|
Deep-level Transient Spectroscopy
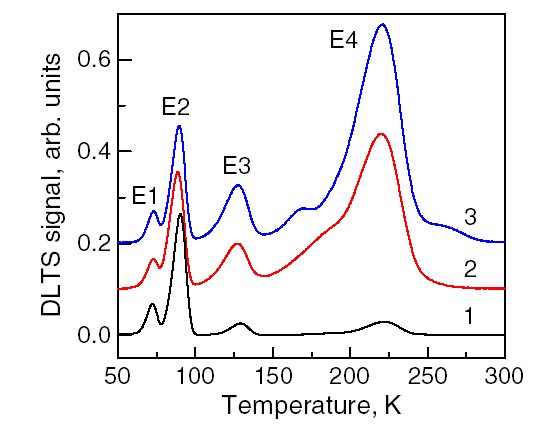
Deep-level transient spectroscopy (DLTS) is an experimental tool for studying electrically active defects (known as charge carrier traps) in semiconductors. DLTS establishes fundamental defect parameters and measures their concentration in the material. Some of the parameters are considered as defect "finger prints" used for their identifications and analysis. DLTS investigates defects present in a space charge ( depletion) region of a simple electronic device. The most commonly used are Schottky diodes or p-n junctions. In the measurement process the steady-state diode reverse polarization voltage is disturbed by a voltage pulse. This voltage pulse reduces the electric field in the space charge region and allows free carriers from the semiconductor bulk to penetrate this region and recharge the defects causing their non-equilibrium charge state. After the pulse, when the voltage returns to its steady-state value, the defects start to emit trapped carriers due to the thermal emis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charge Carrier
In physics, a charge carrier is a particle or quasiparticle that is free to move, carrying an electric charge, especially the particles that carry electric charges in electrical conductors. Examples are electrons, ions and holes. The term is used most commonly in solid state physics. In a conducting medium, an electric field can exert force on these free particles, causing a net motion of the particles through the medium; this is what constitutes an electric current. In conducting media, particles serve to carry charge: *In many metals, the charge carriers are electrons. One or two of the valence electrons from each atom are able to move about freely within the crystal structure of the metal. The free electrons are referred to as conduction electrons, and the cloud of free electrons is called a Fermi gas. Many metals have electron and hole bands. In some, the majority carriers are holes. *In electrolytes, such as salt water, the charge carriers are ions, which are a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arrhenius Equation
In physical chemistry, the Arrhenius equation is a formula for the temperature dependence of reaction rates. The equation was proposed by Svante Arrhenius in 1889, based on the work of Dutch chemist Jacobus Henricus van 't Hoff who had noted in 1884 that the van 't Hoff equation for the temperature dependence of equilibrium constants suggests such a formula for the rates of both forward and reverse reactions. This equation has a vast and important application in determining the rate of chemical reactions and for calculation of energy of activation. Arrhenius provided a physical justification and interpretation for the formula. Laidler, K. J. (1987) ''Chemical Kinetics'', Third Edition, Harper & Row, p. 42 Currently, it is best seen as an empirical relationship.Kenneth Connors, Chemical Kinetics, 1990, VCH Publishers It can be used to model the temperature variation of diffusion coefficients, population of crystal vacancies, creep rates, and many other thermally-induced processes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stress (physics)
In continuum mechanics, stress is a physical quantity. It is a quantity that describes the magnitude of forces that cause deformation. Stress is defined as ''force per unit area''. When an object is pulled apart by a force it will cause elongation which is also known as deformation, like the stretching of an elastic band, it is called tensile stress. But, when the forces result in the compression of an object, it is called compressive stress. It results when forces like tension or compression act on a body. The greater this force and the smaller the cross-sectional area of the body on which it acts, the greater the stress. Therefore, stress is measured in newton per square meter (N/m2) or pascal (Pa). Stress expresses the internal forces that neighbouring particles of a continuous material exert on each other, while strain is the measure of the deformation of the material. For example, when a solid vertical bar is supporting an overhead weight, each particle in the bar pushe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inverse Laplace Transform
In mathematics, the inverse Laplace transform of a function ''F''(''s'') is the piecewise-continuous and exponentially-restricted real function ''f''(''t'') which has the property: :\mathcal\(s) = \mathcal\(s) = F(s), where \mathcal denotes the Laplace transform. It can be proven that, if a function ''F''(''s'') has the inverse Laplace transform ''f''(''t''), then ''f''(''t'') is uniquely determined (considering functions which differ from each other only on a point set having Lebesgue measure zero as the same). This result was first proven by Mathias Lerch in 1903 and is known as Lerch's theorem. The Laplace transform and the inverse Laplace transform together have a number of properties that make them useful for analysing linear dynamical systems. Mellin's inverse formula An integral formula for the inverse Laplace transform, called the ''Mellin's inverse formula'', the ''Bromwich integral'', or the '' Fourier– Mellin integral'', is given by the line integral: :f(t) = \ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digitizing
DigitizationTech Target. (2011, April). Definition: digitization. ''WhatIs.com''. Retrieved December 15, 2021, from https://whatis.techtarget.com/definition/digitization is the process of converting information into a digital (i.e. computer-readable) format.Collins Dictionary. (n.d.). Definition of 'digitize'. Retrieved December 15, 2021, from https://www.collinsdictionary.com/dictionary/english/digitize The result is the representation of an object, image, sound, document, or signal (usually an analog signal) obtained by generating a series of numbers that describe a discrete set of points or samples. The result is called '' digital representation'' or, more specifically, a '' digital image'', for the object, and ''digital form'', for the signal. In modern practice, the digitized data is in the form of binary numbers, which facilitates processing by digital computers and other operations, but digitizing simply means "the conversion of analog source material into a numer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laplace Transform
In mathematics, the Laplace transform, named after its discoverer Pierre-Simon Laplace (), is an integral transform that converts a function of a real variable (usually t, in the '' time domain'') to a function of a complex variable s (in the complex frequency domain, also known as ''s''-domain, or s-plane). The transform has many applications in science and engineering because it is a tool for solving differential equations. In particular, it transforms ordinary differential equations into algebraic equations and convolution into multiplication. For suitable functions ''f'', the Laplace transform is the integral \mathcal\(s) = \int_0^\infty f(t)e^ \, dt. History The Laplace transform is named after mathematician and astronomer Pierre-Simon, marquis de Laplace, who used a similar transform in his work on probability theory. Laplace wrote extensively about the use of generating functions in ''Essai philosophique sur les probabilités'' (1814), and the integral form of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lapl2
The Los Angeles Public Library system (LAPL) is a public library system in Los Angeles, California. The system holds more than six million volumes, and with around 19 million residents in the Greater Los Angeles, Los Angeles Metropolitan area, it serves the largest population of any public library system in the United States. The system is overseen by a Board of Library Commissioners with five members appointed by the mayor of Los Angeles in staggered terms. In 1997 a local historian described it as "one of the biggest and best-regarded library systems in the nation." History The Los Angeles Library Association was formed in late 1872, and by early 1873, a well-stocked reading room had opened in the Downey Block at Temple and Main streets under the first librarian, John Littlefield. The original library consisted of two rooms. The larger room was called the "Book Room," and the smaller room was called the "Conversation Room," which contained newspapers, tables, chairs, and sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronic Band Structure
In solid-state physics, the electronic band structure (or simply band structure) of a solid describes the range of energy levels that electrons may have within it, as well as the ranges of energy that they may not have (called ''band gaps'' or ''forbidden bands''). Band theory derives these bands and band gaps by examining the allowed quantum mechanical wave functions for an electron in a large, periodic lattice of atoms or molecules. Band theory has been successfully used to explain many physical properties of solids, such as electrical resistivity and optical absorption, and forms the foundation of the understanding of all solid-state devices (transistors, solar cells, etc.). Why bands and band gaps occur The electrons of a single, isolated atom occupy atomic orbitals each of which has a discrete energy level. When two or more atoms join together to form a molecule, their atomic orbitals overlap and hybridize. Similarly, if a large number ''N'' of identical atoms co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photon
A photon () is an elementary particle that is a quantum of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are massless, so they always move at the speed of light in vacuum, (or about ). The photon belongs to the class of bosons. As with other elementary particles, photons are best explained by quantum mechanics and exhibit wave–particle duality, their behavior featuring properties of both waves and particles. The modern photon concept originated during the first two decades of the 20th century with the work of Albert Einstein, who built upon the research of Max Planck. While trying to explain how matter and electromagnetic radiation could be in thermal equilibrium with one another, Planck proposed that the energy stored within a material object should be regarded as composed of an integer number of discrete, equal-sized parts. To explain the photoelectr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charge Carriers In Semiconductors
In physics, a charge carrier is a particle or quasiparticle that is free to move, carrying an electric charge, especially the particles that carry electric charges in electrical conductors. Examples are electrons, ions and holes. The term is used most commonly in solid state physics. In a conducting medium, an electric field can exert force on these free particles, causing a net motion of the particles through the medium; this is what constitutes an electric current. In conducting media, particles serve to carry charge: *In many metals, the charge carriers are electrons. One or two of the valence electrons from each atom are able to move about freely within the crystal structure of the metal. The free electrons are referred to as conduction electrons, and the cloud of free electrons is called a Fermi gas. Many metals have electron and hole bands. In some, the majority carriers are holes. *In electrolytes, such as salt water, the charge carriers are ions, which are atoms or mole ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perovskite Solar Cell
A perovskite solar cell (PSC) is a type of solar cell that includes a perovskite-structured compound, most commonly a hybrid organic–inorganic lead or tin halide-based material as the light-harvesting active layer. Perovskite materials, such as methylammonium lead halides and all-inorganic caesium lead halide, are cheap to produce and simple to manufacture. Efficiencies of laboratory-scale devices using these materials have increased from 3.8% in 2009 to 25.7% in 2021 in single-junction architectures, and, in silicon-based tandem cells, to 29.8%, exceeding the maximum efficiency achieved in single-junction silicon solar cells. Perovskite solar cells have therefore been the fastest-advancing solar technology . With the potential of achieving even higher efficiencies and very low production costs, perovskite solar cells have become commercially attractive. Core problems and research subjects include their short- and long-term stability. Advantages The raw materials used and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |