|
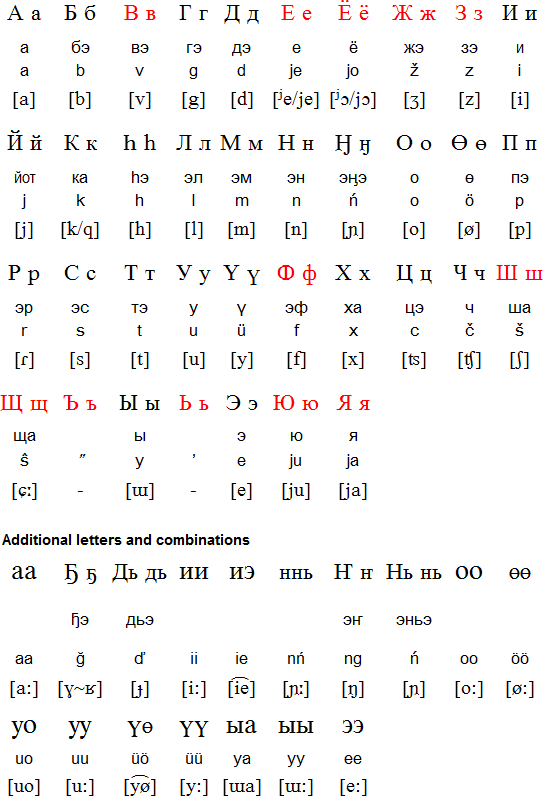
Dolgan Language
The Dolgan language is a Turkic language with around 1,000 speakers, spoken in the Taymyr Peninsula in Russia. The speakers are known as the Dolgans. The word "Dolgan" means 'tribe living on the middle reaches of the river'. This is most likely signifying the geographical location of the Dolgan tribe. The language is very local and restricted to a certain area and has declined in usage over the years. As of 2010 there are only about 1,050 speakers of the language. The language has expressed a few changes since the beginning of its formation, such as alphabet and phrasing terms. The issue as of recently has become the weak integration of this local language within families with mixed marriages. Instead of speaking either of the parents' local languages, the family incorporates Russian as the more dominant language to ease interfamilial and external communication. This results in children learning the language only slightly or as a second language. Over generations, the lang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eighth of Earth's inhabitable landmass. Russia extends across eleven time zones and shares land boundaries with fourteen countries, more than any other country but China. It is the world's ninth-most populous country and Europe's most populous country, with a population of 146 million people. The country's capital and largest city is Moscow, the largest city entirely within Europe. Saint Petersburg is Russia's cultural centre and second-largest city. Other major urban areas include Novosibirsk, Yekaterinburg, Nizhny Novgorod, and Kazan. The East Slavs emerged as a recognisable group in Europe between the 3rd and 8th centuries CE. Kievan Rus' arose as a state in the 9th century, and in 988, it adopted Orthodox Christianity from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grammatical Gender
In linguistics, grammatical gender system is a specific form of noun class system, where nouns are assigned with gender categories that are often not related to their real-world qualities. In languages with grammatical gender, most or all nouns inherently carry one value of the grammatical category called ''gender''; the values present in a given language (of which there are usually two or three) are called the ''genders'' of that language. Whereas some authors use the term "grammatical gender" as a synonym of "noun class", others use different definitions for each; many authors prefer "noun classes" when none of the inflections in a language relate to sex. Gender systems are used in approximately one half of the world's languages. According to one definition: "Genders are classes of nouns reflected in the behaviour of associated words." Overview Languages with grammatical gender usually have two to four different genders, but some are attested with up to 20. #Gender contras ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Declension
In linguistics, declension (verb: ''to decline'') is the changing of the form of a word, generally to express its syntactic function in the sentence, by way of some inflection. Declensions may apply to nouns, pronouns, adjectives, adverbs, and articles to indicate number (e.g. singular, dual, plural), case (e.g. nominative case, accusative case, genitive case, dative case), gender (e.g. masculine, neuter, feminine), and a number of other grammatical categories. Meanwhile, the inflectional change of verbs is called ''conjugation''. Declension occurs in many of the world's languages. It is an important aspect of language families like Quechuan (i.e., languages native to the Andes), Indo-European (e.g. German, Lithuanian, Latvian, Slavic, Sanskrit, Latin, Ancient Greek, Modern Greek, Classical Armenian and Modern Armenian and Kurdish), Bantu (e.g. Zulu, Kikuyu), Semitic (e.g. Modern Standard Arabic), Finno-Ugric (e.g. Hungarian, Finnish, Estonian), and Turkic (e. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Partitive
In linguistics, the partitive is a word, phrase, or case that indicates partialness. Nominal partitives are syntactic constructions, such as "some of the children", and may be classified semantically as either set partitives or entity partitives based on the quantifier and the type of embedded noun used. Partitives should not be confused with '' quantitives'' (also known as pseudopartitives), which often look similar in form, but behave differently syntactically and have a distinct meaning. In many Romance and Germanic languages, nominal partitives usually take the form: DP Det. + ''of'' + [DP Det. + NP">sub>DP Det. + ''of'' + [DP Det. + NPMartí i Girbau, M. N. (2010). The syntax of partitives. where the first determiner is a Quantifier (linguistics), quantifier word, using a prepositional element to link it to the larger set or whole from which that quantity is partitioned. The partitive constructions of the following languages all have the same translation, with a very ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grammatical Person
In linguistics, grammatical person is the grammatical distinction between deictic references to participant(s) in an event; typically the distinction is between the speaker (first person), the addressee ( second person), and others ( third person). A language's set of ''personal'' pronouns are defined by grammatical person, but other pronouns would not. ''First person'' includes the speaker (English: ''I'', ''we'', ''me'', and ''us''), ''second person'' is the person or people spoken to (English: ''you''), and ''third person'' includes all that are not listed above (English: ''he'', ''she'', ''it'', ''they'', ''him'', ''her'', ''them''). It also frequently affects verbs, and sometimes nouns or possessive relationships. Related classifications Number In Indo-European languages, first-, second-, and third-person pronouns are typically also marked for singular and plural forms, and sometimes dual form as well ( grammatical number). Inclusive/exclusive distinction Some oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grammatical Mood
In linguistics, grammatical mood is a grammatical feature of verbs, used for signaling modality. That is, it is the use of verbal inflections that allow speakers to express their attitude toward what they are saying (for example, a statement of fact, of desire, of command, etc.). The term is also used more broadly to describe the syntactic expression of modality – that is, the use of verb phrases that do not involve inflection of the verb itself. Mood is distinct from grammatical tense or grammatical aspect, although the same word patterns are used for expressing more than one of these meanings at the same time in many languages, including English and most other modern Indo-European languages. (See tense–aspect–mood for a discussion of this.) Some examples of moods are indicative, interrogative, imperative, subjunctive, injunctive, optative, and potential. These are all finite forms of the verb. Infinitives, gerunds, and participles, which are non-finite form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grammatical Aspect
In linguistics, aspect is a grammatical category that expresses how an action, event, or state, as denoted by a verb, extends over time. Perfective aspect is used in referring to an event conceived as bounded Boundedness or bounded may refer to: Economics * Bounded rationality, the idea that human rationality in decision-making is bounded by the available information, the cognitive limitations, and the time available to make the decision * Bounded e ... and unitary, without reference to any flow of time during ("I helped him"). Imperfective aspect is used for situations conceived as existing continuously or repetitively as time flows ("I was helping him"; "I used to help people"). Further distinctions can be made, for example, to distinguish states and ongoing actions ( continuous and progressive aspects) from repetitive actions ( habitual aspect). Certain aspectual distinctions express a relation between the time of the event and the time of reference. This is the cas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voice (grammar)
In grammar, the voice of a verb describes the relationship between the action (or state) that the verb expresses and the participants identified by its arguments (subject, object, etc.). When the subject is the agent or doer of the action, the verb is in the active voice. When the subject is the patient, target or undergoer of the action, the verb is said to be in the passive voice. When the subject both performs and receives the action expressed by the verb, the verb is in the middle voice. Voice is sometimes called diathesis. The following pair of examples illustrates the contrast between active and passive voice in English. In sentence (1), the verb form ''ate'' is in the active voice, but in sentence (2), the verb form ''was eaten'' is in the passive voice. Independent of voice, ''the cat'' is the Agent (the doer) of the action of eating in both sentences. # ''The cat ate the mouse.'' # ''The mouse was eaten by the cat.'' In a transformation from an active-voice clause t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Possession (linguistics)
In linguistics, possession is an asymmetric relationship between two constituents, the referent of one of which (the possessor) in some sense possesses (owns, has as a part, rules over, etc.) the referent of the other (the possessed). Possession may be marked in many ways, such as simple juxtaposition of nouns, possessive case, possessed case, construct state (as in Arabic, and Nêlêmwa), or adpositions ( possessive suffixes, possessive adjectives). For example, English uses a possessive clitic, '' 's''; a preposition, ''of''; and adjectives, ''my'', ''your'', ''his'', ''her'', etc. Predicates denoting possession may be formed either by using a verb such as English ''have'' or by other means, such as existential clauses (as is usual in languages such as Russian). Some languages have more than two possessive classes. In Papua New Guinea, for example, Anêm has at least 20 and Amele has 32. Alienable and inalienable There are many types of possession, but a common di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grammatical Number
In linguistics, grammatical number is a grammatical category of nouns, pronouns, adjectives and verb agreement that expresses count distinctions (such as "one", "two" or "three or more"). English and other languages present number categories of singular or plural, both of which are cited by using the hash sign (#) or by the numero signs "No." and "Nos." respectively. Some languages also have a dual, trial and paucal number or other arrangements. The count distinctions typically, but not always, correspond to the actual count of the referents of the marked noun or pronoun. The word "number" is also used in linguistics to describe the distinction between certain grammatical aspects that indicate the number of times an event occurs, such as the semelfactive aspect, the iterative aspect, etc. For that use of the term, see " Grammatical aspect". Overview Most languages of the world have formal means to express differences of number. One widespread distinction, found in English ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grammatical Case
A grammatical case is a category of nouns and noun modifiers ( determiners, adjectives, participles, and Numeral (linguistics), numerals), which corresponds to one or more potential grammatical functions for a nominal group in a wording. In various languages, nominal groups consisting of a noun and its modifiers belong to one of a few such categories. For instance, in English language, English, one says ''I see them'' and ''they see me'': the nominative case, nominative pronouns ''I/they'' represent the perceiver and the accusative case, accusative pronouns ''me/them'' represent the phenomenon perceived. Here, nominative case, nominative and accusative case, accusative are cases, that is, categories of pronouns corresponding to the functions they have in representation. English language, English has largely lost its inflected case system but personal pronouns still have three cases, which are simplified forms of the Nominative case, nominative, Accusative case, accusative and g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Putorana Plateau
The Putorana Plateau () or the Putorana Mountains is a mountainous area in the Russian Federation. It is a large massif or plateau crossed by mountain ranges. The nearest large settlement is Norilsk, where foreign travel is restricted. The city is served by Alykel Airport. The area of the mountains contains some of the largest known nickel deposits in the world. Geography The Putorana Plateau is a high-lying plateau crossed by mountain ranges at the northwestern edge of the Central Siberian Plateau. It is located east of the Yenisei River valley, between 67° and 70° N of latitude, southwest of the Anabar Plateau, north of the Syverma and Tunguska plateaus and south of the North Siberian Lowland.Google Earth The main subranges of the Putorana are the Keta Range, Lontokoisky Kamen, Kharayelakh Range, Chaya-Ayan, Brus Kamen, and Lama Range, among others. The highest mountain in the range system is Mount Kamen which stands above sea level and is also the highest point of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |