|
Deutsche Hochschule Für Politik
The Deutsche Hochschule für Politik (DHfP), or ''German Academy for Politics'', was a private academy in Berlin, founded in October 1920. It was integrated into the Faculty for Foreign Studies (''Auslandswissenschaftliche Fakultät'') of the Friedrich-Wilhelms-Universität in 1940, was re-founded in 1948 and turned into the Otto-Suhr-Institut of the Freie Universität Berlin in 1959. Purpose The DHfP was to establish the elementary principles of a democratic community in Germany in a liberal spirit and thus help to strengthen the young Weimar Republic against anti-democratic tendencies. Political science was at this time still understood as the study of democracy. The predecessor institution of the Deutsche Hochschule für Politik was the "Staatsbürgerschule" (Citizens' Academy) in Berlin, founded in 1918. Sponsors or members of the founding board of trustees were amongst others Walter Simons, Ernst Jäckh, Friedrich Naumann, Friedrich Meinecke, Max Weber, Hugo Preuß, Gert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berlin
Berlin is Capital of Germany, the capital and largest city of Germany, both by area and List of cities in Germany by population, by population. Its more than 3.85 million inhabitants make it the European Union's List of cities in the European Union by population within city limits, most populous city, as measured by population within city limits having gained this status after the United Kingdom's, and thus London's, Brexit, departure from the European Union. Simultaneously, the city is one of the states of Germany, and is the List of German states by area, third smallest state in the country in terms of area. Berlin is surrounded by the state of Brandenburg, and Brandenburg's capital Potsdam is nearby. The urban area of Berlin has a population of over 4.5 million and is therefore the most populous urban area in Germany. The Berlin/Brandenburg Metropolitan Region, Berlin-Brandenburg capital region has around 6.2 million inhabitants and is Germany's second-largest metropolitan reg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theodor Heuss
Theodor Heuss (; 31 January 1884 – 12 December 1963) was a German liberal politician who served as the first president of West Germany from 1949 to 1959. His cordial nature – something of a contrast to the stern character of chancellor Konrad Adenauer – largely contributed to the stabilization of democracy in West Germany during the ''Wirtschaftswunder'' years. Before beginning his career as a politician, Heuss had been a political journalist. Early life and education Heuss was born in Brackenheim, a small town and wine-making community near Heilbronn in Württemberg, on the border between the historic regions of Swabia and Franconia. He attended the Karlsgymnasium in Heilbronn, from which he graduated in 1902. This selective secondary school has since been renamed the Theodor-Heuss-Gymnasium, in honor of its famous alumnus. Heuss studied economics, art history and political science at the universities of Munich and Berlin. He received his doctorate at Munich, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hans Staudinger
Hans Staudinger (born 16 August 1889 in Worms, Germany; died 25 February 1980 in New York City, NY) was a politician of the Social Democratic Party of Germany (SPD) and an economist, as well as a secretary of state in the Prussian trade ministry from 1929 to 1932. From November 1932 to June 1933 he was a Social Democrat member of the Reichstag. Youth Staudinger was born to the gymnasium (high school) teacher Franz Staudinger and his wife Auguste Staudinger, née Wenck, and was baptised as a Protestant. He had two brothers and one sister. His father was a leading theorist of the cooperative movement and was connected to prominent Social Democrats such as August Bebel and Eduard Bernstein. His friendship with the latter lasted his whole life. Hans Staudinger acquired his Abitur at the Ludwig-Georgs-Gymnasium in Darmstadt. He started an apprenticeship as a carpenter while still at school, but did not pursue this. He also temporarily worked as an engine stoker. The incentive for this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arnold Brecht
Arnold Brecht (26 January 1884 – 11 September 1977) was a German jurist and one of the leading government officials in the Weimar Republic. He was one of the few democratically minded high-placed officials that opposed the Machtergreifung in 1933. An alumnus of the University of Göttingen, Brecht served as a government official from 1918 to 1933. He was dismissed from his post shortly after the Nazi seizure of power, and emigrated to the United States. He became a lecturer at The New School, and also a foreign policy adviser to the United States government. After World War II he returned to Germany and helped drafting the Basic Law for the Federal Republic of Germany. In 1959 he received the Federal Cross of Merit. Brecht also made contributions to political science. Brecht's law is the academic basis for one of the components of the equalization payments Equalization payments are cash payments made in some federal systems of government from the federal government to subnati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hermann Pünder
Hermann Josef Pünder (1 April 1888 in Trier – 3 October 1976 in Fulda) was a German politician in the German Centre Party and the Christian Democratic Union. His older brother was the lawyer Werner Pünder. Life After attending school in Bad Münstereifel, Pünder studied Law in Freiburg im Breisgau, Berlin and London. He finished his studies in 1911 with a ''Dr. jur.'' In 1919 he became a senior official in the Reich Ministry of Finance, and was then the state secretary from 1926 to 1932 in the Reich Chancellery under the Chancellors Hans Luther (Centre Party), Wilhelm Marx (Centre Party), Hermann Müller (SPD) and Heinrich Brüning (Centre Party). In his spare time he also taught at the Deutsche Hochschule für Politik in Berlin, partly at the same time as the later President of Germany Theodor Heuss. After the assassination attempt against Hitler on 20 July 1944, Pünder was arrested by the Gestapo, and deported for participating in the conspiracy against Hitler to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Veit Valentin
Veit Valentin (25 March 1885, Frankfurt – 12 January 1947, Washington D.C.) was a German historian who was Professor of History at the University of Freiburg. In comments that caused a storm of controversy in Germany, Valentin attacked Ernst Graf zu Reventlow's ''Deutschlands Auswärtige Politik'' in 1916: "It is a classic example of historiographical demagogy and we have no choice but to warn the public against the book and its author".G. P. Gooch, 'Recent Revelations on European Diplomacy', ''Journal of the British Institute of International Affairs'' Vol. 2, No. 1 (Jan., 1923), p. 5. During the First World War, Gustav Stresemann tried to have Valentin sent to court for alleged treasonable utterances. Hans W. Gatzke, 'The Stresemann Papers', ''The Journal of Modern History'' Vol. 26, No. 1 (Mar., 1954), p. 55, n. 29. Valentin was appointed by the German Foreign Office to write a history of German foreign policy, permitting him access to their papers. This was published i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eckart Kehr
Eckart Kehr (21 June 1902 in Brandenburg an der Havel, Brandenburg, Germany – 29 May 1933 in Washington, DC) was a Marxist German historian who was one of the first historians to emphasize the importance of social structure and economic interests in influencing political decisions, instead of heroic personalities. A student of Friedrich Meinecke, whom he broke from, he was called the "enfant terrible" of the German historical profession during the Weimar Republic. His most important work is his 1930 doctoral thesis (published 1931) ''Schlachtflottenbau und Parteipolitik 1894–1901: Versuch eines Querschnitts durch die innenpolitischen, sozialen und ideologischen Voraussetzungen des deutschen Imperialismus '' ("Battle Fleet Construction and Party Politics in Germany, 1894–1901: A Cross-Section of the Political, Social and Ideological Preconditions of German Imperialism"), which describes the domestic economic sources of Germany's naval policy during the years 1894 to 1901, rever ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hajo Holborn
Hajo Holborn (18 May 1902, Berlin – 20 June 1969, Bonn) was a German-American historian and specialist in modern German history. Early life Hajo Holborn was born the son of Ludwig Holborn, the German physicist and "Direktor der Physikalisch-Technischen Reichsanstalt," and became a student of Friedrich Meinecke at Berlin University, where he achieved a doctor of philosophy in 1924. After establishing at Heidelberg in 1926 as lecturer in medieval and modern history, he became Privatdozent there until he was called back to Berlin as Carnegie Professor of History and International Relationships at the private Deutsche Hochschule für Politik. He was dismissed from his appointments in 1933 by the Nazi government, but he had already left the country. Emigration Unwilling to participate in National Socialism, that same year he fled to the United Kingdom, then emigrated to the United States in 1934. Shortly after coming to America, he was appointed visiting professor of Germ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hans Delbrück
Hans Gottlieb Leopold Delbrück (; 11 November 1848 – 14 July 1929) was a German historian. Delbrück was one of the first modern military historians, basing his method of research on the critical examination of ancient sources, using auxiliary disciplines, like demography and economics, to complete the analysis and the comparison between epochs, to trace the evolution of military institutions. Delbrück's writings are chiefly concerned with the history of the art of war, his most ambitious work being ''Geschichte der Kriegskunst im Rahmen der politischen Geschichte'' ("History of Warfare in the Framework of Political History" in four volumes, third edition published in 1920). Other works are ''Die Perserkriege und die Burgunderkriege'' (The Persian and Burgundian Wars, 1887), ''Die Strategie des Perikles erläutert durch die Strategie Friedrichs des Grossen'' (The Strategy of Pericles Described Through the Strategy of Frederick the Great, 1890) and ''Das Leben des Feldmarschal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arnold Wolfers
Arnold Oscar Wolfers (June 14, 1892July 16, 1968) was a Swiss-American lawyer, economist, historian, and international relations scholar, most known for his work at Yale University and for being a pioneer of classical international relations realism. Educated in his native Switzerland and in Germany, Wolfers was a lecturer at the Deutsche Hochschule für Politik in Berlin in the late 1920s and then became its director in the early 1930s. Initially having some sympathies with the ideas of Nazi Germany, he left that country to become a visiting professor at Yale in 1933, stayed there, and became a U.S. citizen in 1939. In 1935 he was co-founder of the influential Yale Institute of International Studies. As master of Pierson College at Yale, he played a significant role during World War II by recruiting for the Office of Strategic Services. In 1957 he left Yale and became director of the Washington Center of Foreign Policy Research at Johns Hopkins University, where he serv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albert Salomon (sociologist)
Albert Salomon (8 December 1891, in Berlin – 18 December 1966, in New York) was a German-Jewish sociologist. He was the nephew of Alice Salomon, a pioneer of the academic discipline of social work. Studies He first studied history of art, history of religions and philosophy at the Humboldt University of Berlin from 1910. He later studied philosophy in Freiburg and Heidelberg, where he came into contact with Max Weber and Georg Lukács, among others. During World War I, he served as a nurse, and in 1921 he took his doctorate in the culture of friendship in Germany in the 19th Century. In 1926 he started to work at the Deutsche Hochschule für Politik in Berlin. In the same year, he wrote an article on Max Weber in «Die Gesellschaft. Internationale Revue für Sozialismus und Politik», a publication that he later became editor of. Here, he introduced young writers such as Hannah Arendt, Walter Benjamin and Herbert Marcuse. In 1931 he contracted polio, and in 1933 he lost ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ernst Niekisch
Ernst Niekisch (23 May 1889 – 23 May 1967) was a German writer and politician. Initially a member of the Social Democratic Party (SPD), he later became a prominent exponent of National Bolshevism. Early life Born in Trebnitz (Silesia), and brought up in Nördlingen, he became a schoolteacher by profession.Philip Rees, ''Biographical Dictionary of the Extreme Right Since 1890'', 1990, p. 279 He joined the Social Democratic Party in 1917 and was instrumental in the setting up of a short-lived Bavarian Soviet Republic in 1919. Indeed, for a time at the start of the year, after the resignation of Kurt Eisner and immediately before the establishment of the Bavarian Soviet Republic, Niekisch wielded effective power as chairman of the central executive of Bavarian councils, an interim governing body. He left the SPD soon afterward and was the Independent Social Democratic Party of Germany (USPD) for a time before he returned to his former party. He served a brief spell in prison in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


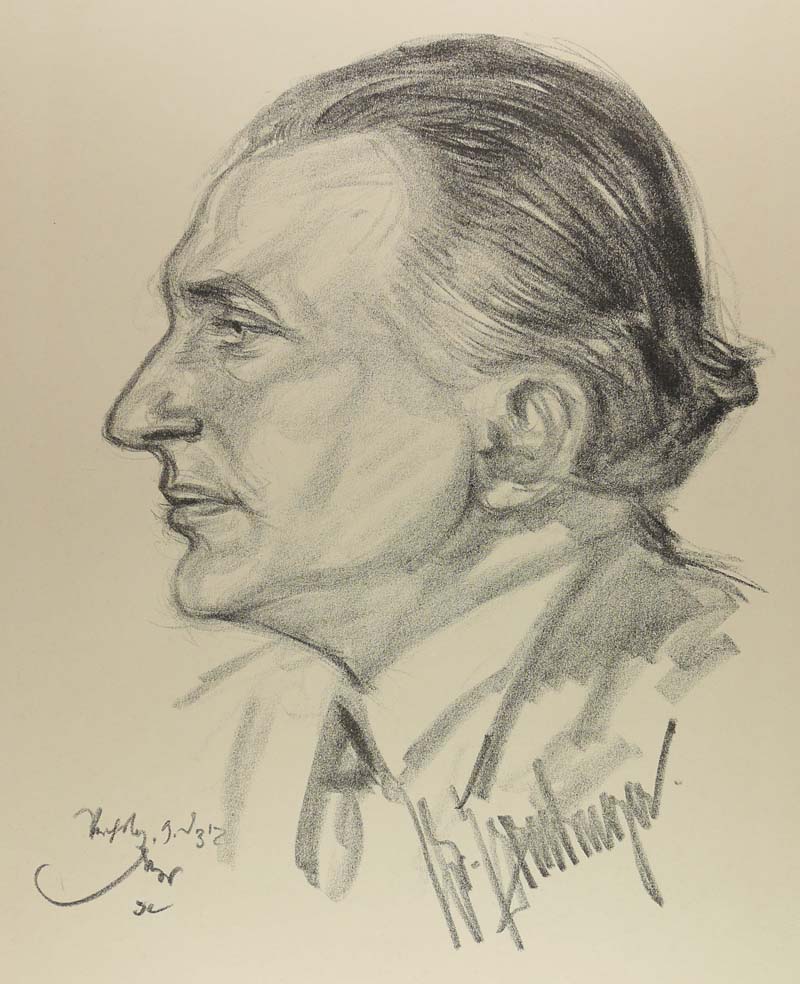
.jpg)
