|
Denmark–Sweden Border
The current national border between Denmark and Sweden dates to 1658. It is entirely a maritime border, along Kattegat and Øresund, and in the Baltic Sea between Bornholm and Scania. The territorial waters (12 mile zone) of the two countries meet exclusively along the Øresund, extending to about , approximately between Höganäs and Falsterbo. There is one road and rail connection, the long Øresund fixed link, opened in 2000, besides a number of ferry links. History Sweden and Denmark–Norway became separate countries with the breakup of the Kalmar Union in 1523. Until 1658, the historic provinces of Scania, Blekinge and Bohuslän (and until 1645 also Halland) belonged to Denmark, so that the Denmark–Sweden border ran across what is now southern Sweden. In 1645 and 1658 respectively, these provinces were ceded to Sweden in the Treaty of Roskilde, establishing the Øresund as national boundary. The Westrogothic law mentions six border marks used in the 11th century w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Denmark Map
) , song = ( en, "King Christian stood by the lofty mast") , song_type = National and royal anthem , image_map = EU-Denmark.svg , map_caption = , subdivision_type = Sovereign state , subdivision_name = Danish Realm, Kingdom of Denmark , established_title = History of Denmark#Middle ages, Consolidation , established_date = 8th century , established_title2 = Christianization , established_date2 = 965 , established_title3 = , established_date3 = 5 June 1849 , established_title4 = Faroese home rule , established_date4 = 24 March 1948 , established_title5 = European Economic Community, EEC 1973 enlargement of the European Communities, accession , established_date5 = 1 January 1973 , established_title6 = Greenlandic home rule , established_date6 = 1 May 1979 , official_languages = Danish language, Danish , languages_type = Regional languages , languages_sub = yes , languages = German language, GermanGerman is recognised as a protected minority language in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kalmar Union
The Kalmar Union (Danish language, Danish, Norwegian language, Norwegian, and sv, Kalmarunionen; fi, Kalmarin unioni; la, Unio Calmariensis) was a personal union in Scandinavia, agreed at Kalmar in Sweden, that from 1397 to 1523 joined under a single monarch the three kingdoms of Denmark, Sweden (then including most of present-day Finland), and Norway, together with List of possessions of Norway#Former dependencies and homelands, Norway's overseas colonies Norway retained none of its prior possessions, however. Christian I pledged the Northern Isles to Scotland as insurance for his daughter’s dowery in 1468; when the dowery wasn’t paid the islands transferred to perpetual Scottish sovereignty in 1470. Following the Union’s dissolution, all remaining overseas possessions brought into the Union by Norway became property of the Danish monarch; who retained ownership following the transfer of the Kingdom of Norway from the Danish crown to Swedish crown (discussed in further ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
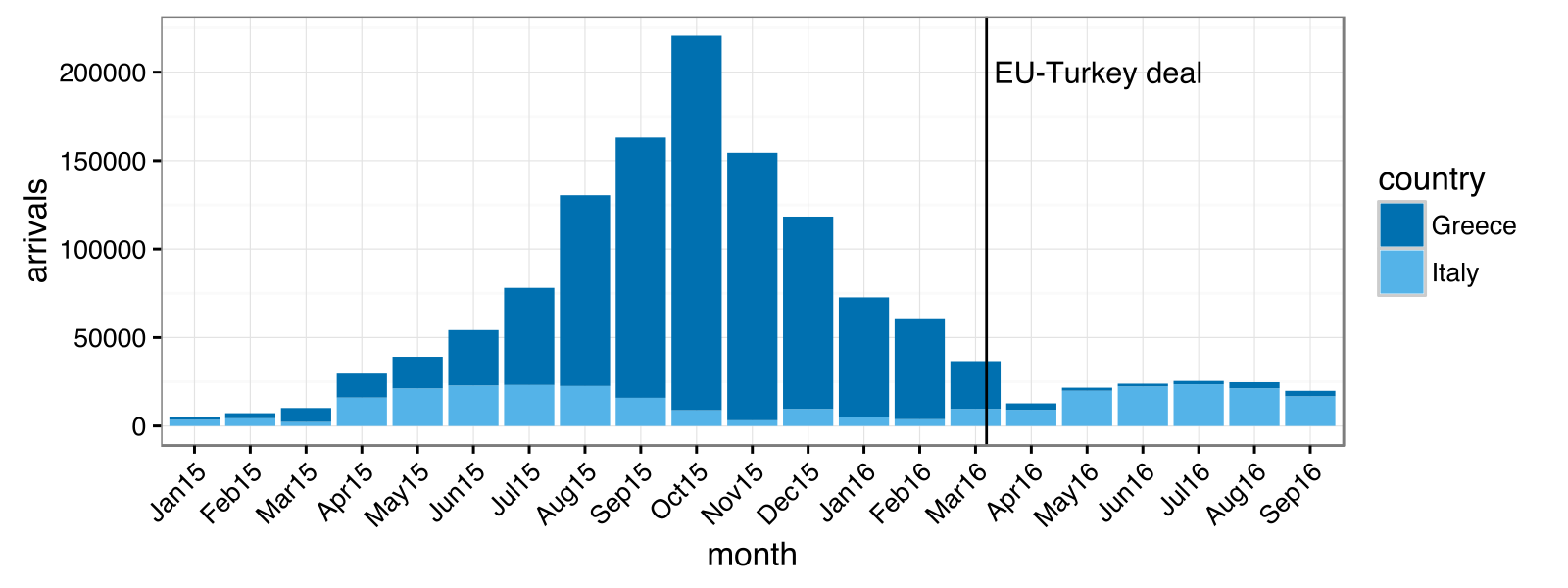
European Migrant Crisis
The 2015 European migrant crisis, also known internationally as the Syrian refugee crisis, was a period of significantly increased movement of refugees and migrants into Europe in 2015, when 1.3 million people came to the continent to request asylum, the most in a single year since World War II. Those requesting asylum in Europe in 2015 were mostly Syrians, but also included significant numbers of Afghans, Nigerians, Pakistanis, Iraqis and Eritreans, as well as economic migrants from the Balkans. Europe had already begun registering increased numbers of refugee arrivals in 2010 due to a confluence of conflicts in parts of the Middle East, Asia and Africa, particularly the wars in Syria, Iraq and Afghanistan, but also terrorist insurgencies in Nigeria and Pakistan, and long-running human rights abuses in Eritrea, all contributing to refugee flows. Many millions initially sought refuge in comparatively stable countries near their origin, but while these countries were largely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schengen Acquis
The Schengen acquis is a set of rules and legislation, integrated into European Union law, which regulate the abolition of border controls at the internal borders within the Schengen Area, as well as the strengthening of border controls at the external borders. Description The Schengen acquis comprises: * the Schengen Agreement, signed on 14 June 1985 by Benelux, Germany and France; * the Schengen Convention, implementing the Schengen Agreement, signed on 19 June 1990; * agreements accession to the Schengen Convention by Italy, Spain, Portugal, Greece, Austria, Denmark, Finland and Sweden; * the decisions of the Executive Committee and the Central Group; * Union acts (regulations, directives and decisions) adopted by the European Parliament and/or the Council after the Schengen acquis was integrated into Union law History The free movement of persons was a core part of the original Treaty of Rome and, from the early days of the European Economic Community, nationals of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nordic Passport Union
The Nordic Passport Union allows citizens of the Nordic countriesIceland, Denmark, Norway, Sweden, and Finlandto travel and reside in another Nordic country without any travel documentation (e.g. a passport or national identity card) or a residence permit. Since 25 March 2001, all five states have also been within the Schengen Area. For Nordic citizens, no identity documentation is legally required to enter or reside within any Nordic country. However, identity documentation is still useful, as companies may require proof of identity for certain services, such as trains, airports, age check for alcohol purchase, or for services aimed at residents, like banking, picking up postal packages or dealing with authorities. Usually any valid proof of identity is accepted, in many cases local identity documentation like ID card from bank or other trusted private institute are accepted. An important exception is the "temporary" border controls which were introduced in 2015 and which as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Invasion Of Denmark (1940)
The German invasion of Denmark (german: Operation Weserübung – Süd), was the German attack on Denmark on 9 April 1940, during the Second World War. The attack was a prelude to the invasion of Norway (german: Weserübung Nord, 9 April – 10 June 1940). Denmark's strategic importance for Germany was limited. The invasion's primary purpose was to use Denmark as a staging ground for operations against Norway, and to secure supply lines to the forces about to be deployed there. An extensive network of radar systems was built in Denmark to detect British bombers bound for Germany. The attack on Denmark was a breach of the non-aggression pact Denmark had signed with Germany less than a year earlier. The initial plan was to push Denmark to accept that German land, naval and air forces could use Danish bases, but Adolf Hitler subsequently demanded that both Norway and Denmark be invaded. Denmark's military forces were inferior in numbers and equipment, and after a short battle we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German-occupied Europe
German-occupied Europe refers to the sovereign countries of Europe which were wholly or partly occupied and civil-occupied (including puppet governments) by the military forces and the government of Nazi Germany at various times between 1939 and 1945, during and shortly before World War II, generally administered by the Nazi regime, under the dictatorship of Adolf Hitler.Encyclopædia Britannica German occupied Europe.World War II. Retrieved 1 September 2015 from the Internet Archive. The German Wehrmacht occupied European territory: * as far east as the town of Mozdok in the North Caucasus in the Soviet Union (1942–1943) * as far north as the settlement of Barentsburg in Svalbard in the Kingdom of Norway * as far south as the island of Gavdos in the Kingdom of Greece * as far west as the island of Ushant in the French Republic Outside of Europe proper, German forces effectively controlled areas of North Africa in Egypt, Libya, and Tunisia at times between 1941 and 1943. G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Union Between Sweden And Norway
Sweden and Norway or Sweden–Norway ( sv, Svensk-norska unionen; no, Den svensk-norske union(en)), officially the United Kingdoms of Sweden and Norway, and known as the United Kingdoms, was a personal union of the separate kingdoms of Sweden and Norway under a common monarch and common foreign policy that lasted from 1814 until its peaceful dissolution in 1905. The two states kept separate constitutions, laws, legislatures, administrations, state churches, armed forces, and currencies; the kings mostly resided in Stockholm, where foreign diplomatic representations were located. The Norwegian government was presided over by viceroys: Swedes until 1829, Norwegians until 1856. That office was later vacant and then abolished in 1873. Foreign policy was conducted through the Swedish foreign ministry until the dissolution of the union in 1905. Norway had been in a closer union with Denmark, but Denmark-Norway's alliance with Napoleonic France caused the United Kingdom and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norway–Sweden Border
The Norway–Sweden border ( no, Svenskegrensa, sv, Norska gränsen) is a long land national border, and the longest border for both Norway and Sweden. History The border has changed several times because of war. Before 1645, Jämtland, Härjedalen, Idre/Särna parish, and Bohuslän belonged to Norway. The border changes were defined in the Treaty of Brömsebro (1645), the Treaty of Roskilde (1658) and the Treaty of Copenhagen (1660). In 1751 a treaty was signed in Strömstad, defining the border based on field investigations and negotiations done 1738–1751. The border was based on knowledge among local people, mainly which farm belonged to which parish and which parish to which diocese. In the unpopulated mountains, the border mainly followed the water divide. There were disagreements on the parishes of Särna, Idre, Lierne, Kautokeino and Karasjok, which had to be solved by give-and-take. Based on that, in 1752–1765 border cairns were erected between Norway and Sweden i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Roskilde
The Treaty of Roskilde (concluded on 26 February ( OS), or 8 March 1658) ( NS) during the Second Northern War between Frederick III of Denmark–Norway and Karl X Gustav of Sweden in the Danish city of Roskilde. After a devastating defeat, Denmark–Norway was forced to give up a third of its territory to save the rest, the ceded lands comprising Blekinge, Bornholm, Bohuslän (Båhuslen), Scania (Skåne) and Trøndelag, as well as her claims to Halland. After the treaty entered into force, Swedish forces continued to campaign in the remainder of Denmark–Norway, but had to withdraw from the Danish isles and Trøndelag in face of a Danish–Norwegian–Dutch alliance. The Treaty of Copenhagen restored Bornholm to Denmark and Trøndelag to Norway in 1660, while the other provinces transferred in Roskilde remained Swedish. Background As the Northern Wars progressed, Charles X Gustav of Sweden crossed the frozen straits from Jutland and occupied the Danish island of Ze ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halland
Halland () is one of the traditional provinces of Sweden (''landskap''), on the western coast of Götaland, southern Sweden. It borders Västergötland, Småland, Scania and the sea of Kattegat. Until 1645 and the Second Treaty of Brömsebro, it was part of the Kingdom of Denmark. Its name means ''Land of Rocky Slabs'' (Swedish: ''hällar'') referring to the coastal cliffs of the region. Administration The provinces of Sweden serve no administrative function. Instead, that function is served by the Counties of Sweden. However, the province of Halland is almost coextensive with the administrative Halland County, though parts of the province belong to Västra Götaland County and Skåne County, while the county also includes parts of Småland and Västergötland. As of 31 December 2016 Halland had a population of 327,093. Of these, 310,536 lived in Halland County; 14,205 lived in Västra Götaland County; and 2,352 lived in Skåne County. Heraldry During the Danish era unt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |