|
Don–Volga Portage
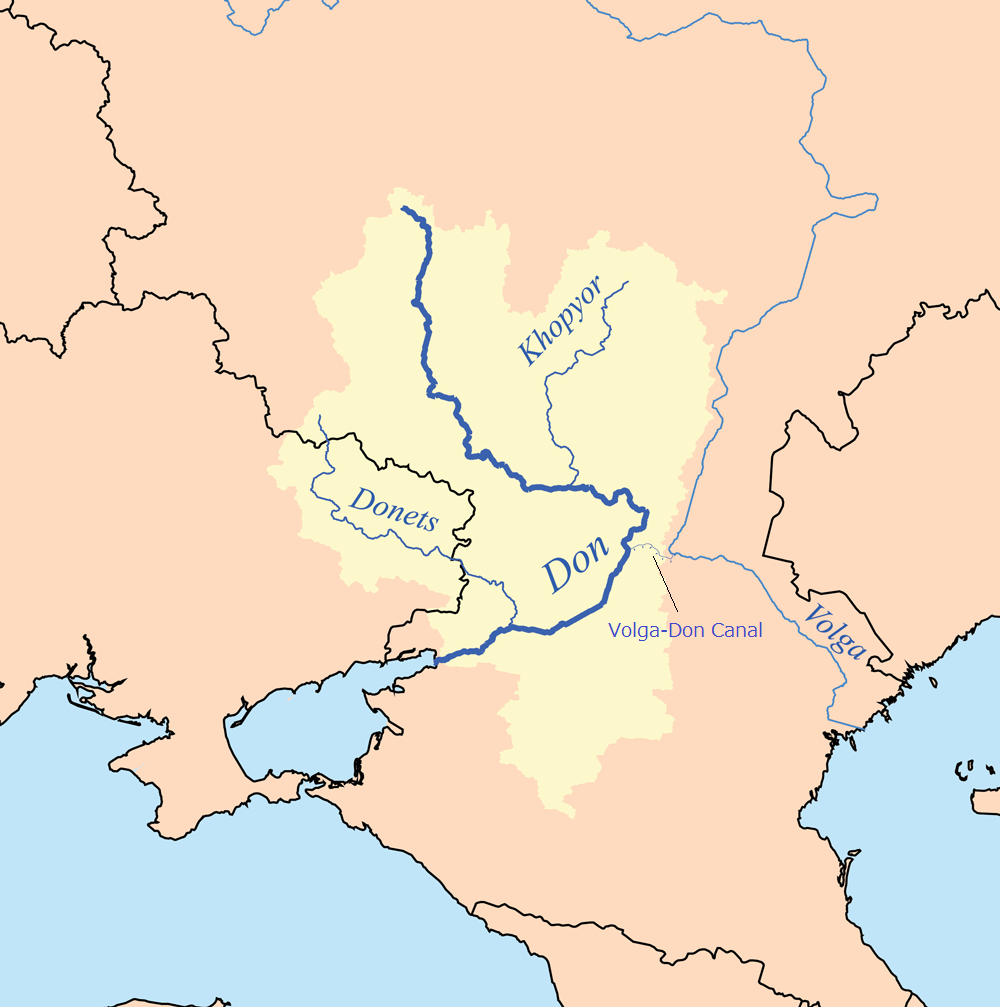
Don–Volga Portage (Russian: ''Волгодонская переволока'', ''Volgodonskaya Perevoloka'') refers to the ancient trade and military route located on the shortest distance (ca. 70 kilometers) between the major rivers Volga and Don, in today's Volgograd Oblast. The portage, where cargo and ships would be drawn over land either manually or by horse-drawn vehicles, was in use from the 1st millennium BCE to 1952 CE, when the Volga–Don Canal was opened. Maps File:Varangian routes.png, Trade routes between the 8th and 11th centuries AD, with the Don Portage controlled by the Khazar fortress Sarkel Sarkel (or Šarkel, literally ''white house'' in the Khazar language was a large limestone-and-brick fortress in the present-day Rostov Oblast of Russia, on the left bank of the lower Don River. It was built by the Khazars with Byzantine ass .... File:Nova Absolutaque Russiae, Moscoviae et Tartariae descriptio (1562).jpg, Volgodonskaya Perevoloka on the map (1562) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Language
Russian (russian: русский язык, russkij jazyk, link=no, ) is an East Slavic languages, East Slavic language mainly spoken in Russia. It is the First language, native language of the Russians, and belongs to the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family. It is one of four living East Slavic languages, and is also a part of the larger Balto-Slavic languages. Besides Russia itself, Russian is an official language in Belarus, Kazakhstan, and Kyrgyzstan, and is used widely as a lingua franca throughout Ukraine, the Caucasus, Central Asia, and to some extent in the Baltic states. It was the De facto#National languages, ''de facto'' language of the former Soviet Union,1977 Soviet Constitution, Constitution and Fundamental Law of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics, 1977: Section II, Chapter 6, Article 36 and continues to be used in public life with varying proficiency in all of the post-Soviet states. Russian has over 258 million total speakers worldwide. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trade Route
A trade route is a logistical network identified as a series of pathways and stoppages used for the commercial transport of cargo. The term can also be used to refer to trade over bodies of water. Allowing goods to reach distant markets, a single trade route contains long-distance arteries, which may further be connected to smaller networks of commercial and noncommercial transportation routes. Among notable trade routes was the Amber Road, which served as a dependable network for long-distance trade. Maritime trade along the Spice Route became prominent during the Middle Ages, when nations resorted to military means for control of this influential route. During the Middle Ages, organizations such as the Hanseatic League, aimed at protecting interests of the merchants and trade became increasingly prominent. In modern times, commercial activity shifted from the major trade routes of the Old World to newer routes between modern nation-states. This activity was sometimes carried ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distinct military uniform. It may consist of one or more military branches such as an army, navy, air force, space force, marines, or coast guard. The main task of the military is usually defined as defence of the state and its interests against external armed threats. In broad usage, the terms ''armed forces'' and ''military'' are often treated as synonymous, although in technical usage a distinction is sometimes made in which a country's armed forces may include both its military and other paramilitary forces. There are various forms of irregular military forces, not belonging to a recognized state; though they share many attributes with regular military forces, they are less often referred to as simply ''military''. A nation's military may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volga
The Volga (; russian: Во́лга, a=Ru-Волга.ogg, p=ˈvoɫɡə) is the List of rivers of Europe#Rivers of Europe by length, longest river in Europe. Situated in Russia, it flows through Central Russia to Southern Russia and into the Caspian Sea. The Volga has a length of , and a catchment area of «Река Волга» , Russian State Water Registry which is more than twice the size of Ukraine. It is also Europe's largest river in terms of average discharge (hydrology), discharge at delta – between and – and of drainage basin. It is widely regarded as the Rivers in Russia, national river of Russia. The hypothetical old Russian state, the Rus' Khaganate, arose along the Volga . Historically, the river served as an important meeting place of various Eurasian civilizations. The river flows in Russia through forests, Fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Don River (Russia)
The Don ( rus, Дон, p=don) is the fifth-longest river in Europe. Flowing from Central Russia to the Sea of Azov in Southern Russia, it is one of Russia's largest rivers and played an important role for traders from the Byzantine Empire. Its basin is between the Dnieper basin to the west, the lower Volga basin immediately to the east, and the Oka basin (tributary of the Volga) to the north. Native to much of the basin were Slavic nomads. The Don rises in the town of Novomoskovsk southeast of Tula (in turn south of Moscow), and flows 1,870 kilometres to the Sea of Azov. The river's upper half ribbles (meanders subtly) south; however, its lower half consists of a great eastern curve, including Voronezh, making its final stretch, an estuary, run west south-west. The main city on the river is Rostov-on-Don. Its main tributary is the Seversky Donets, centred on the mid-eastern end of Ukraine, thus the other country in the overall basin. To the east of a series of thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volgograd Oblast
Volgograd Oblast (russian: Волгогра́дская о́бласть, ''Volgogradskaya oblast'') is a federal subjects of Russia, federal subject (an oblast) of Russia, located in the Volga region, Volga region of Southern Russia. Its administrative center is Volgograd. The population of the oblast was 2,610,161 in the Russian Census (2010), 2010 Census. Formerly known as Stalingrad Oblast, it was given its present name in 1961, when the city of Stalingrad was renamed Volgograd as part of de-Stalinization. Volgograd Oblast borders Rostov Oblast in the southwest, Voronezh Oblast in the northwest, Saratov Oblast in the north, Astrakhan Oblast and the Republic of Kalmykia in the southeast, and has an Kazakhstan–Russia border, international border with Kazakhstan in the east. The two main rivers in European Russia, the Don River (Russia), Don and the Volga River, Volga, run through the oblast and are connected by the Volga–Don Canal. Volgograd Oblast's strategic waterway ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portage
Portage or portaging (Canada: ; ) is the practice of carrying water craft or cargo over land, either around an obstacle in a river, or between two bodies of water. A path where items are regularly carried between bodies of water is also called a ''portage.'' The term comes from French, where means "to carry," as in "portable". In Canada, the term "carrying-place" was sometimes used. Early French explorers in New France and French Louisiana encountered many rapids and cascades. The Native Americans carried their canoes over land to avoid river obstacles. Over time, important portages were sometimes provided with canals with locks, and even portage railways. Primitive portaging generally involves carrying the vessel and its contents across the portage in multiple trips. Small canoes can be portaged by carrying them inverted over one's shoulders and the center strut may be designed in the style of a yoke to facilitate this. Historically, voyageurs often employed tump lines on t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volga–Don Canal
Lenin Volga–Don Shipping Canal (Russian:Волго-Донской судоходный канал имени, ''В. И. Ленина, Volga-Donskoy soudokhodniy kanal imeni V. I. Lenina'', abbreviated ВДСК, ''VDSK'') is a ship canal in Russia. It connects the Volga and the Don at their closest points. Opened in 1952, its length is , of which is through rivers and reservoirs. The canal forms a part of the Unified Deep Water System of European Russia. Together with the lower Volga and the lower Don, the canal provides the shortest navigable connection between the Caspian Sea and the world's oceans, if the Mediterranean is counted, via the Sea of Azov and the Black Sea. History There has been a trade and military route between the Volga and Don rivers from early human history. The existence of fortified settlement Tanais in the Don River delta, present since a time in the Bosporan Kingdom 438 BC– 370 AD, strongly suggests the route may have been notable enough to be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarkel
Sarkel (or Šarkel, literally ''white house'' in the Khazar language was a large limestone-and-brick fortress in the present-day Rostov Oblast of Russia, on the left bank of the lower Don River. It was built by the Khazars with Byzantine assistance in the 830s or 840s. It was named Sarkel, or 'white-house', because of the white limestone bricks used in its construction. Location Sarkel was located on a hill, on the left bank of the Don River. It is currently under water, after the construction of the Tsimlyansk Reservoir. The left bank of the river was much lower, compared to the right, so a lot of it was flooded. Across the Don River from Sarkel, on the right bank, there was located another large Khazar fortress roughly contemporary with Sarkel. This site is known as , although its ancient name is unknown. It is still there, on the much higher right bank, although suffering from erosion because of encroaching water. Construction Sarkel was built to protect the north-western ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trade Routes
A trade route is a Logistics, logistical network identified as a series of pathways and stoppages used for the commercial transport of cargo. The term can also be used to refer to trade over bodies of water. Allowing Good (economics and accounting), goods to reach distant Market (economics), markets, a single trade route contains long-distance Arterial road, arteries, which may further be connected to smaller networks of commercial and noncommercial transportation routes. Among notable trade routes was the Amber Road, which served as a dependable network for long-distance trade. Maritime trade along the Spice Route became prominent during the Middle Ages, when nations resorted to military means for control of this influential route. During the Middle Ages, organizations such as the Hanseatic League, aimed at protecting interests of the merchants and trade became increasingly prominent. In modern history, modern times, commercial activity shifted from the major trade routes of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |