|
Directband
DirectBand was a North American wireless datacast network owned and operated by Microsoft. It used FM radio broadcasts in over 100 cities to constantly transmit data to a variety of devices, including portable GPS devices, wristwatches and home weather stations. How it works DirectBand used the 67.65 kHz subcarrier leased by Microsoft from commercial radio broadcasters. This subcarrier delivers about 12 kbit/s (net after ECC) of data per tower, for over 100 MB per day per city. Data included traffic, sports, weather, stocks, news, movie times, calendar appointments, and local time. Not like RDS DirectBand did not use the RDS ( Radio Data System) subcarrier. RDS is a different system and has much lower data rate (~730 bit/s after ECC, including framing). Its much narrower subcarrier is primarily used for radio station information and traffic. DirectBand and RDS can co-exist on the same FM station. Forward acting error correction Since many DirectBand us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smart Personal Objects Technology
The Smart Personal Objects Technology (SPOT) is a discontinued initiative by Microsoft to create intelligent and personal home appliances, consumer electronics, and other objects through new hardware capabilities and software features. Development of SPOT began as an incubation project initiated by the Microsoft Research division. SPOT was first announced by Bill Gates at the COMDEX computer exposition event in 2002, and additional details were revealed by Microsoft at the 2003 Consumer Electronics Show where Gates demonstrated a set of prototype smart watches—the first type of device that would support the technology. Unlike more recent technologies, SPOT did not use more traditional forms of connectivity, such as 3G or Wi-Fi, but relied on FM broadcasting subcarrier transmission as a method of data distribution. While several types of electronics would eventually support the technology throughout its lifecycle, SPOT was considered a commercial failure. Reasons that have bee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Datacasting
Datacasting (data broadcasting) is the broadcasting of data over a wide area via radio waves. It most often refers to supplemental information sent by television stations along with digital terrestrial television (DTT), but may also be applied to digital signals on analog TV or radio. It generally does not apply to data which is inherent to the medium, such as PSIP data which defines virtual channels for DTT or direct broadcast satellite systems; or to things like cable modem or satellite modem, which use a completely separate channel for data. Overview Datacasting often provides news, weather, traffic, stock market, and other information which may or may not relate to the programs it is carried with. It may also be interactive, such as gaming, shopping, or education. An electronic program guide is usually included, although this stretches the definition somewhat, as this is often considered inherent to the digital broadcast standard. The ATSC, DVB and IS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radio Data System
Radio Data System (RDS) is a communications protocol standard for embedding small amounts of digital information in conventional FM radio broadcasts. RDS standardizes several types of information transmitted, including time, station identification and program information. The standard began as a project of the European Broadcasting Union (EBU), but has since become an international standard of the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). Radio Broadcast Data System (RBDS) is the official name used for the U.S. version of RDS. The two standards are only slightly different, with receivers able to work with either system and only minor inconsistencies in the displayed data. Both versions carry data at 1,187.5 bits per second on a 57 kHz subcarrier, so there are exactly 48 cycles of subcarrier during every data bit. The RBDS/RDS subcarrier was set to the third harmonic of the 19 kHz FM stereo pilot tone to minimize interference and intermodulation between t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FM Broadcasting
FM broadcasting is a method of radio broadcasting using frequency modulation (FM). Invented in 1933 by American engineer Edwin Armstrong, wide-band FM is used worldwide to provide high fidelity sound over broadcast radio. FM broadcasting is capable of higher fidelity—that is, more accurate reproduction of the original program sound—than other broadcasting technologies, such as AM broadcasting. It is also less susceptible to common forms of interference, reducing static and popping sounds often heard on AM. Therefore, FM is used for most broadcasts of music or general audio (in the audio spectrum). FM radio stations use the very high frequency range of radio frequencies. Broadcast bands Throughout the world, the FM broadcast band falls within the VHF part of the radio spectrum. Usually 87.5 to 108.0 MHz is used, or some portion thereof, with few exceptions: * In the former Soviet republics, and some former Eastern Bloc countries, the older 65.8–74 M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subcarrier
A subcarrier is a sideband of a radio frequency carrier wave, which is modulated to send additional information. Examples include the provision of colour in a black and white television system or the provision of stereo in a monophonic radio broadcast. There is no physical difference between a carrier and a subcarrier; the "sub" implies that it has been derived from a carrier, which has been amplitude modulated by a steady signal and has a constant frequency relation to it. FM stereo Stereo broadcasting is made possible by using a subcarrier on FM radio stations, which takes the left channel and "subtracts" the right channel from it — essentially by hooking up the right-channel wires backward (reversing polarity) and then joining left and reversed-right. The result is modulated with suppressed carrier AM, more correctly called sum and difference modulation or SDM, at 38 kHz in the FM signal, which is joined at 2% modulation with the mono left+right audio (which r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MSN Direct
MSN Direct was an FM radio-based digital service which allowed 'SPOT' portable devices to receive information from MSN services. Devices that supported MSN Direct included wristwatches, desktop clocks, in-car GPS satellite navigation units, and even small appliances such as coffee makers. Information available through paid "channels" included weather, horoscopes, stocks, news, sports results and calendar notifications. The service also allowed users to receive short messages from Windows Live Messenger. Some Garmin GPS units, such as the ''nüvi 680'', allowed traffic notifications, weather forecasts, movie schedules and local gas prices to be received through MSN Direct. As a radio-based service, MSN Direct did not have universal coverage, but was available in populated parts of the United States and Canada. It was not launched in other areas. Microsoft's latest expansion of MSN Direct was to the Windows Mobile platform. MSN Direct for Windows Mobile took advantage of both cellu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
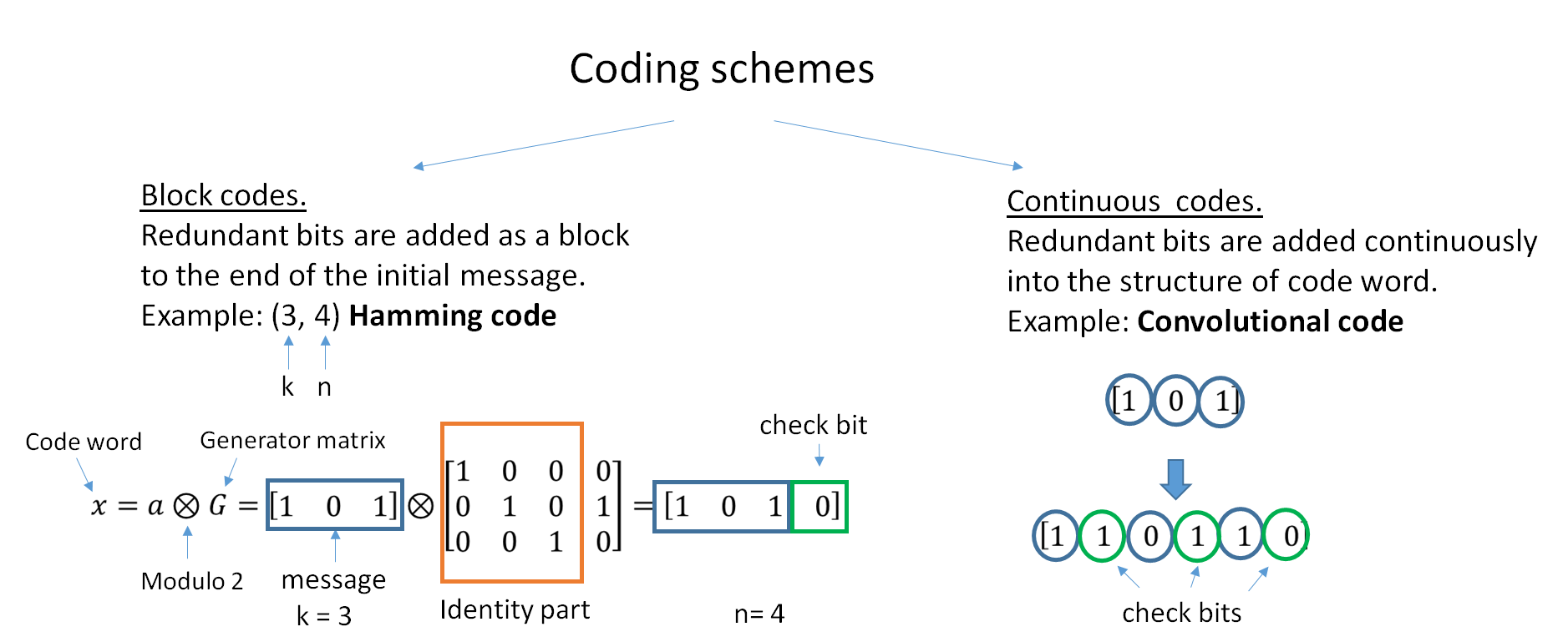
Error-correcting Code
In computing, telecommunication, information theory, and coding theory, an error correction code, sometimes error correcting code, (ECC) is used for controlling errors in data over unreliable or noisy communication channels. The central idea is the sender encodes the message with redundant information in the form of an ECC. The redundancy allows the receiver to detect a limited number of errors that may occur anywhere in the message, and often to correct these errors without retransmission. The American mathematician Richard Hamming pioneered this field in the 1940s and invented the first error-correcting code in 1950: the Hamming (7,4) code. ECC contrasts with error detection in that errors that are encountered can be corrected, not simply detected. The advantage is that a system using ECC does not require a reverse channel to request retransmission of data when an error occurs. The downside is that there is a fixed overhead that is added to the message, thereby requiring a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trellis Modulation
In telecommunication, trellis modulation (also known as trellis coded modulation, or simply TCM) is a modulation scheme that transmits information with high efficiency over band-limited channels such as telephone lines. Gottfried Ungerboeck invented trellis modulation while working for IBM in the 1970s, and first described it in a conference paper in 1976. It went largely unnoticed, however, until he published a new, detailed exposition in 1982 that achieved sudden and widespread recognition. In the late 1980s, modems operating over plain old telephone service (''POTS'') typically achieved 9.6 kbit/s by employing four bits per symbol QAM modulation at 2,400 baud (symbols/second). This bit rate ceiling existed despite the best efforts of many researchers, and some engineers predicted that without a major upgrade of the public phone infrastructure, the maximum achievable rate for a POTS modem might be 14 kbit/s for two-way communication (3,429 baud × 4 bits/symbol, using ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ARMv7
ARM (stylised in lowercase as arm, formerly an acronym for Advanced RISC Machines and originally Acorn RISC Machine) is a family of reduced instruction set computer (RISC) instruction set architectures for computer processors, configured for various environments. Arm Ltd. develops the architectures and licenses them to other companies, who design their own products that implement one or more of those architectures, including system on a chip (SoC) and system on module (SOM) designs, that incorporate different components such as memory, interfaces, and radios. It also designs cores that implement these instruction set architectures and licenses these designs to many companies that incorporate those core designs into their own products. There have been several generations of the ARM design. The original ARM1 used a 32-bit internal structure but had a 26-bit address space that limited it to 64 MB of main memory. This limitation was removed in the ARMv3 series, which ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ARM7
ARM7 is a group of 32-bit RISC ARM processor cores licensed by ARM Holdings for microcontroller use. The ARM7 core family consists of ARM700, ARM710, ARM7DI, ARM710a, ARM720T, ARM740T, ARM710T, ARM7TDMI, ARM7TDMI-S, ARM7EJ-S. The ARM7TDMI and ARM7TDMI-S were the most popular cores of the family. Since ARM7 cores were released from 1993 to 2001, they are no longer recommended for new IC designs; instead ARM Cortex-M or ARM Cortex-R cores are preferred. Overview This generation introduced the Thumb 16-bit instruction set providing improved code density compared to previous designs. The most widely used ARM7 designs implement the ARMv4T architecture, but some implement ARMv3 or ARMv5TEJ. ARM7TDMI has 37 registers (31 GPR and 6 SPR). All these designs use a Von Neumann architecture, thus the few versions containing a cache do not separate data and instruction caches. Some ARM7 cores are obsolete. One historically significant model, the ARM7DI"ARM7DI Data Sheet"; Docu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American multinational corporation, multinational technology company, technology corporation producing Software, computer software, consumer electronics, personal computers, and related services headquartered at the Microsoft Redmond campus located in Redmond, Washington, United States. Its best-known software products are the Microsoft Windows, Windows line of operating systems, the Microsoft Office Productivity software#Office suite, suite, and the Internet Explorer and Microsoft Edge, Edge web browsers. Its flagship hardware products are the Xbox video game consoles and the Microsoft Surface lineup of touchscreen personal computers. Microsoft ranked No. 21 in the 2020 Fortune 500 rankings of the largest United States corporations by total revenue; it was the world's List of the largest software companies, largest software maker by revenue as of 2019. It is one of the Big Tech, Big Five American information technology companies, alongside Alphabet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SCA Data Systems
SCA may refer to: Biology and health * Sickle cell disease, also known as sickle cell anaemia * Spinocerebellar ataxia, a neurological condition * Statistical coupling analysis, a method to identify covarying pairs of amino acids in protein multiple sequence alignments * Sudden cardiac arrest, a condition in which the heart suddenly stops beating, leading to sudden cardiac death * Superior cerebellar artery, a major blood supplier to the cerebellum Commercial entities * Sebastian Conran Associates, a British product and brand development consultancy * Sony Corporation of America, holding company for Sony's American companies * Southern Cross Austereo, an Australian media company * Supercheap Auto, an Australian automotive parts and accessories retailer * SCA (company) (''Svenska Cellulosa Aktiebolaget''), a Swedish hygiene products and paper manufacturer Computing * SCA (computer virus), an Amiga virus referencing the Swiss Cracking Association * Service Component Archit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |