|
Donogh O'Brien, 4th Earl Of Thomond
Donogh O'Brien, 4th Earl of Thomond and Baron Ibrickan, PC (Ire) (died 1624), was a Protestant Irish nobleman and soldier. He fought for Queen Elizabeth during Tyrone's Rebellion and participated in the Siege of Kinsale. He obtained the transfer of County Clare, where most of his lands lay, from the Province of Connacht to that of Munster. He was made president of Munster in 1605. Birth and origins Donogh was born in the 1560s. He was the eldest son of Conor O'Brien, and his second wife, Una O'Brien-Arra. His father was the 3rd Earl of Thomond. His father's first wife had died in 1560. His father's family, the O'Briens, were a Gaelic Irish dynasty that descended from Brian Boru, medieval high king of Ireland. Donogh's mother was a daughter of Turlough O'Brien of Arra, County Tipperary. This Arra is in the north of the Owney and Arra barony around the Arra Hills. His mother's family was a cadet branch of his father's family. His parents married in or after 1560 as his fath ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brian Boru
Brian Boru ( mga, Brian Bóruma mac Cennétig; modern ga, Brian Bóramha; 23 April 1014) was an Irish king who ended the domination of the High King of Ireland, High Kingship of Ireland by the Uí Néill and probably ended Viking invasion/domination of Ireland. Brian built on the achievements of his father, Cennétig mac Lorcain, and especially his elder brother, Mathgamain mac Cennétig, Mathgamain. Brian first made himself king of Munster, then subjugated Kingdom of Leinster, Leinster, eventually becoming High King of Gaelic Ireland, Ireland. He was the founder of the O'Brien dynasty, and is widely regarded as one of the most successful and unifying monarchs in medieval Ireland. With a population of under 500,000 people, Ireland had over 150 kings, with greater or lesser domains. The Uí Néill king Máel Sechnaill mac Domnaill, abandoned by his northern kinsmen of the Cenél nEógain and Cenél Conaill, acknowledged Brian as High King at Athlone in 1002. In the decade that f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
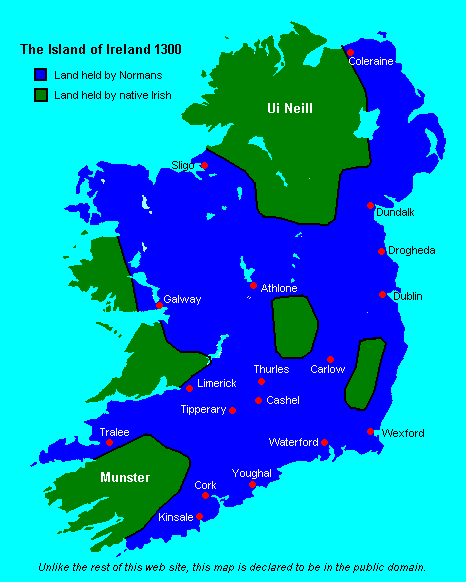
O'Brien Dynasty
The O'Brien dynasty ( ga, label=Classical Irish, Ua Briain; ga, label=Modern Irish, Ó Briain ; genitive ''Uí Bhriain'' ) is a nobility, noble house of Munster, founded in the 10th century by Brian Boru of the Dál gCais (Dalcassians). After becoming King of Munster, through conquest he established himself as ''Ard Rí na hÉireann'' (High King of Ireland). Brian's descendants thus carried the name Ó Briain, continuing to rule the Kingdom of Munster until the 12th century where their territory had shrunk to the Kingdom of Thomond which they would hold for just under five centuries. In total, four Ó Briains ruled in Munster, and two held the High Kingship of Ireland (with opposition). After the partition of Munster into Thomond and the MacCarthy Kingdom of Desmond by Tairrdelbach Ua Conchobair in the 12th century, the dynasty would go on to provide around thirty monarchs of Thomond until 1542. During part of this period in the late 13th century they had a rivalry with the N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earl Of Thomond
Earl of Thomond was an hereditary title in the Peerage of Ireland. It was created twice for the O'Brien dynasty which is an ancient Irish sept native to north Munster. History and background First creation Under the Crown of Ireland Act 1542, King Henry VIII of England was created King of Ireland by the Parliament of Ireland. In consequence, all reigning monarchs and clan chiefs in Ireland were ordered to surrender their native titles in return for peerages. This surrender and regrant offer was conditional upon the adoption of Tudor customs and laws, including pledging allegiance to the Irish Crown and apostatising from the Catholic faith by accepting the articles of the state established Church of Ireland. Through surrender and regrant, the earldom of Thomond was created in 1543 for Murrough O'Brien. He had previously been styled King of Thomond and was descended from the ' or High King of Ireland, Brian Boru. O'Brien was also created Baron Inchiquin, on 1 July 1543. On the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Donough O'Brien, 2nd Earl Of Thomond
Donough O'Brien, 2nd Earl of Thomond ( ga, Donnchadh Ó Briain; died 1 April 1553), also known as "the fat", was the son of Connor O'Brien, King of Thomond and Annabell Burke. He inherited the earldom from his uncle, Murrough O'Brien, by special remainder. O'Brien married Helen Butler, daughter of Piers Butler, 8th Earl of Ormonde and Lady Margaret Fitzgerald. He died on 1 April 1553, after being attacked by his brothers at the family seat of Clonroad. O'Brien's brother Sir Donald was named king of Thomond by the Dalgais, but O'Brien's son, Connor, allied himself with the English and regained control of his lands. Children of Donough O'Brien and Helen Butler: *Margaret O'Brien (d. 1568) married Dermod O'Brien, 2nd Baron Inchiquin he was (also) married to the 2nd Earl of Clanricard according to the Wikipedia entry for him: Richard Burke, 2nd Earl of Clanricarde *Connor O'Brien, 3rd Earl of Thomond (c. 1534 – 1581) *Donal or Daniel *Honora married Teige Macnamara No ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulick Burke, 3rd Earl Of Clanricarde
Ulick Burke, 3rd Earl of Clanricarde (; ; ; ; died 1601), styled Lord Dunkellin (; ) until 1582, was an Irish people, Irish Peerage of Ireland, peer who was the son of Richard Burke, 2nd Earl of Clanricarde and Margaret O'Brien. Career He had long been a rebel against the English Crown, and since the 1560s had instigated the ''Mac an Iarla'' wars in Connaught and Thomond, devastating much of the area, against his father, who was a staunch supporter of Elizabeth I. On his father's death in 1582 it was uncertain who would inherit the title, Ulick or his brother, John. Ulick gained the succession by murdering John and acknowledging the supremacy of the Crown. He remained a loyal subject till his death. Family Burke married Honora Burke, daughter of John Burke, on 25 November 1564 at Athenry, County Galway, Ireland. Their children were: *Sir William Burke (d. 2 Feb 1625), from whom later Earls were descended *Sir Thomas Burke, who married Ursula Malby, daughter of Sir Nichola ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Parliaments Of Ireland ...
This is a list of parliaments of Ireland to 1801. For subsequent parliaments, see the list of parliaments of the United Kingdom. For post-1918 parliaments, see elections in Ireland. Parliaments before 1264 are not currently listed. The Kingdoms of Ireland and Great Britain joined on 1 January 1801. For subsequent Parliaments see the list of Parliaments of the United Kingdom. References * ''A New History of Ireland, Volume IX'', edited by T. W. Moody, F.X. Martin and F.J. Byrne (Clarendon Press 1984), {{Lists of Irish MPs Parliament of Ireland Parliaments In modern politics, and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: representing the electorate, making laws, and overseeing the government via hearings and inquiries. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Partible Succession
Partible inheritance is a system of inheritance in which property is apportioned among heirs. It contrasts in particular with primogeniture, which was common in feudal society and requires that the whole or most of the inheritance passes to the eldest son, and with agnatic seniority, which requires the succession to pass to next senior male. Partible inheritance systems are common ones to be found in legal systems based on both common law and the Napoleonic Code. In the latter case, there may be a further requirement implying division according to a scheme, such as equal shares for legitimate children. Partible inheritance has been common in ancient Celtic and Germanic tribal societies, an example of the latter pattern is the so-called Salic patrimony. Historically speaking, non-partible inheritance has been associated with monarchies and the wish for landed estates to be kept together as units. In the Middle Ages, the partible inheritance systems, for example, of the Merovingi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tanistry
Tanistry is a Gaelic system for passing on titles and lands. In this system the Tanist ( ga, Tánaiste; gd, Tànaiste; gv, Tanishtey) is the office of heir-apparent, or second-in-command, among the (royal) Gaelic patrilineal dynasties of Ireland, Scotland and Mann, to succeed to the chieftainship or to the kingship. The word is preserved in the Republic of Ireland's government, where the prime minister is the ''Taoiseach'' while the deputy prime minister is the ''Tánaiste''. Origins Historically the tanist was chosen from among the heads of the ''roydammna'' or "righdamhna" (literally, those of ''kingly material'') or, alternatively, among all males of the ''sept'', and elected by them in full assembly. The eligibility was based on patrilineal relationship, which meant the electing body and the eligibles were agnates with each other. The composition and the governance of the clan were built upon male-line descent from a similar ancestor. The office was noted from the begi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Normans In Ireland
From the 12th century onwards, a group of Normans invaded and settled in Gaelic Ireland. These settlers later became known as Norman Irish or Hiberno-Normans. They originated mainly among Cambro-Norman families in Wales and Anglo-Normans from England, who were loyal to the Kingdom of England, and the English state supported their claims to territory in the various realms then comprising Ireland. During the High Middle Ages and Late Middle Ages the Hiberno-Normans constituted a feudal aristocracy and merchant oligarchy, known as the Lordship of Ireland. In Ireland, the Normans were also closely associated with the Gregorian Reform of the Catholic Church in Ireland. Over time the descendants of the 12th-century Norman settlers spread throughout Ireland and around the world, as part of the Irish diaspora; they ceased, in most cases, to identify as Norman, Cambro-Norman or Anglo-Norman. The dominance of the Norman Irish declined during the 16th century, after a new English Protest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viscount Fermoy
A viscount ( , for male) or viscountess (, for female) is a title used in certain European countries for a noble of varying status. In many countries a viscount, and its historical equivalents, was a non-hereditary, administrative or judicial position, and did not develop into a hereditary title until much later. In the case of French viscounts, it is customary to leave the title untranslated as vicomte . Etymology The word ''viscount'' comes from Old French (Modern French: ), itself from Medieval Latin , accusative of , from Late Latin "deputy" + Latin (originally "companion"; later Roman imperial courtier or trusted appointee, ultimately count). History During the Carolingian Empire, the kings appointed counts to administer provinces and other smaller regions, as governors and military commanders. Viscounts were appointed to assist the counts in their running of the province, and often took on judicial responsibility. The kings strictly prevented the offices of their coun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maurice Roche, 6th Viscount Fermoy
Maurice may refer to: People *Saint Maurice (died 287), Roman legionary and Christian martyr *Maurice (emperor) or Flavius Mauricius Tiberius Augustus (539–602), Byzantine emperor *Maurice (bishop of London) (died 1107), Lord Chancellor and Lord Keeper of England *Maurice of Carnoet (1117–1191), Breton abbot and saint *Maurice, Count of Oldenburg (fl. 1169–1211) *Maurice of Inchaffray (14th century), Scottish cleric who became a bishop *Maurice, Elector of Saxony (1521–1553), German Saxon nobleman *Maurice, Duke of Saxe-Lauenburg (1551–1612) *Maurice of Nassau, Prince of Orange (1567–1625), stadtholder of the Netherlands *Maurice, Landgrave of Hesse-Kassel or Maurice the Learned (1572–1632) *Maurice of Savoy (1593–1657), prince of Savoy and a cardinal *Maurice, Duke of Saxe-Zeitz (1619–1681) *Maurice of the Palatinate (1620–1652), Count Palatine of the Rhine *Maurice of the Netherlands (1843–1850), prince of Orange-Nassau *Maurice Chevalier (1888–1972), Fre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earl Of Clancarty
Earl of Clancarty is a title that has been created twice in the Peerage of Ireland. History The title was created for the first time in 1658 in favour of Donough MacCarty, 1st Earl of Clancarty, Donough MacCarty, 2nd Viscount Muskerry, of the MacCarthy of Muskerry dynasty. He had earlier represented Cork County (Parliament of Ireland constituency), County Cork in the Irish House of Commons. Lord Clancarty had already been created a baronet in the Baronetage of Nova Scotia in , before he succeeded his father in the viscountcy. The title of Viscount Muskerry had been created in the Peerage of Ireland in 1628 for his father Charles MacCarthy, 1st Viscount Muskerry, Charles MacCarthy. The first Earl Donough MacCarty, 1st Earl of Clancarty, Donough MacCarty was succeeded by his grandson Charles, the second Earl; he was the son of Charles MacCarty, Viscount Muskerry, who was killed during the Second Anglo-Dutch War. Charles, Lord Clancarty died as an infant and was succeeded by his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |