|
Distance Measurement
Length measurement, distance measurement, or range measurement (ranging) all refer to the many ways in which length, distance, or range can be measured. The most commonly used approaches are the rulers, followed by transit-time methods and the interferometer methods based upon the speed of light. Surveying is one ancient use of measuring long distances. For tiny objects such as crystals and diffraction gratings, diffraction is used with X-ray light, or even electron beams. Measurement techniques for three-dimensional structures very small in every dimension use specialized instruments such as ion microscopy coupled with intensive computer modeling. These techniques are employed, for example, to measure the tiny features on wafers during the manufacture of chips. Standard rulers The ruler the simplest kind of length measurement tool: lengths are defined by printed marks or engravings on a stick. The metre was initially defined using a ruler before more accurate methods beca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Length
Length is a measure of distance. In the International System of Quantities, length is a quantity with Dimension (physical quantity), dimension distance. In most systems of measurement a Base unit (measurement), base unit for length is chosen, from which all other units are derived. In the International System of Units (SI) system, the base unit for length is the metre. Length is commonly understood to mean the most extended size, dimension of a fixed object. However, this is not always the case and may depend on the position the object is in. Various terms for the length of a fixed object are used, and these include height, which is vertical length or vertical extent, width, breadth, and depth. ''Height'' is used when there is a base from which vertical measurements can be taken. ''Width'' and ''breadth'' usually refer to a shorter dimension than ''length''. ''Depth'' is used for the measure of a third dimension. Length is the measure of one spatial dimension, whereas area ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vacuum
A vacuum (: vacuums or vacua) is space devoid of matter. The word is derived from the Latin adjective (neuter ) meaning "vacant" or "void". An approximation to such vacuum is a region with a gaseous pressure much less than atmospheric pressure. Physicists often discuss ideal test results that would occur in a ''perfect'' vacuum, which they sometimes simply call "vacuum" or free space, and use the term partial vacuum to refer to an actual imperfect vacuum as one might have in a laboratory or in space. In engineering and applied physics on the other hand, vacuum refers to any space in which the pressure is considerably lower than atmospheric pressure. The Latin term ''in vacuo'' is used to describe an object that is surrounded by a vacuum. The ''quality'' of a partial vacuum refers to how closely it approaches a perfect vacuum. Other things equal, lower gas pressure means higher-quality vacuum. For example, a typical vacuum cleaner produces enough suction to reduce air pressur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corner Cube
A corner reflector is a retroreflector consisting of three mutually perpendicular, intersecting flat reflective surfaces. It reflects waves incident from any direction directly towards the source, but translated. The three intersecting surfaces often are triangles (forming a tetrahedron) or may have square shapes. Radar corner reflectors made of metal are used to reflect radio waves from radar sets. Optical corner reflectors, called corner cubes or cube corners, made of three-sided glass prisms, are used in surveying and laser ranging. Principle The incoming ray is reflected three times, once by each surface, which results in a reversal of direction. To see this, the three corresponding normal vectors of the corner's perpendicular sides can be considered to form a basis (a rectangular coordinate system) (''x'', ''y'', ''z'') in which to represent the direction of an arbitrary incoming ray, . When the ray reflects from the first side, say ''x'', the ray's ''x'' compon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beam Splitter
A beam splitter or beamsplitter is an optical instrument, optical device that splits a beam of light into a transmitted and a reflected beam. It is a crucial part of many optical experimental and measurement systems, such as Interferometry, interferometers, also finding widespread application in fibre optic telecommunications. Designs In its most common form, a cube, a beam splitter is made from two triangular glass prism (optics), prisms which are glued together at their base using polyester, epoxy, or urethane-based adhesives. (Before these synthetic resins, natural ones were used, e.g. Canada balsam.) The thickness of the resin layer is adjusted such that (for a certain wavelength) half of the light incident through one "port" (i.e., face of the cube) is reflection (physics), reflected and the other half is transmitted due to Total internal reflection#Frustrated_TIR, FTIR (frustrated total internal reflection). polarizer, Polarizing beam splitters, such as the Wollaston prism ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michelson Interferometer
The Michelson interferometer is a common configuration for optical interferometry and was invented by the American physicist Albert Abraham Michelson in 1887. Using a beam splitter, a light source is split into two arms. Each of those light beams is reflected back toward the beamsplitter which then combines their amplitudes using the superposition principle. The resulting interference pattern that is not directed back toward the source is typically directed to some type of photoelectric detector or camera. For different applications of the interferometer, the two light paths can be with different lengths or incorporate optical elements or even materials under test. The Michelson interferometer is employed in many scientific experiments and became well known for its use by Michelson and Edward Morley in the famous Michelson–Morley experiment (1887) in a configuration which would have detected the Earth's motion through the supposed luminiferous aether that most physicists a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
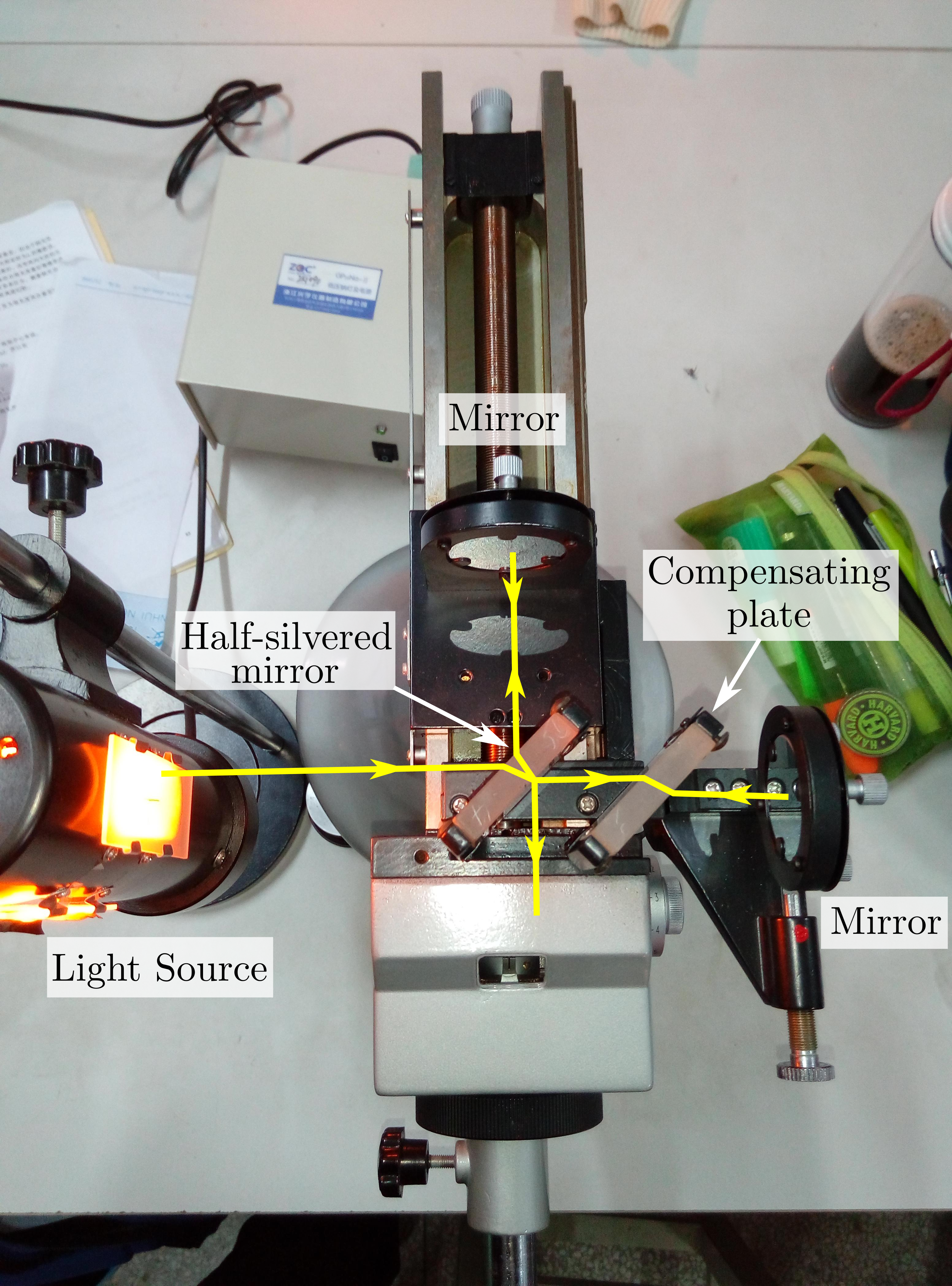
Michelson Interferometer With Corner Cubes
{{disambiguation ...
Michelson may refer to: * Michelson (surname), people with the given name or surname * 27758 Michelson discovered in 1991 * Michelson (crater) on the Moon * Michelson-Gale-Pearson experiment, science * Michelson interferometer, most common configuration for optical interferometry * Michelson–Morley experiment, a scientific experiment regarding the luminiferous ether. * Michelson Museum of Art, Texas, USA * Mount Michelson (Brooks Range), Alaska, USA * USNS Michelson T-AGS-23, United States Naval ship * Michelson, the domain-specific language for smart contracts in Tezos * Michelson, Michigan, an unincorporated community See also * Mickelson * Michaelson Michaelson is an English patronymic surname meaning "son of Michael". There are varied English and Scandinavian spellings. It is rare as a given name. Notable people with the surname include: * Ben Michaelson (born 1981), American swimmer * Ingri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LIDAR
Lidar (, also LIDAR, an acronym of "light detection and ranging" or "laser imaging, detection, and ranging") is a method for determining ranging, ranges by targeting an object or a surface with a laser and measuring the time for the reflected light to return to the receiver. Lidar may operate in a fixed direction (e.g., vertical) or it may scan multiple directions, in a special combination of 3-D scanning and laser scanning. Lidar has terrestrial, airborne, and mobile applications. It is commonly used to make high-resolution maps, with applications in surveying, geodesy, geomatics, archaeology, geography, geology, geomorphology, seismology, forestry, atmospheric physics, laser guidance, airborne laser swathe mapping (ALSM), and Mars Orbiter Laser Altimeter, laser altimetry. It is used to make digital 3D modeling, 3-D representations of areas on the Earth's surface and ocean bottom of the intertidal and near coastal zone by varying the wavelength of light. It has also been in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laser Rangefinder
A laser rangefinder, also known as a laser telemeter or laser distance meter, is a rangefinder that uses a laser beam to determine the distance to an object. The most common form of laser rangefinder operates on the time of flight principle by sending a laser pulse in a narrow beam towards the object and measuring the time taken by the pulse to be reflected off the target and returned to the sender. Due to the high speed of light, this technique is not appropriate for high precision sub-millimeter measurements, where triangulation and other techniques are often used instead. Laser rangefinders are sometimes classified as type of handheld scannerless lidar. Pulse The pulse may be coded to reduce the chance that the rangefinder can be jammed. It is possible to use Doppler effect techniques to judge whether the object is moving towards or away from the rangefinder, and if so, how fast. Precision The precision of an instrument is correlated with the rise time, divergence, and po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wide Area Augmentation System
The Wide Area Augmentation System (WAAS) is an air navigation aid developed by the Federal Aviation Administration to augment the Global Positioning System (GPS), with the goal of improving its accuracy, integrity, and availability. Essentially, WAAS is intended to enable aircraft to rely on GPS for all phases of flight, including approaches with vertical guidance to any airport within its coverage area. It may be further enhanced with the local-area augmentation system (LAAS) also known by the preferred ICAO term ''ground-based augmentation system'' (GBAS) in critical areas. WAAS uses a network of ground-based reference stations, in North America and Hawaii, to measure small variations in the GPS satellites' signals in the western hemisphere. Measurements from the reference stations are routed to master stations, which queue the received deviation correction (DC) and send the correction messages to geostationary WAAS satellites in a timely manner (every 5 seconds or better) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Differential GPS
Differential Global Positioning Systems (DGPSs) supplement and enhance the positional data available from global navigation satellite systems (GNSSs). A DGPS can increase accuracy of positional data by about a thousandfold, from approximately to . DGPSs consist of networks of fixed position, ground-based reference stations. Each reference station calculates the difference between its highly accurate known position and its less accurate satellite-derived position. The stations broadcast this data locally—typically using ground-based transmitters of shorter range. Non-fixed (mobile) receivers use it to correct their position by the same amount, thereby improving their accuracy. The United States Coast Guard (USCG) previously ran DGPS in the United States on longwave radio frequencies between and near major waterways and harbors. It was discontinued in March 2022. The USCG's DGPS was known as NDGPS (Nationwide DGPS) and was jointly administered by the Coast Guard and the United ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Global Positioning System
The Global Positioning System (GPS) is a satellite-based hyperbolic navigation system owned by the United States Space Force and operated by Mission Delta 31. It is one of the global navigation satellite systems (GNSS) that provide geolocation and time information to a GPS receiver anywhere on or near the Earth where there is an unobstructed line of sight to four or more GPS satellites. It does not require the user to transmit any data, and operates independently of any telephone or Internet reception, though these technologies can enhance the usefulness of the GPS positioning information. It provides critical positioning capabilities to military, civil, and commercial users around the world. Although the United States government created, controls, and maintains the GPS system, it is freely accessible to anyone with a GPS receiver. Overview The GPS project was started by the U.S. Department of Defense in 1973. The first prototype spacecraft was launched in 1978 an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LORAN
LORAN (Long Range Navigation) was a hyperbolic navigation, hyperbolic radio navigation system developed in the United States during World War II. It was similar to the UK's Gee (navigation), Gee system but operated at lower frequencies in order to provide an improved range up to with an accuracy of tens of miles. It was first used for ship convoys crossing the Atlantic Ocean, and then by long-range patrol aircraft, but found its main use on the ships and aircraft operating in the Pacific theater during World War II. LORAN, in its original form, was an expensive system to implement, requiring a cathode ray tube (CRT) display and a well trained operator. This limited use to the military and large commercial users. Automated receivers became available in the 1950s, but the same improved electronics also opened the possibility of new systems with higher accuracy. The U.S. Navy began development of Loran-B, which offered accuracy on the order of a few tens of feet, but ran into signi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |