|
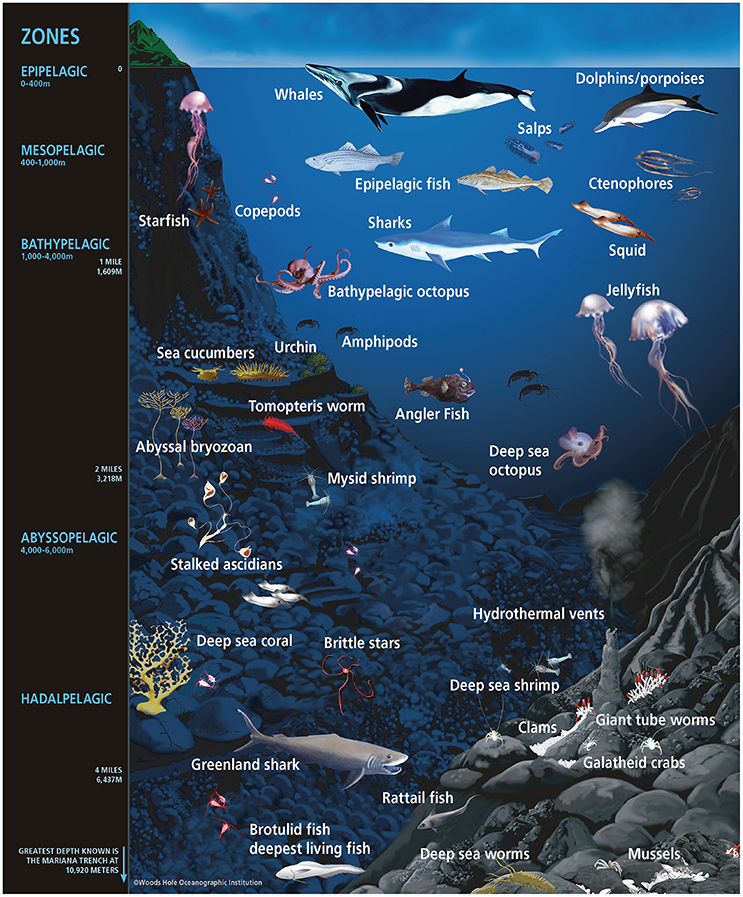
Deep Sea
The deep sea is broadly defined as the ocean depth where light begins to fade, at an approximate depth of 200 metres (656 feet) or the point of transition from continental shelves to continental slopes. Conditions within the deep sea are a combination of low temperatures, darkness and high pressure The deep sea is considered the least explored Earth biome, with the extreme conditions making the environment difficult to access and explore. Organisms living within the deep sea have a variety of adaptations to survive in these conditions. Organisms can survive in the deep sea through a number of feeding methods including scavenging, predation and filtration, with a number of organisms surviving by feeding on marine snow. Marine snow is organic material that has fallen from upper waters into the deep sea. In 1960, the bathyscaphe '' Trieste'' descended to the bottom of the Mariana Trench near Guam, at , the deepest known spot in any ocean. If Mount Everest () were submerged there, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
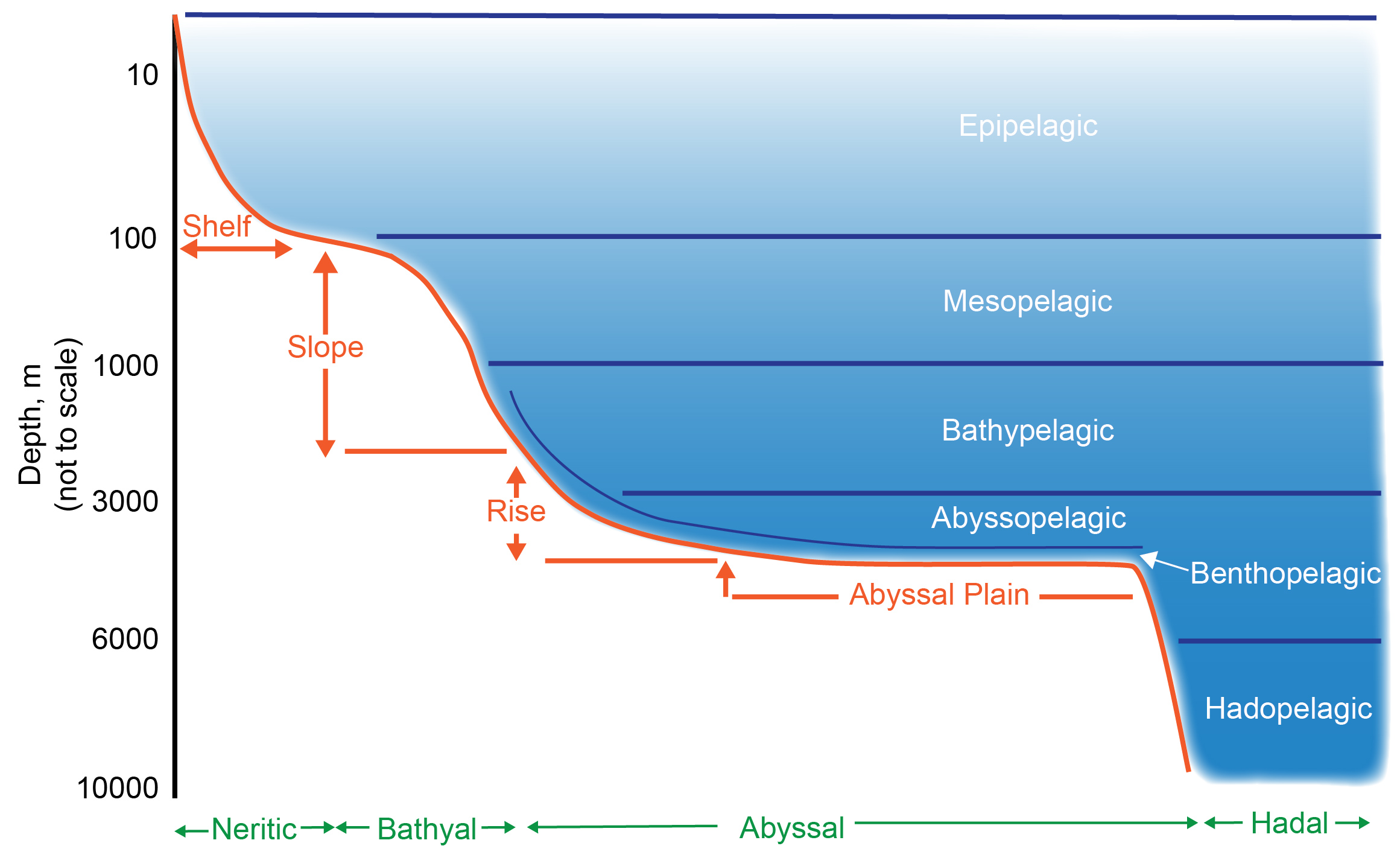
Schematic Representation Of Pelagic And Benthic Zones
A schematic, or schematic diagram, is a designed representation of the elements of a system using abstract, graphic symbols rather than realistic pictures. A schematic usually omits all details that are not relevant to the key information the schematic is intended to convey, and may include oversimplified elements in order to make this essential meaning easier to grasp, as well as additional organization of the information. For example, a subway map intended for passengers may represent a subway station with a dot. The dot is not intended to resemble the actual station at all but aims to give the viewer information without unnecessary visual clutter. A schematic diagram of a chemical process uses symbols in place of detailed representations of the vessels, piping, valves, pumps, and other equipment that compose the system, thus emphasizing the functions of the individual elements and the interconnections among them and suppresses their physical details. In an electronic circuit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmosphere (unit)
The standard atmosphere (symbol: atm) is a unit of pressure defined as Pa. It is sometimes used as a ''reference pressure'' or ''standard pressure''. It is approximately equal to Earth's average atmospheric pressure at sea level. History The standard atmosphere was originally defined as the pressure exerted by 760 mm of mercury at and standard gravity (''g''n = ). It was used as a reference condition for physical and chemical properties, and was implicit in the definition of the Celsius temperature scale, which defined as the boiling point of water at this pressure. In 1954, the 10th General Conference on Weights and Measures (CGPM) adopted ''standard atmosphere'' for general use and affirmed its definition of being precisely equal to dynes per square centimetre (). This defined both temperature and pressure independent of the properties of particular substance. In addition, the CGPM noted that there had been some misapprehension that it "led some physicists to believe t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continental Slope
A continental margin is the outer edge of continental crust abutting oceanic crust under coastal waters. It is one of the three major zones of the ocean floor, the other two being deep-ocean basins and mid-ocean ridges. The continental margin consists of three different features: the continental rise, the continental slope, and the continental shelf. The continental shelf is the relatively shallow water area found in proximity to continents. Continental margins constitute about 28% of the oceanic area. Zones of the continental margin The continental shelf is the portion of the continental margin that transitions from the shore out towards to ocean. Continental shelves are believed to make up 7% of the sea floor. The width of continental shelves worldwide varies in the range of 0.03–1500 km. The continental shelf is generally flat, and ends at the shelf break, where there is a drastic increase in slope angle: The mean angle of continental shelves worldwide is 0° 07� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bathyal Zone
The bathypelagic zone or bathyal zone (from Greek βαθύς (bathýs), deep) is the part of the open ocean that extends from a depth of below the ocean surface. It lies between the mesopelagic above, and the abyssopelagic below. The bathypelagic is known as the midnight zone because of the lack of sunlight; this feature does not allow for photosynthesis-driven primary production, preventing growth of phytoplankton or aquatic plants. Although larger by volume than the photic zone, our knowledge of the bathypelagic zone remains limited by our ability to explore the deep ocean. Physical characteristics The bathypelagic zone is characterized by a nearly constant temperature of approximately and a salinity range of 33-35 g/kg. This region has little to no light, because sunlight does not reach this deep in the ocean and bioluminescence is limited. The hydrostatic pressure in this zone ranges 100-400 atmospheres (atm), due to the increase of 1 atm for every 10 m depth. It is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pelagic Zone
The pelagic zone consists of the water column of the open ocean, and can be further divided into regions by depth (as illustrated on the right). The word ''pelagic'' is derived . The pelagic zone can be thought of as an imaginary cylinder or water column between the surface of the sea and the bottom. Conditions in the water column change with depth: pressure increases; temperature and light decrease; salinity, oxygen, micronutrients (such as iron, magnesium and calcium) all change. Marine life is affected by bathymetry (underwater topography) such as the seafloor, shoreline, or a submarine seamount, as well as by proximity to the boundary between the ocean and the atmosphere at the ocean surface, which brings light for photosynthesis, predation from above, and wind stirring up waves and setting currents in motion. The pelagic zone refers to the open, free waters away from the shore, where marine life can swim freely in any direction unhindered by topographical constraints. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polar Regions Of Earth
The polar regions, also called the frigid zones or polar zones, of Earth are the regions of the planet that surround its geographical poles (the North and South Poles), lying within the polar circles. These high latitudes are dominated by floating sea ice covering much of the Arctic Ocean in the north, and by the Antarctic ice sheet on the continent of Antarctica and the Southern Ocean in the south. Definitions The Arctic has various definitions, including the region north of the Arctic Circle (currently Epoch 2010 at 66°33'44" N), or just the region north of 60° north latitude, or the region from the North Pole north to the timberline. The Antarctic is usually defined simply as south of 60° south latitude, or the continent of Antarctica. The 1959 Antarctic Treaty uses the former definition. The two polar regions are distinguished from the other two climatic and biometric belts of Earth, a tropics belt near the equator, and two middle latitude regions located between t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermohaline Circulation
Thermohaline circulation (THC) is a part of the large-scale ocean circulation that is driven by global density gradients created by surface heat and freshwater fluxes. The adjective ''thermohaline'' derives from '' thermo-'' referring to temperature and ' referring to salt content, factors which together determine the density of sea water. Wind-driven surface currents (such as the Gulf Stream) travel polewards from the equatorial Atlantic Ocean, cooling en route, and eventually sinking at high latitudes (forming North Atlantic Deep Water). This dense water then flows into the ocean basins. While the bulk of it upwells in the Southern Ocean, the oldest waters (with a transit time of about 1000 years) upwell in the North Pacific. Extensive mixing therefore takes place between the ocean basins, reducing differences between them and making the Earth's oceans a global system. The water in these circuits transport both energy (in the form of heat) and mass (dissolved solids an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epipelagic Zone
The photic zone, euphotic zone, epipelagic zone, or sunlight zone is the uppermost layer of a body of water that receives sunlight, allowing phytoplankton to perform photosynthesis. It undergoes a series of physical, chemical, and biological processes that supply nutrients into the upper water column. The photic zone is home to the majority of aquatic life due to the activity (primary production) of the phytoplankton. Photosynthesis in photic zone In the photic zone, the photosynthesis rate exceeds the respiration rate. This is due to the abundant solar energy which is used as an energy source for photosynthesis by primary producers such as phytoplankton. These phytoplankton grow extremely quickly because of sunlight's heavy influence, enabling it to be produced at a fast rate. In fact, ninety five percent of photosynthesis in the ocean occurs in the photic zone. Therefore, if we go deeper, beyond the photic zone, such as into the compensation point, there is little to no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homogeneous
Homogeneity and heterogeneity are concepts often used in the sciences and statistics relating to the uniformity of a substance or organism. A material or image that is homogeneous is uniform in composition or character (i.e. color, shape, size, weight, height, distribution, texture, language, income, disease, temperature, radioactivity, architectural design, etc.); one that is heterogeneous is distinctly nonuniform in at least one of these qualities. Heterogeneous Mixtures, in chemistry, is where certain elements are unwillingly combined and, when given the option, will separate. Etymology and spelling The words ''homogeneous'' and ''heterogeneous'' come from Medieval Latin ''homogeneus'' and ''heterogeneus'', from Ancient Greek ὁμογενής (''homogenēs'') and ἑτερογενής (''heterogenēs''), from ὁμός (''homos'', “same”) and ἕτερος (''heteros'', “other, another, different”) respectively, followed by γένος (''genos'', “kind”); - ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Sea
The Red Sea ( ar, البحر الأحمر - بحر القلزم, translit=Modern: al-Baḥr al-ʾAḥmar, Medieval: Baḥr al-Qulzum; or ; Coptic: ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϩⲁϩ ''Phiom Enhah'' or ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϣⲁⲣⲓ ''Phiom ǹšari''; Tigrinya: ቀይሕ ባሕሪ ''Qeyih Bahri''; ) is a seawater inlet of the Indian Ocean, lying between Africa and Asia. Its connection to the ocean is in the south, through the Bab el Mandeb strait and the Gulf of Aden. To its north lie the Sinai Peninsula, the Gulf of Aqaba, and the Gulf of Suez (leading to the Suez Canal). It is underlain by the Red Sea Rift, which is part of the Great Rift Valley. The Red Sea has a surface area of roughly 438,000 km2 (169,100 mi2), is about 2250 km (1398 mi) long, and — at its widest point — 355 km (220.6 mi) wide. It has an average depth of 490 m (1,608 ft), and in the central ''Suakin Trough'' it reaches its maximum depth of . The Red Sea also ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the east by the Levant. The Sea has played a central role in the history of Western civilization. Geological evidence indicates that around 5.9 million years ago, the Mediterranean was cut off from the Atlantic and was partly or completely desiccated over a period of some 600,000 years during the Messinian salinity crisis before being refilled by the Zanclean flood about 5.3 million years ago. The Mediterranean Sea covers an area of about , representing 0.7% of the global ocean surface, but its connection to the Atlantic via the Strait of Gibraltar—the narrow strait that connects the Atlantic Ocean to the Mediterranean Sea and separates the Iberian Peninsula in Europe from Morocco in Africa—is only wide. The Mediterranean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geological Survey Of Denmark And Greenland
The Geological Survey of Denmark and Greenland ( da, Danmarks og Grønlands Geologiske Undersøgelse, GEUS) is the independent sector research institute under the Danish Ministry of Climate and Energy. GEUS is an advisory, research and survey institute in hydrogeology, geophysics, geochemistry, stratigraphy, glaciology, ore geology, marine geology, mineralogy, climatology, environmental history, air photo interpretation, geothermal energy fields concerning Denmark and Greenland. GEUS works in close corporation with Geologisk Institut and Geologisk Museum, both part of University of Copenhagen The University of Copenhagen ( da, Københavns Universitet, KU) is a prestigious public university, public research university in Copenhagen, Copenhagen, Denmark. Founded in 1479, the University of Copenhagen is the second-oldest university in .... It publishes a service paper called ''Greenland Hydrocarbon Exploration Information Service'' (GHEXIS) and a newsletter called Greenl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |