|
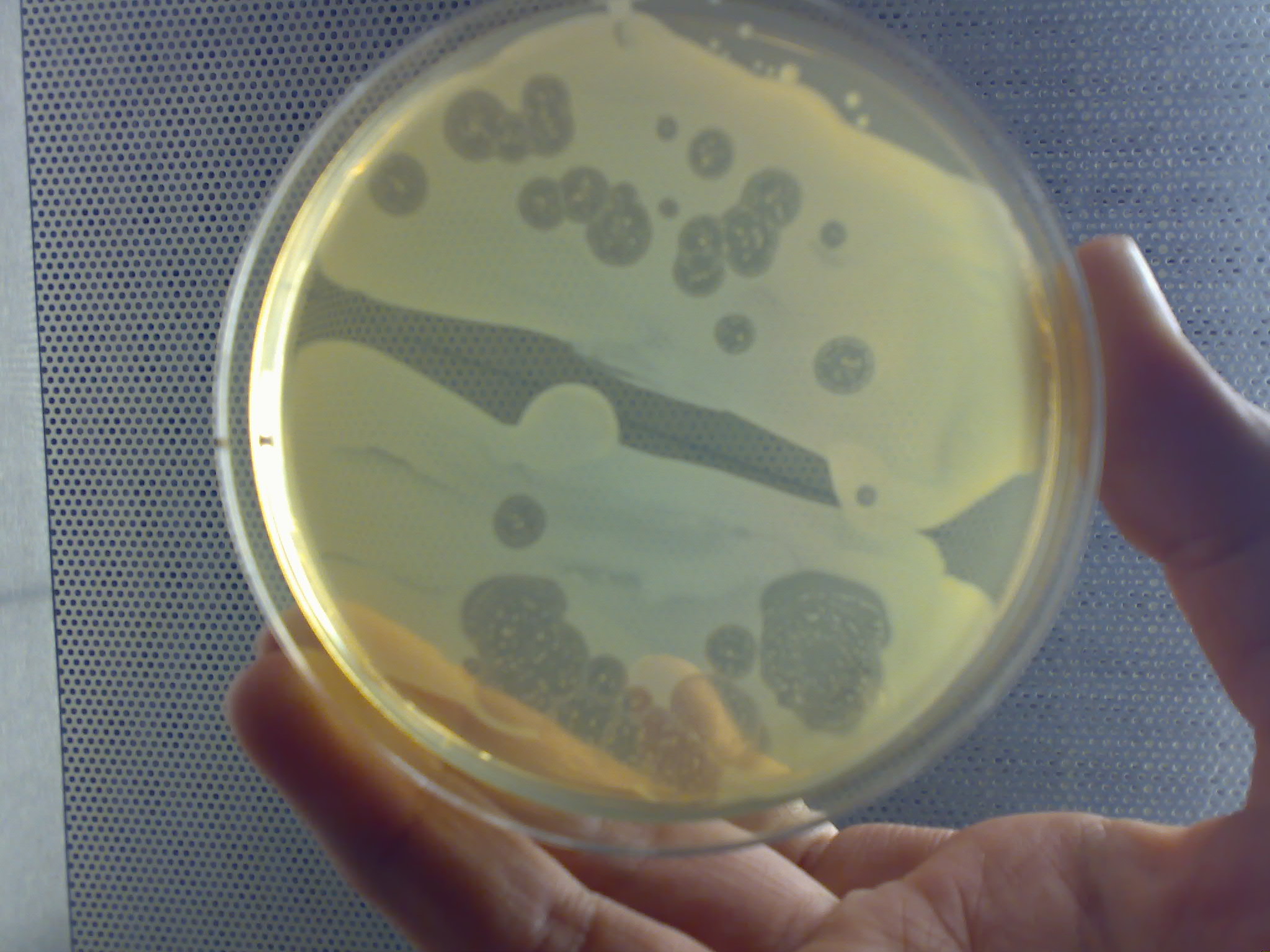
Dictyosteliid
The dictyostelids (Dictyostelia/Dictyostelea, ICZN, or Dictyosteliomycetes, ICBN) are a group of cellular slime molds, or social amoebae. Multicellular behavior When food (normally bacteria) is readily available dictyostelids behave as individual amoebae, which feed and divide normally. However, when the food supply is exhausted, they aggregate to form a multicellular assembly, called a pseudoplasmodium, grex, or slug (not to be confused with the gastropod mollusc called a slug). The grex has a definite anterior and posterior, responds to light and temperature gradients, and has the ability to migrate. Under the correct circumstances the grex matures forming a sorocarp (fruiting body) with a stalk supporting one or more sori (balls of spores). These spores are inactive cells protected by resistant cell walls, and become new amoebae once food is available. In ''Acytostelium'', the sorocarp is supported by a stalk composed of cellulose, but in other dictyostelids the stal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dictyosteliales
The dictyostelids (Dictyostelia/Dictyostelea, International Code of Zoological Nomenclature, ICZN, or Dictyosteliomycetes, ICBN) are a group of cellular slime molds, or social amoebae. Multicellular behavior When food (normally bacteria) is readily available dictyostelids behave as individual amoebae, which feed and divide normally. However, when the food supply is exhausted, they aggregate to form a multicellular assembly, called a pseudoplasmodium, Grex (biology), grex, or slug (not to be confused with the gastropoda, gastropod mollusca, mollusc called a slug). The grex has a definite anterior and posterior, responds to light and temperature gradients, and has the ability to migrate. Under the correct circumstances the grex matures forming a sorocarp (fruiting body) with a stalk supporting one or more Sorus, sori (balls of spores). These spores are inactive cells protected by resistant cell walls, and become new amoebae once food is available. In ''Acytostelium'', the soro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slime Mold
Slime mold or slime mould is an informal name given to several kinds of unrelated eukaryotic organisms with a life cycle that includes a free-living single-celled stage and the formation of spores. Spores are often produced in macroscopic multicellular or multinucleate fruiting bodies which may be formed through aggregation or fusion. Slime molds were formerly classified as fungi but are no longer considered part of that kingdom. Although not forming a single monophyletic clade, they are grouped within the paraphyletic group Protista. More than 900 species of slime mold occur globally. Their common name refers to part of some of these organisms' life cycles where they can appear as gelatinous "slime". This is mostly seen with the Myxogastria, which are the only macroscopic slime molds. Most slime molds are smaller than a few centimetres, but some species may reach sizes up to several square metres and masses up to 20 kilograms. They feed on microorganisms that live in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grex (biology)
A grex, (also called a pseudoplasmodium, or slug) starts as a crowd of single-celled amoebae of the groups Acrasiomycota or Dictyosteliida; ''grex'' is the Latin word for ''flock''. The cells flock together, forming a mass that behaves as an organised, slug-like unit. Before they get stimulated to crowd together to form a grex, the amoebae simply wander as independent cells grazing on bacteria and other suitable food items. They continue in that way of life as long as conditions are favourable. When the amoebae are stressed, typically by a shortage of food, they form a grex. According to species and circumstances, details of the shape of the grex and how it may form will vary but typically the stressed amoebae first produce pheromones that stimulate the flock to vertically assemble in a column. When the column of aggregated cells becomes too high and narrow to stay upright, it topples and becomes a slug-shaped mass: the grex. The grex is mobile; in its form as a slug-like unit i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dictyostelium Discoideum
''Dictyostelium discoideum'' is a species of soil-dwelling amoeba belonging to the phylum Amoebozoa, infraphylum Mycetozoa. Commonly referred to as slime mold, ''D. discoideum'' is a eukaryote that transitions from a collection of unicellular amoebae into a multicellular slug and then into a fruiting body within its lifetime. Its unique asexual lifecycle consists of four stages: vegetative, aggregation, migration, and culmination. The lifecycle of ''D. discoideum'' is relatively short, which allows for timely viewing of all stages. The cells involved in the lifecycle undergo movement, chemical signaling, and development, which are applicable to human cancer research. The simplicity of its lifecycle makes ''D. discoideum'' a valuable model organism to study genetic, cellular, and biochemical processes in other organisms. Natural habitat and diet In the wild, ''D. discoideum'' can be found in soil and moist leaf litter. Its primary diet consists of bacteria, such as ''Escherichia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sorocarp
A sorocarp (from the Greek word ''soros'' "a heap" + ''karpos'' "fruit") is the fruiting body characteristic of certain cellular slime moulds (e.g., Dictyosteliida). Each sorocarp consists of both a sorophore (stalk) and a sorus.Lawrence, E. 2005. Henderson's Dictionary of Biology, 13th Ed. Prentice Hall, London Sorocarps release spore In biology, a spore is a unit of sexual or asexual reproduction that may be adapted for dispersal and for survival, often for extended periods of time, in unfavourable conditions. Spores form part of the life cycles of many plants, algae, f ...s. References Mycetozoa {{microbiology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amoeba
An amoeba (; less commonly spelled ameba or amœba; plural ''am(o)ebas'' or ''am(o)ebae'' ), often called an amoeboid, is a type of Cell (biology), cell or unicellular organism with the ability to alter its shape, primarily by extending and retracting pseudopodia, pseudopods. Amoebae do not form a single Taxonomy (biology), taxonomic group; instead, they are found in every major Lineage (evolution), lineage of eukaryote, eukaryotic organisms. Amoeboid cells occur not only among the protozoa, but also in fungi, algae, and animals. Microbiologists often use the terms "amoeboid" and "amoeba" interchangeably for any organism that exhibits amoeboid movement. In older classification systems, most amoebae were placed in the Class (biology), class or subphylum Sarcodina, a grouping of Unicellular organism, single-celled organisms that possess pseudopods or move by protoplasmic flow. However, molecular phylogenetic studies have shown that Sarcodina is not a monophyletic group whose memb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dictyostelium
''Dictyostelium'' is a genus of single- and multi-celled eukaryotic, phagotrophic bacterivores. Though they are Protista and in no way fungal, they traditionally are known as "slime molds". They are present in most terrestrial ecosystems as a normal and often abundant component of the soil microflora, and play an important role in the maintenance of balanced bacterial populations in soils. The genus ''Dictyostelium'' is in the order Dictyosteliida, the so-called cellular slime molds or social amoebae. In turn the order is in the infraphylum Mycetozoa. Members of the order are Protista of great theoretical interest in biology because they have aspects of both unicellularity and multicellularity. The individual cells in their independent phase are common on organic detritus or in damp soils and caves. In this phase they are amoebae. Typically, the amoebal cells grow separately and wander independently, feeding mainly on bacteria. However, they interact to form multi-cellula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dicty Life Cycle H01
''Dictyostelium discoideum'' is a species of soil-dwelling amoeba belonging to the phylum Amoebozoa, infraphylum Mycetozoa. Commonly referred to as slime mold, ''D. discoideum'' is a eukaryote that transitions from a collection of unicellular amoebae into a multicellular slug and then into a fruiting body within its lifetime. Its unique asexual lifecycle consists of four stages: vegetative, aggregation, migration, and culmination. The lifecycle of ''D. discoideum'' is relatively short, which allows for timely viewing of all stages. The cells involved in the lifecycle undergo movement, chemical signaling, and development, which are applicable to human cancer research. The simplicity of its lifecycle makes ''D. discoideum'' a valuable model organism to study genetic, cellular, and biochemical processes in other organisms. Natural habitat and diet In the wild, ''D. discoideum'' can be found in soil and moist leaf litter. Its primary diet consists of bacteria, such as ''Escherichia c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dicty Signal Relay
''Dictyostelium discoideum'' is a species of soil-dwelling amoeba belonging to the phylum Amoebozoa, infraphylum Mycetozoa. Commonly referred to as slime mold, ''D. discoideum'' is a eukaryote that transitions from a collection of unicellular amoebae into a multicellular slug and then into a fruiting body within its lifetime. Its unique asexual lifecycle consists of four stages: vegetative, aggregation, migration, and culmination. The lifecycle of ''D. discoideum'' is relatively short, which allows for timely viewing of all stages. The cells involved in the lifecycle undergo movement, chemical signaling, and development, which are applicable to human cancer research. The simplicity of its lifecycle makes ''D. discoideum'' a valuable model organism to study genetic, cellular, and biochemical processes in other organisms. Natural habitat and diet In the wild, ''D. discoideum'' can be found in soil and moist leaf litter. Its primary diet consists of bacteria, such as ''Escherichia c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cellular Differentiation
Cellular differentiation is the process in which a stem cell alters from one type to a differentiated one. Usually, the cell changes to a more specialized type. Differentiation happens multiple times during the development of a multicellular organism as it changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of tissues and cell types. Differentiation continues in adulthood as adult stem cells divide and create fully differentiated daughter cells during tissue repair and during normal cell turnover. Some differentiation occurs in response to antigen exposure. Differentiation dramatically changes a cell's size, shape, membrane potential, metabolic activity, and responsiveness to signals. These changes are largely due to highly controlled modifications in gene expression and are the study of epigenetics. With a few exceptions, cellular differentiation almost never involves a change in the DNA sequence itself. Although metabolic composition does get altered quite dramaticall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Programmed Cell Death
Programmed cell death (PCD; sometimes referred to as cellular suicide) is the death of a cell as a result of events inside of a cell, such as apoptosis or autophagy. PCD is carried out in a biological process, which usually confers advantage during an organism's lifecycle. For example, the differentiation of fingers and toes in a developing human embryo occurs because cells between the fingers apoptose; the result is that the digits are separate. PCD serves fundamental functions during both plant and animal tissue development. Apoptosis and autophagy are both forms of programmed cell death. Necrosis is the death of a cell caused by external factors such as trauma or infection and occurs in several different forms. Necrosis was long seen as a non-physiological process that occurs as a result of infection or injury, but in the 2000s, a form of programmed necrosis, called necroptosis, was recognized as an alternative form of programmed cell death. It is hypothesized that necroptosis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DictyBase
dictyBase is an online bioinformatics database for the model organism ''Dictyostelium discoideum ''Dictyostelium discoideum'' is a species of soil-dwelling amoeba belonging to the phylum Amoebozoa, infraphylum Mycetozoa. Commonly referred to as slime mold, ''D. discoideum'' is a eukaryote that transitions from a collection of unicellular ...''. Tools dictyBase offers many ways of searching and retrieving data from the database: * dictyMart - a tool for retrieving varied information on many genes (or the sequences of those genes). * Genome Browser - browse the genes of ''D. discoideum'' in their genomic context. References External links dictyBase Developmental biology Model organism databases Mycetozoa {{Database-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |