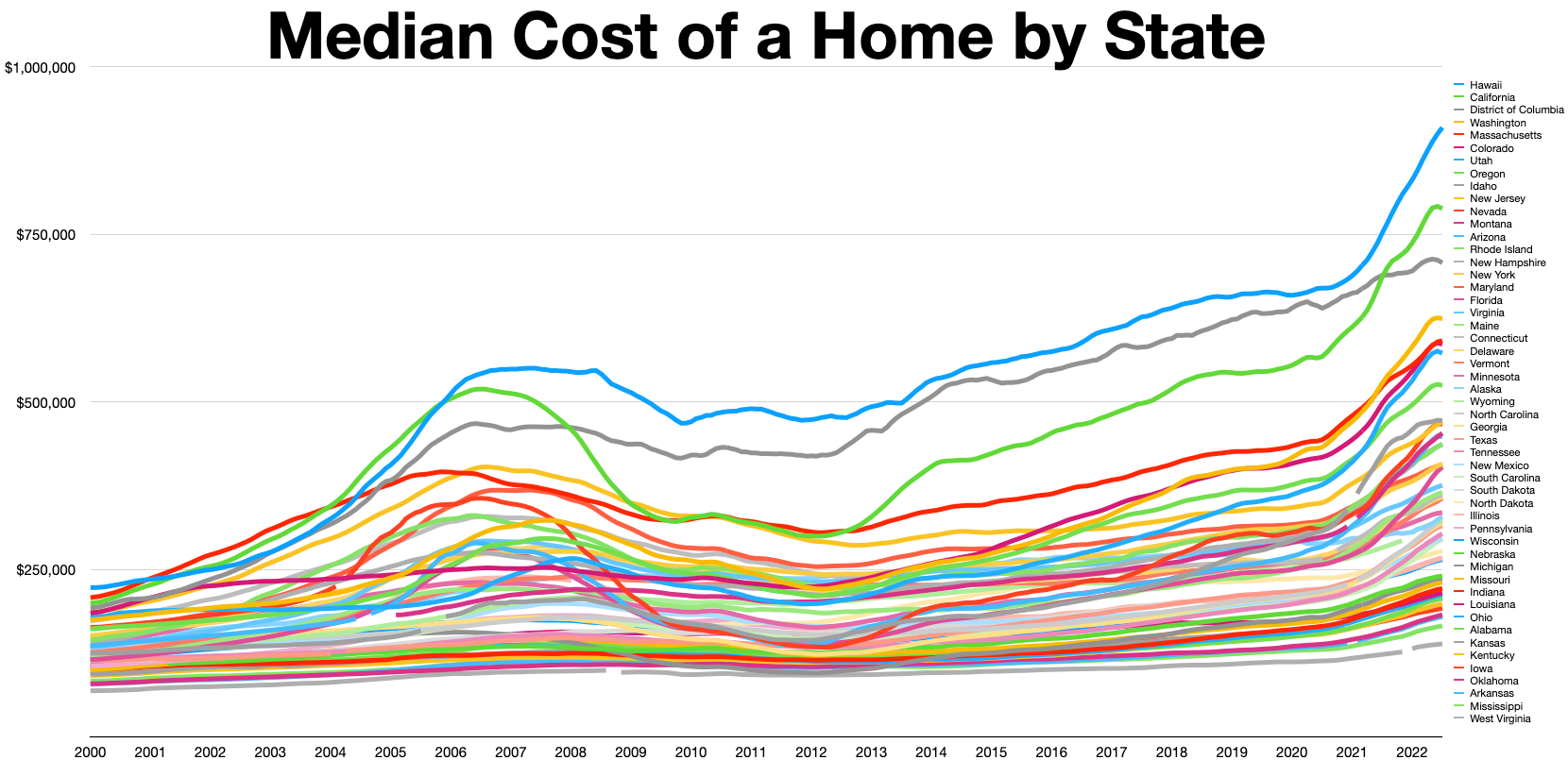
United States Housing Bubble
The 2000s United States housing bubble was a real-estate bubble affecting over half of the U.S. states. It was the impetus for the subprime mortgage crisis. Housing prices peaked in early 2006, started to decline in 2006 and 2007, and reached new lows in 2011. On December 30, 2008, the Case–Shiller home price index reported its largest price drop in its history. The credit crisis resulting from the bursting of the housing bubble is an important cause of the Great Recession in the United States. Increased foreclosure rates in 2006–2007 among U.S. homeowners led to a crisis in August 2008 for the subprime, Alt-A, collateralized debt obligation (CDO), mortgage, credit, hedge fund, and foreign bank markets. In October 2007, Henry Paulson, the U.S. Secretary of the Treasury, called the bursting housing bubble "the most significant risk to our economy". Any collapse of the U.S. housing bubble has a direct impact not only on home valuations, but mortgage markets, home buil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late-2000s Recession
The Great Recession was a period of marked general decline, i.e. a recession, observed in national economies globally that occurred from late 2007 into 2009. The scale and timing of the recession varied from country to country (see map). At the time, the International Monetary Fund (IMF) concluded that it was the most severe economic and financial meltdown since the Great Depression. One result was a serious disruption of normal international relations. The causes of the Great Recession include a combination of vulnerabilities that developed in the financial system, along with a series of triggering events that began with the bursting of the United States housing bubble in 2005–2012. When housing prices fell and homeowners began to abandon their mortgages, the value of mortgage-backed securities held by investment banks declined in 2007–2008, causing several to collapse or be bailed out in September 2008. This 2007–2008 phase was called the subprime mortgage crisis. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
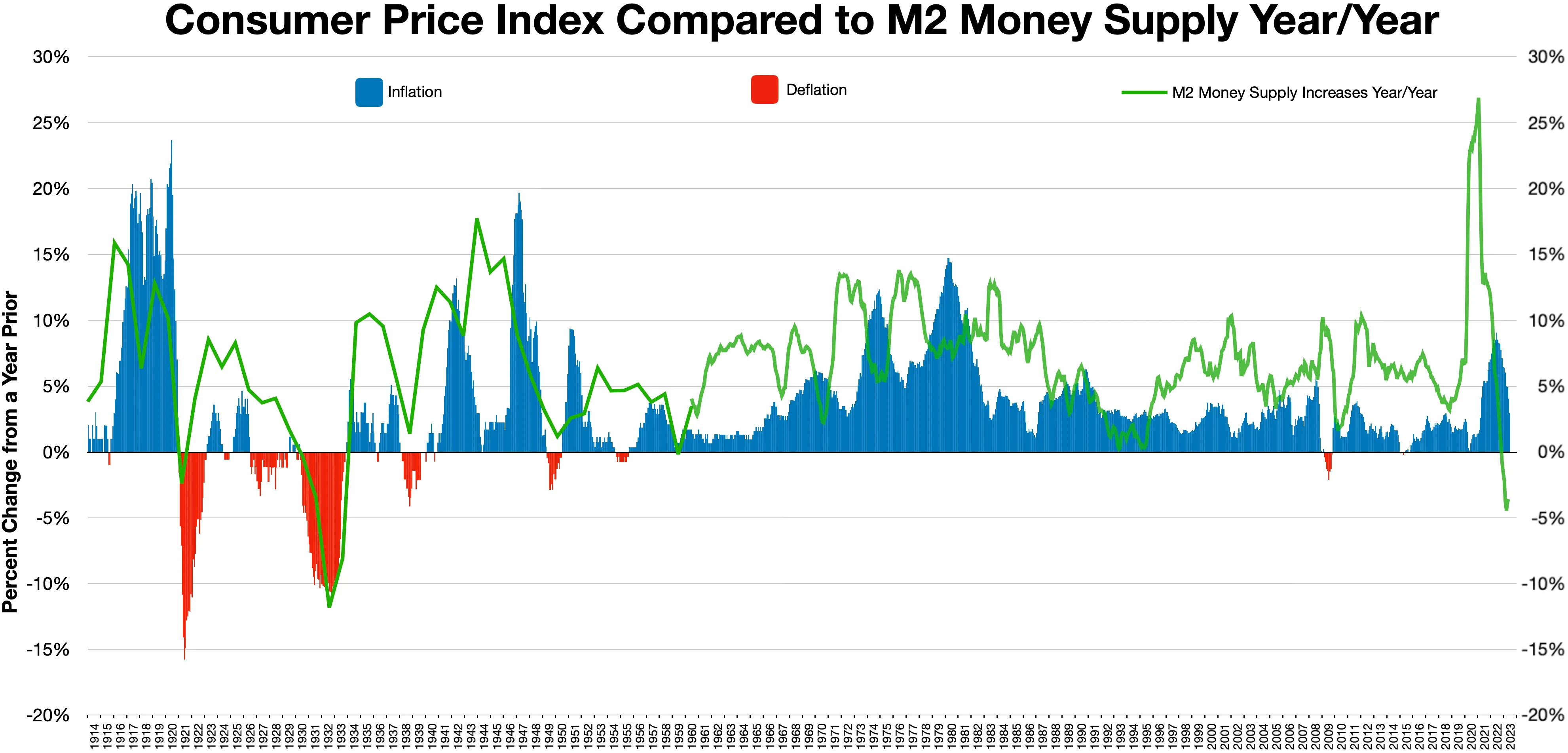
Deflation
In economics, deflation is a decrease in the general price level of goods and services. Deflation occurs when the inflation rate falls below 0% (a negative inflation rate). Inflation reduces the value of currency over time, but sudden deflation increases it. This allows more goods and services to be bought than before with the same amount of currency. Deflation is distinct from disinflation, a slow-down in the inflation rate, i.e. when inflation declines to a lower rate but is still positive. Economists generally believe that a sudden deflationary shock is a problem in a modern economy because it increases the Real versus nominal value (economics), real value of debt, especially if the deflation is unexpected. Deflation may also aggravate recessions and lead to a deflationary spiral. Some economists argue that prolonged deflationary periods are related to the underlying of technological progress in an economy, because as productivity increases (Total factor productivity, TFP), t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economic Bubble
An economic bubble (also called a speculative bubble or a financial bubble) is a period when current asset prices greatly exceed their intrinsic valuation, being the valuation that the underlying long-term fundamentals justify. Bubbles can be caused by overly optimistic projections about the scale and sustainability of growth (e.g. dot-com bubble), and/or by the belief that intrinsic valuation is no longer relevant when making an investment (e.g. Tulip mania). They have appeared in most asset classes, including equities (e.g. Roaring Twenties), commodities (e.g. Uranium bubble), real estate (e.g. 2000s US housing bubble), and even esoteric assets (e.g. Cryptocurrency bubble). Bubbles usually form as a result of either excess liquidity in markets, and/or changed investor psychology. Large multi-asset bubbles (e.g. 1980s Japanese asset bubble and the 2020–21 Everything bubble), are attributed to central banking liquidity (e.g. overuse of the Fed put). In the early stages o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Asset Price Bubble
The was an economic bubble in Japan from 1986 to 1991 in which real estate and stock market prices were greatly inflated. In early 1992, this price bubble burst and Japan's economy stagnated. The bubble was characterized by rapid acceleration of asset prices and overheated economic activity, as well as an uncontrolled money supply and credit expansion.Kunio Okina, Masaaki Shirakawa, and Shigenori Shiratsuka (February 2001):The Asset Price Bubble and Monetary Policy: Japan's Experience in the Late 1980s and the Lessons More specifically, over-confidence and speculation regarding asset and stock prices were closely associated with excessive monetary easing policy at the time.Edgardo Demaestri, Pietro Masci (2003): Financial Crises in Japan and Latin America, Inter-American Development Bank Through the creation of economic policies that cultivated the marketability of assets, eased the access to credit, and encouraged speculation, the Japanese government started a prolonged an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
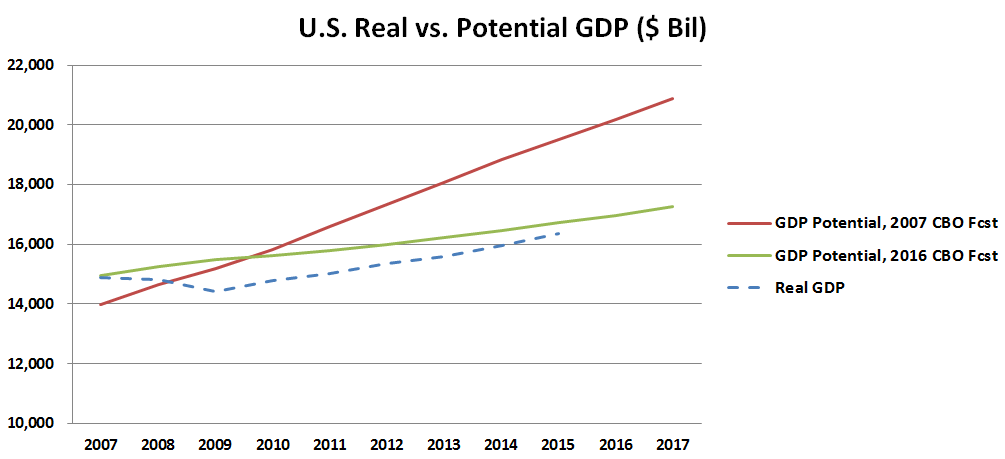
Economic Malaise
Economic stagnation is a prolonged period of slow economic growth (traditionally measured in terms of the GDP growth), usually accompanied by high unemployment. Under some definitions, "slow" means significantly slower than potential growth as estimated by macroeconomists, even though the growth rate may be nominally higher than in other countries not experiencing economic stagnation. Secular stagnation theory The term "secular stagnation" was originally coined by Alvin Hansen in 1938 to "describe what he feared was the fate of the American economy following the Great Depression of the early 1930s: a check to economic progress as investment opportunities were stunted by the closing of the frontier and the collapse of immigration". Warnings similar to secular stagnation theory have been issued after all deep recessions, but they usually turned out to be wrong because they underestimated the potential of existing technologies.Pagano and Sbracia (2014"The secular stagnation hypo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lost Decade (Japan)
The was a period of economic stagnation in Japan caused by the asset price bubble's collapse in late 1991. The term originally referred to the 1990s, but the 2000s (Lost 20 Years, 失われた20年) and the 2010s (Lost 30 Years, 失われた30年) have been included by commentators as the phenomenon continued. From 1991 to 2003, the Japanese economy, as measured by GDP, grew only 1.14% annually, while average real growth rate between 2000 to 2010 was about 1%, both well below other industrialized nations. Debt levels continued to rise in response to the Global Financial Crisis in Great Recession in 2008, the Tōhoku Earthquake and Tsunami and Fukushima Nuclear Disaster in 2011, and with the COVID-19 pandemic, the subsequent recession in 2020 further damaged the Japanese economy. Broadly impacting the entire Japanese economy, over the period of 1995 to 2007, GDP fell from $5.33 trillion to $4.36 trillion in nominal terms, real wages fell around 5%, while the country experien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Depression (economics)
An economic depression is a period of carried long-term economical downturn that is result of lowered economic activity in one major or more national economies. Economic depression maybe related to one specific country were there is some economic crisis that has worsened but most often reflexes historically the American Great Depression and similar economic status that may be recognized as existing at some country, several countries or even in many countries. It is often understood in economics that economic crisis and the following recession that maybe named economic depression are part of economic cycles where slowdown of economy follows the economic growth and vice versa. It is a result of more severe economic problems or a ''downturn'' than the economic recession, recession itself, which is a slowdown in economic activity over the course of the normal business cycle of growing economy. Economic depressions maybe also characterized by their length or duration, and maybe showing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brexit
Brexit (; a portmanteau of "British exit") was the withdrawal of the United Kingdom (UK) from the European Union (EU) at 23:00 GMT on 31 January 2020 (00:00 1 February 2020 CET).The UK also left the European Atomic Energy Community (EAEC or Euratom). The UK is the only sovereign country to have left the EU or the EC. Greenland left the EC (but became an OTC) on 1 February 1985. The UK had been a member state of the EU or its predecessor the European Communities (EC), sometimes of both at the same time, since 1 January 1973. Following Brexit, EU law and the Court of Justice of the European Union no longer have primacy over British laws, except in select areas in relation to Northern Ireland. The European Union (Withdrawal) Act 2018 retains relevant EU law as domestic law, which the UK can now amend or repeal. Under the terms of the Brexit withdrawal agreement, Northern Ireland continues to participate in the European Single Market in relation to goods, and to be a member o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |