|
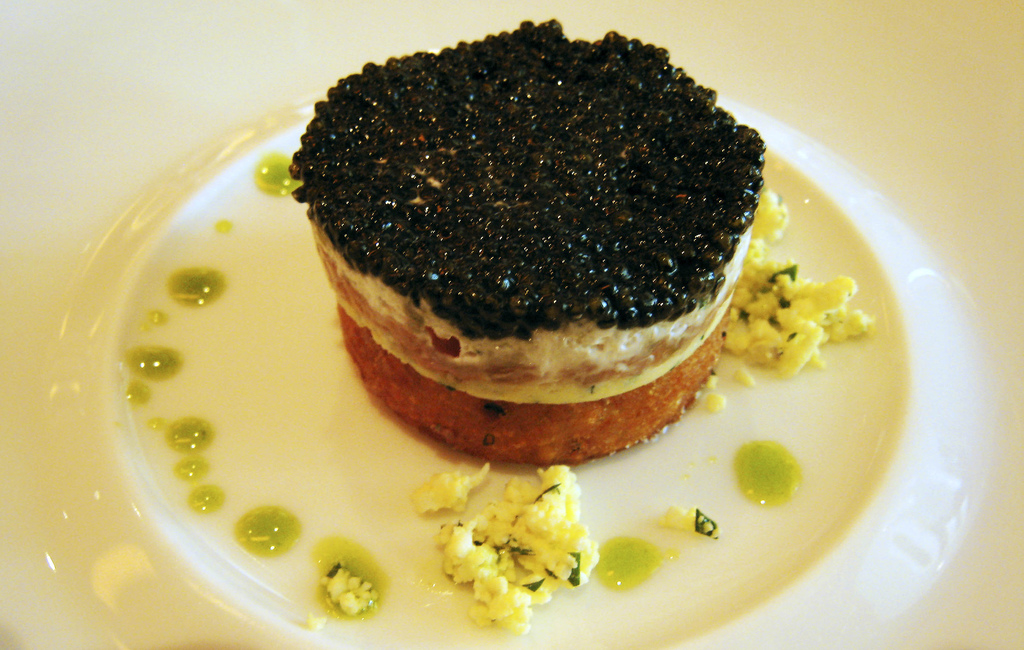
Delicacy
A delicacy is usually a rare and expensive food item that is considered highly desirable, sophisticated, or peculiarly distinctive within a given culture. Irrespective of local preferences, such a label is typically pervasive throughout a region. Often this is because of unusual flavors or characteristics or because it is rare or expensive compared to standard staple foods. Delicacies vary per different countries, customs and ages. Flamingo tongue was a highly prized dish in ancient Rome, but is not commonly eaten in modern times. Lobsters were considered poverty food in North America until the mid-19th century when they started being treated, as they were in Europe, as a delicacy. Some delicacies are confined to a certain culture, such as fugu in Japan, bird's nest soup (made out of swiftlet nests) in China, and ant larvae (escamoles) in Mexico or refer to specific local products, such as porcino, venison or anchovy. Examples of delicacies * Abalone (Bao Yu/Jeonb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fugu
The fugu (; ; ) in Japanese, ''bogeo'' (; 鰒魚) or ''bok'' () in Korean, and ''hétún'' (河豚; 河魨) in Standard Modern Chinese is a pufferfish, normally of the genus '' Takifugu'', '' Lagocephalus'', or '' Sphoeroides'', or a porcupinefish of the genus ''Diodon'', or a dish prepared from these fish. Fugu can be lethally poisonous to humans due to its tetrodotoxin, meaning it must be carefully prepared to remove toxic parts and to avoid contaminating the meat. The restaurant preparation of fugu is strictly controlled by law in Japan and several other countries, and only chefs who have qualified after three or more years of rigorous training are allowed to prepare the fish. Domestic preparation occasionally leads to accidental death. Fugu is served as sashimi and nabemono. The liver was served as a traditional dish named ''fugu-kimo'', being widely thought to be a tasty part, but it is also the most poisonous, and serving this organ in restaurants was banned in Jap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lobster
Lobsters are a family (Nephropidae, synonym Homaridae) of marine crustaceans. They have long bodies with muscular tails and live in crevices or burrows on the sea floor. Three of their five pairs of legs have claws, including the first pair, which are usually much larger than the others. Highly prized as seafood, lobsters are economically important and are often one of the most profitable commodities in coastal areas they populate. Commercially important species include two species of '' Homarus'' from the northern Atlantic Ocean and scampi (which look more like a shrimp, or a "mini lobster")—the Northern Hemisphere genus ''Nephrops'' and the Southern Hemisphere genus ''Metanephrops''. Distinction Although several other groups of crustaceans have the word "lobster" in their names, the unqualified term "lobster" generally refers to the clawed lobsters of the family Nephropidae. Clawed lobsters are not closely related to spiny lobsters or slipper lobsters, which have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
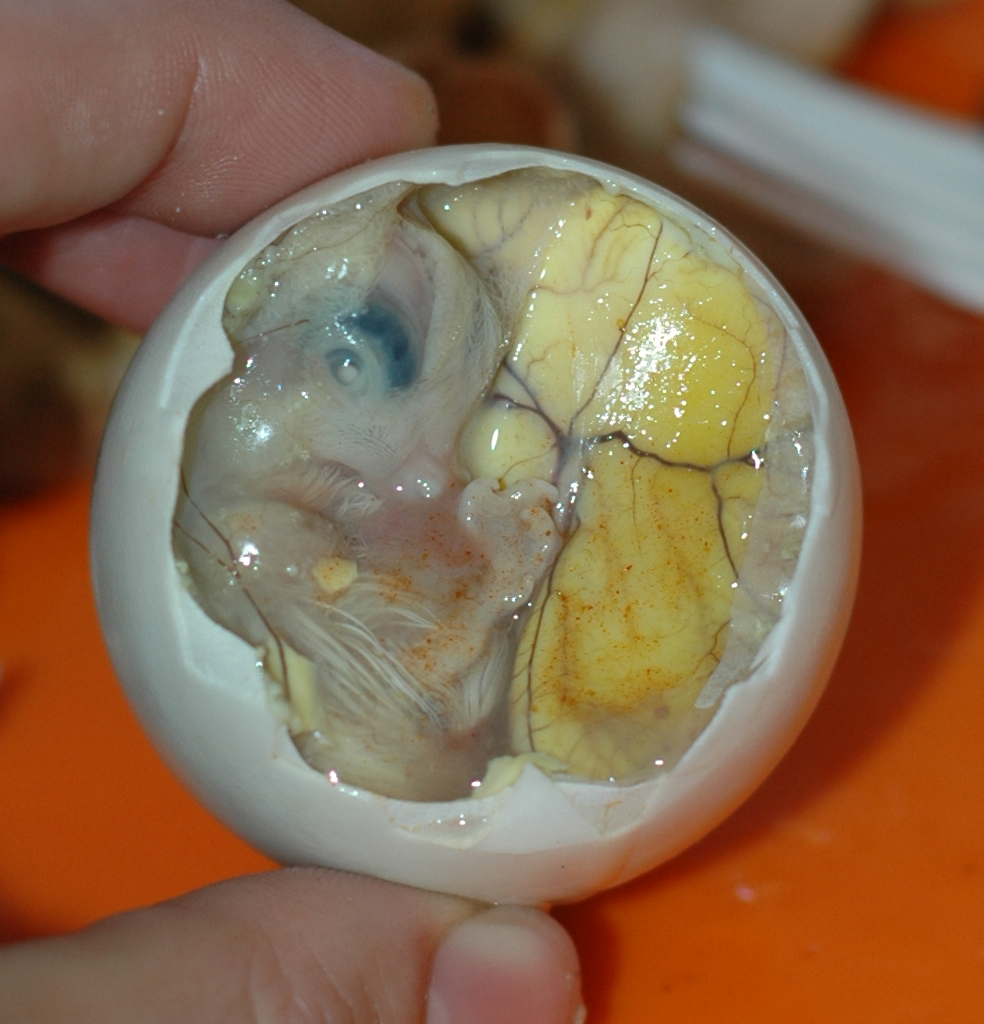
Balut (food)
Balut ( , ; also spelled as balot) is a fertilized developing egg embryo that is boiled or steamed and eaten from the shell. It is commonly sold as street food in South China and Southeast Asian countries, notably the Philippines, Cambodia ( km, ពងទាកូន, ) and Vietnam ( vi, trứng vịt lộn). The term comes from the Filipino language. The length of incubation before the egg is cooked is a matter of local preference, but generally ranges between 14 and 21 days. Description A balut is a fertilized bird egg (usually a duck) which is incubated for a period of 30 to 53 days, depending on the local culture, and then steamed. The contents are eaten directly from the shell. Balut that is incubated for longer periods have a well-developed embryo and the features of the duckling are recognizable. The partially-developed embryo bones are soft enough to chew and swallow as a whole. The mallard duck (''Anas platyrhynchus''), also known as the "Pateros duck", is often used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jellyfish Sesame Oil And Chili Sauce
Jellyfish and sea jellies are the informal common names given to the medusa-phase of certain gelatinous members of the subphylum Medusozoa, a major part of the phylum Cnidaria. Jellyfish are mainly free-swimming marine animals with umbrella-shaped bells and trailing tentacles, although a few are anchored to the seabed by stalks rather than being mobile. The bell can pulsate to provide propulsion for highly efficient locomotion. The tentacles are armed with stinging cells and may be used to capture prey and defend against predators. Jellyfish have a complex life cycle; the medusa is normally the sexual phase, which produces planula larvae that disperse widely and enter a sedentary polyp phase before reaching sexual maturity. Jellyfish are found all over the world, from surface waters to the deep sea. Scyphozoans (the "true jellyfish") are exclusively marine, but some hydrozoans with a similar appearance live in freshwater. Large, often colorful, jellyfish are common in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
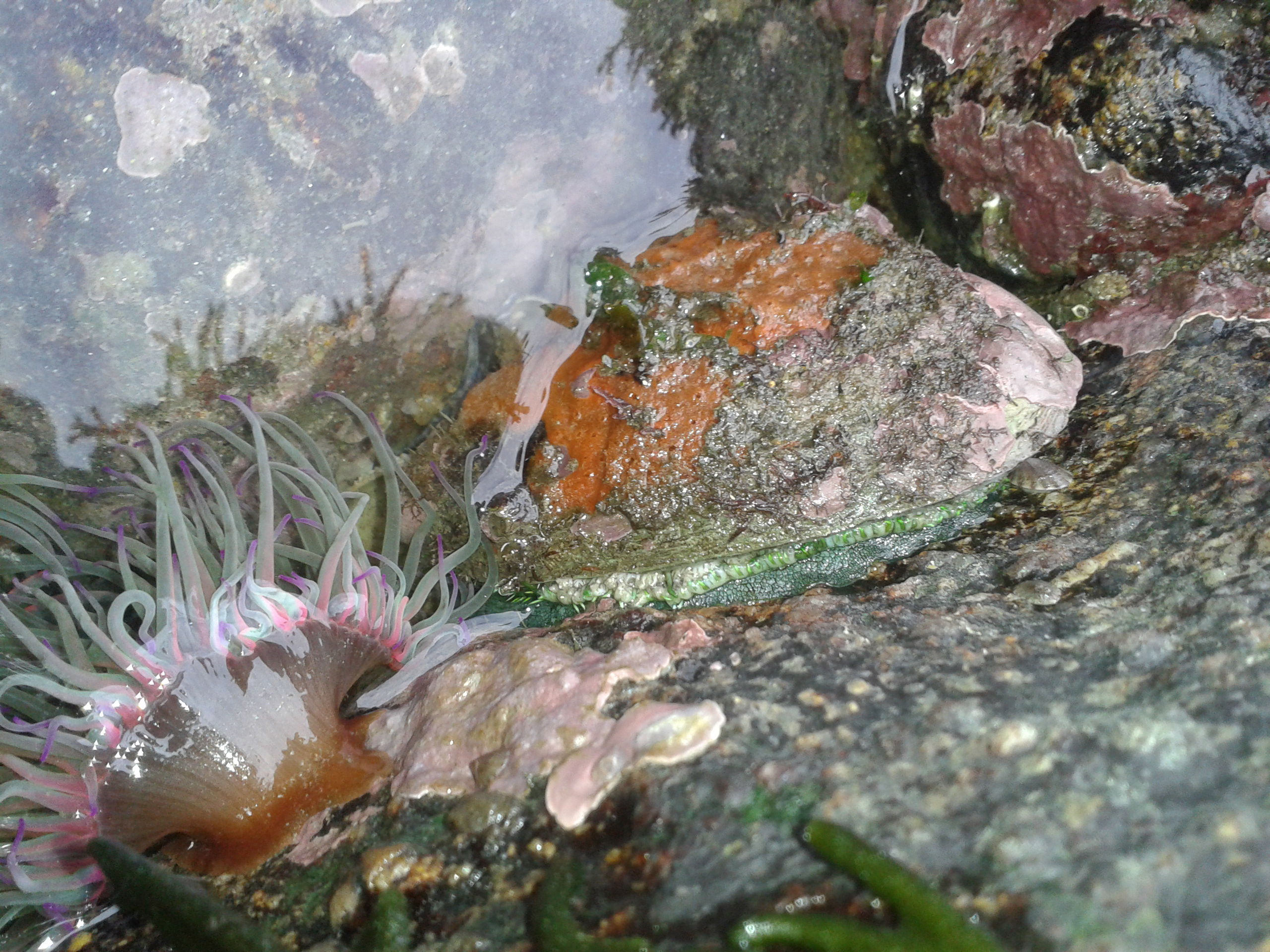
Abalone
Abalone ( or ; via Spanish , from Rumsen ''aulón'') is a common name for any of a group of small to very large marine gastropod molluscs in the family Haliotidae. Other common names are ear shells, sea ears, and, rarely, muttonfish or muttonshells in parts of Australia, ormer in the UK, perlemoen in South Africa, and paua in New Zealand. Abalones are marine snails. Their taxonomy puts them in the family Haliotidae, which contains only one genus, '' Haliotis'', which once contained six subgenera. These subgenera have become alternate representations of ''Haliotis''. The number of species recognized worldwide ranges between 30 and 130 with over 230 species-level taxa described. The most comprehensive treatment of the family considers 56 species valid, with 18 additional subspecies. The shells of abalones have a low, open spiral structure, and are characterized by several open respiratory pores in a row near the shell's outer edge. The thick inner layer of the shell is comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bird's Nest Soup
Edible bird's nests are bird nests created by edible-nest swiftlets, Indian swiftlets, and other swiftlets using solidified saliva, which are harvested for human consumption. They are particularly prized in Chinese culture due to their rarity, high protein content and rich flavor. Edible bird's nests are among the most expensive animal products consumed by humans, with nests being sold at prices up to about , depending on grading. The type or grading of a bird's nest depends on the type of bird as well as the shape and color of the bird's nest. It is usually white in color, but there also exists a red version that is sometimes called "blood" nest. According to traditional Chinese medicine, it promotes good health, especially for the skin. The nests have been used in Chinese cuisine for over 400 years, most often as bird's nest soup. Etymology The Chinese name for edible bird's nest, ('), translates literally as "swallow's (or swift's) nest"; in Indonesia "''sarang burung wal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swiftlet
Swiftlets are birds contained within the four genera ''Aerodramus'', ''Hydrochous'', ''Schoutedenapus'' and ''Collocalia''. They form the Collocaliini tribe within the swift family Apodidae. The group contains around thirty species mostly confined to southern Asia, south Pacific islands, and northeastern Australia, all within the tropical and subtropical regions. They are in many respects typical members of the Apodidae, having narrow wings for fast flight, with a wide gape and small reduced beak surrounded by bristles for catching insects in flight. What distinguishes many but not all species from other swifts and indeed almost all other birdsThe oilbird is a notable exception. The presence of echolocation was formerly used to argue for a close relationship of the Apodiformes and the oilbird, but the actual situation is more complicated. ''See also'': Caprimulgiformes. is their ability to use a simple but effective form of echolocation to navigate in total darkness through the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poverty Food
A famine food or poverty food is any inexpensive or readily available food used to nourish people in times of hunger and starvation, whether caused by extreme poverty, such as during economic depression or war, or by natural disasters such as drought. Foods associated with famine need not be nutritionally deficient, or unsavory. People who eat famine food in large quantity over a long period of time may become averse to it over time. In times of relative affluence, these foods may become the targets of social stigma and rejection. The characterization of some foodstuffs as "famine" or "poverty" food can be social. For example lobster and other crustaceans may be considered poverty food in some societies and luxury food in others depending on time period and situation. Examples A number of foodstuffs have been strongly associated with famine, war, or times of hardship throughout history: *The breadnut or Maya nut was cultivated by the ancient Mayans but is largely rejec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of California Press
The University of California Press, otherwise known as UC Press, is a publishing house associated with the University of California that engages in academic publishing. It was founded in 1893 to publish scholarly and scientific works by faculty of the University of California, established 25 years earlier in 1868, and has been officially headquartered at the university's flagship campus in Berkeley, California, since its inception. As the non-profit publishing arm of the University of California system, the UC Press is fully subsidized by the university and the State of California. A third of its authors are faculty members of the university. The press publishes over 250 new books and almost four dozen multi-issue journals annually, in the humanities, social sciences, and natural sciences, and maintains approximately 4,000 book titles in print. It is also the digital publisher of Collabra and Luminos open access (OA) initiatives. The University of California Press publishes i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akutaq
Alaskan ice cream (also known as Alaskan Indian ice cream, Inuit ice cream, Indian ice cream or Native ice cream, and Inuit-Yupik varieties of which are known as ''akutaq'' or ''akutuq'') is a dessert made by Alaskan Athabaskans and other Alaska Natives. It is traditionally made of whipped fat or tallow (e.g. caribou, moose, or walrus tallow, or seal oil) and meat (such as dried fish, especially pike, sheefish or inconnu, whitefish or cisco, or freshwater whitefishes, or dried moose or caribou) mixed with berries (especially cowberry, bilberry, '' Vaccinium oxycoccos'' or other cranberries, bearberry, crowberry, salmonberry, cloudberry or low-bush salmonberry, raspberry The raspberry is the edible fruit of a multitude of plant species in the genus ''Rubus'' of the rose family, most of which are in the subgenus '' Idaeobatus''. The name also applies to these plants themselves. Raspberries are perennial with ..., blueberry, or Rosa acicularis, prickly rose) or mild ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alaska
Alaska ( ; russian: Аляска, Alyaska; ale, Alax̂sxax̂; ; ems, Alas'kaaq; Yup'ik: ''Alaskaq''; tli, Anáaski) is a state located in the Western United States on the northwest extremity of North America. A semi-exclave of the U.S., it borders the Canadian province of British Columbia and the Yukon territory to the east; it also shares a maritime border with the Russian Federation's Chukotka Autonomous Okrug to the west, just across the Bering Strait. To the north are the Chukchi and Beaufort Seas of the Arctic Ocean, while the Pacific Ocean lies to the south and southwest. Alaska is by far the largest U.S. state by area, comprising more total area than the next three largest states ( Texas, California, and Montana) combined. It represents the seventh-largest subnational division in the world. It is the third-least populous and the most sparsely populated state, but by far the continent's most populous territory located mostly north of the 60th paralle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Canada
Northern Canada, colloquially the North or the Territories, is the vast northernmost region of Canada variously defined by geography and politics. Politically, the term refers to the three territories of Canada: Yukon, Northwest Territories and Nunavut. This area covers about 48 per cent of Canada's total land area, but has less than 1 per cent of Canada's population. The terms "northern Canada" or "the North" may be used in contrast with ''the far north'', which may refer to the Canadian Arctic, the portion of Canada that lies north of the Arctic Circle, east of Alaska and west of Greenland. However, in many other uses the two areas are treated as a single unit. __TOC__ Definitions Subdivisions As a social rather than political region, the Canadian North is often subdivided into two distinct regions based on climate, the ''near north'' and the ''far north''. The different climates of these two regions result in vastly different vegetation, and therefore very different ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |