|
Dhori Virus
Dhori virus (DHOV) is a species of the genus ''Thogotovirus'' and a member of the family ''Orthomyxoviridae''. Its hosts are ticks, mosquitoes, and mammal Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur or ...s (including humans). DHOV is lethal to mice, causing systemic pathologic changes similar to those reported in humans with virulent influenza A (H5N1) virus infection. Batken virus (BKNV) is considered a subtype of DHOV. Serological cross-reactions between BKNV and DHOV indicate a phylogenetic relationship between these viruses. References Orthomyxoviridae {{virus-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Batken Virus
''Thogotovirus'' is a genus of enveloped RNA viruses, one of seven genera in the virus family ''Orthomyxoviridae''. Their single-stranded, negative-sense RNA genome has six or seven segments. Thogotoviruses are distinguished from most other orthomyxoviruses by being arboviruses – viruses that are transmitted by arthropods, in this case usually ticks. Thogotoviruses can replicate in both tick cells and vertebrate cells; one subtype has also been isolated from mosquitoes. A consequence of being transmitted by blood-sucking vectors is that the virus must spread systemically in the vertebrate host – unlike influenza viruses, which are transmitted by respiratory droplets and are usually confined to the respiratory system. The genus contains the species '' Thogoto thogotovirus'' and ''Dhori virus'' (DHOV), and the latter's subtype Batken virus, as well as the species or strains Araguari virus, Aransas Bay virus (ABV), Bourbon virus, Jos virus (JOSV) and Upolu virus (UPOV), whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thogotovirus
''Thogotovirus'' is a genus of enveloped RNA viruses, one of seven genera in the virus family ''Orthomyxoviridae''. Their single-stranded, negative-sense RNA genome has six or seven segments. Thogotoviruses are distinguished from most other orthomyxoviruses by being arboviruses – viruses that are transmitted by arthropods, in this case usually ticks. Thogotoviruses can replicate in both tick cells and vertebrate cells; one subtype has also been isolated from mosquitoes. A consequence of being transmitted by blood-sucking vectors is that the virus must spread systemically in the vertebrate host – unlike influenza viruses, which are transmitted by respiratory droplets and are usually confined to the respiratory system. The genus contains the species '' Thogoto thogotovirus'' and ''Dhori virus'' (DHOV), and the latter's subtype Batken virus, as well as the species or strains Araguari virus, Aransas Bay virus (ABV), Bourbon virus, Jos virus (JOSV) and Upolu virus (UPOV), whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
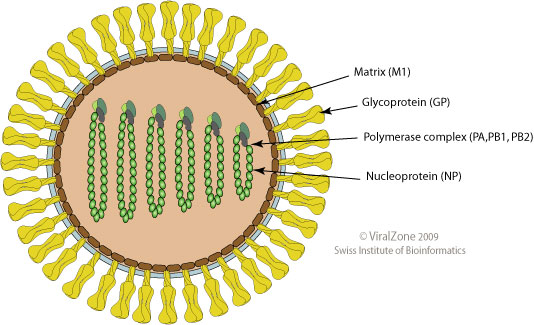
Orthomyxoviridae
''Orthomyxoviridae'' (from Greek language, Greek ὀρθός, ''orthós'' 'straight' + μύξα, ''mýxa'' 'mucus') is a family of negative-sense single-stranded RNA virus, negative-sense RNA viruses. It includes seven genus, genera: ''Influenza A virus, Alphainfluenzavirus'', ''Influenza B virus, Betainfluenzavirus'', ''Influenza C virus, Gammainfluenzavirus'', ''Influenza D virus, Deltainfluenzavirus'', ''Isavirus'', ''Thogotovirus'', and ''Quaranjavirus''. The first four genera contain viruses that cause influenza in birds (see also avian influenza) and mammals, including humans. Isaviruses infect salmon; the thogotoviruses are arboviruses, infecting vertebrates and invertebrates (such as ticks and mosquitoes). The Quaranjaviruses are also arboviruses, infecting vertebrates (birds) and invertebrates (arthropods). The four genera of Influenza virus that infect vertebrates, which are identified by antigenic differences in their nucleoprotein and matrix protein, are as follows: * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tick
Ticks (order Ixodida) are parasitic arachnids that are part of the mite superorder Parasitiformes. Adult ticks are approximately 3 to 5 mm in length depending on age, sex, species, and "fullness". Ticks are external parasites, living by feeding on the blood of mammals, birds, and sometimes reptiles and amphibians. The timing of the origin of ticks is uncertain, though the oldest known tick fossils are from the Cretaceous period, around 100 million years old. Ticks are widely distributed around the world, especially in warm, humid climates. Ticks belong to two major families, the Ixodidae or hard ticks, and the Argasidae, or soft ticks. ''Nuttalliella,'' a genus of tick from southern Africa is the only member of the family Nuttalliellidae, and represents the most primitive living lineage of ticks. Adults have ovoid/pear-shaped bodies (idiosomas) which become engorged with blood when they feed, and eight legs. Their cephalothorax and abdomen are completely fused. In addit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mosquito
Mosquitoes (or mosquitos) are members of a group of almost 3,600 species of small flies within the family Culicidae (from the Latin ''culex'' meaning " gnat"). The word "mosquito" (formed by ''mosca'' and diminutive ''-ito'') is Spanish for "little fly". Mosquitoes have a slender segmented body, one pair of wings, one pair of halteres, three pairs of long hair-like legs, and elongated mouthparts. The mosquito life cycle consists of egg, larva, pupa, and adult stages. Eggs are laid on the water surface; they hatch into motile larvae that feed on aquatic algae and organic material. These larvae are important food sources for many freshwater animals, such as dragonfly nymphs, many fish, and some birds such as ducks. The adult females of most species have tube-like mouthparts (called a proboscis) that can pierce the skin of a host and feed on blood, which contains protein and iron needed to produce eggs. Thousands of mosquito species feed on the blood of various hosts � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammal
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur or hair, and three middle ear bones. These characteristics distinguish them from reptiles (including birds) from which they diverged in the Carboniferous, over 300 million years ago. Around 6,400 extant species of mammals have been described divided into 29 orders. The largest orders, in terms of number of species, are the rodents, bats, and Eulipotyphla (hedgehogs, moles, shrews, and others). The next three are the Primates (including humans, apes, monkeys, and others), the Artiodactyla ( cetaceans and even-toed ungulates), and the Carnivora (cats, dogs, seals, and others). In terms of cladistics, which reflects evolutionary history, mammals are the only living members of the Synapsida (synapsids); this clade, together with Saur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |