|
DNA Damage Theory Of Aging
The DNA damage theory of aging proposes that aging is a consequence of unrepaired accumulation of naturally occurring DNA damage. Damage in this context is a DNA alteration that has an abnormal structure. Although both mitochondrial and nuclear DNA damage can contribute to aging, nuclear DNA is the main subject of this analysis. Nuclear DNA damage can contribute to aging either indirectly (by increasing apoptosis or cellular senescence) or directly (by increasing cell dysfunction). Several review articles have shown that deficient DNA repair, allowing greater accumulation of DNA damage, causes premature aging; and that increased DNA repair facilitates greater longevity. Mouse models of nucleotide-excision–repair syndromes reveal a striking correlation between the degree to which specific DNA repair pathways are compromised and the severity of accelerated aging, strongly suggesting a causal relationship. Human population studies show that single-nucleotide polymorphisms in D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aging
Ageing ( BE) or aging ( AE) is the process of becoming older. The term refers mainly to humans, many other animals, and fungi, whereas for example, bacteria, perennial plants and some simple animals are potentially biologically immortal. In a broader sense, ageing can refer to single cells within an organism which have ceased dividing, or to the population of a species. In humans, ageing represents the accumulation of changes in a human being over time and can encompass physical, psychological, and social changes. Reaction time, for example, may slow with age, while memories and general knowledge typically increase. Ageing increases the risk of human diseases such as cancer, Alzheimer's disease, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, stroke and many more. Of the roughly 150,000 people who die each day across the globe, about two-thirds die from age-related causes. Current ageing theories are assigned to the damage concept, whereby the accumulation of damage (such as DNA ox ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon
A polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) is a class of organic compounds that is composed of multiple aromatic rings. The simplest representative is naphthalene, having two aromatic rings and the three-ring compounds anthracene and phenanthrene. PAHs are uncharged, non-polar and planar. Many are colorless. Many of them are found in coal and in oil deposits, and are also produced by the combustion of organic matter—for example, in engines and incinerators or when biomass burns in forest fires. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons are discussed as possible starting materials for abiotic syntheses of materials required by the earliest forms of life. Nomenclature and structure The terms polyaromatic hydrocarbon or polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbon are also used for this concept. By definition, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons have multiple rings, precluding benzene from being considered a PAH. Some sources, such as the US EPA and CDC, consider naphthalene to be the simplest PAH. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
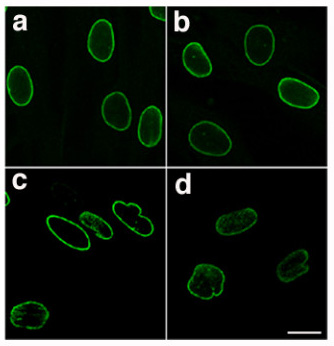
Lamin
Lamins, also known as nuclear lamins are fibrous proteins in type V intermediate filaments, providing structural function and transcriptional regulation in the cell nucleus. Nuclear lamins interact with inner nuclear membrane proteins to form the nuclear lamina on the interior of the nuclear envelope. Lamins have elastic and mechanosensitive properties, and can alter gene regulation in a feedback response to mechanical cues. Lamins are present in all animals but are not found in microorganisms, plants or fungi. Lamin proteins are involved in the disassembling and reforming of the nuclear envelope during mitosis, the positioning of nuclear pores, and programmed cell death. Mutations in lamin genes can result in several genetic laminopathies, which may be life-threatening. History Lamins were first identified in the cell nucleus, using electron-microscopy. However, they were not recognized as vital components of nuclear structural support until 1975. During this time period, inv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Base Excision Repair
Base excision repair (BER) is a cellular mechanism, studied in the fields of biochemistry and genetics, that repairs damaged DNA throughout the cell cycle. It is responsible primarily for removing small, non-helix-distorting base lesions from the genome. The related nucleotide excision repair pathway repairs bulky helix-distorting lesions. BER is important for removing damaged bases that could otherwise cause mutations by mispairing or lead to breaks in DNA during replication. BER is initiated by DNA glycosylases, which recognize and remove specific damaged or inappropriate bases, forming AP sites. These are then cleaved by an AP endonuclease. The resulting single-strand break can then be processed by either short-patch (where a single nucleotide is replaced) or long-patch BER (where 2–10 new nucleotides are synthesized). Lesions processed by BER Single bases in DNA can be chemically damaged by a variety of mechanisms, the most common ones being deamination, oxidation, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cockayne Syndrome
Cockayne syndrome (CS), also called Neill-Dingwall syndrome, is a rare and fatal autosomal recessive neurodegenerative disorder characterized by growth failure, impaired development of the nervous system, abnormal sensitivity to sunlight (photosensitivity), eye disorders and premature aging.Bender M, Potocki L, Metry D. What syndrome is this? Cockayne syndrome. Pediatric Dermatology erial online November 2003;20(6):538-540. Available from: MEDLINE with Full Text, Ipswich, MA. Accessed April 30, 2015. Failure to thrive and neurological disorders are criteria for diagnosis, while photosensitivity, hearing loss, eye abnormalities, and cavities are other very common features. Problems with any or all of the internal organs are possible. It is associated with a group of disorders called leukodystrophies, which are conditions characterized by degradation of neurological white matter. The underlying disorder is a defect in a DNA repair mechanism. Unlike other defects of DNA repair, pati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huchinson–Gilford Progeria
Progeria is a specific type of progeroid syndrome, also known as Hutchinson–Gilford syndrome. A single gene mutation is responsible for progeria. The gene, known as lamin A (LMNA), makes a protein necessary for holding the Nucleus of the cell together. When this gene gets mutated an abnormal form of lamin A protein called Progerin is produced. Progeroid syndromes are a group of diseases that causes individuals to age faster than usual, leading to them appearing older than they actually are. Patients born with progeria typically live to an age of mid-teens to early twenties. Severe cardiovascular complications usually develop by puberty, resulting in death. Signs and symptoms Children with progeria usually develop the first symptoms during their first few months of life. The earliest symptoms may include a failure to thrive and a localized scleroderma-like skin condition. As a child ages past infancy, additional conditions become apparent, usually around 18–24 months. Limite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Werner Syndrome
Werner syndrome (WS) or Werner's syndrome, also known as "adult progeria",James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005). ''Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology''. (10th ed.). Saunders. . is a rare, autosomal recessive disorder which is characterized by the appearance of premature aging. Werner syndrome is named after the German scientist Otto Werner. He identified the syndrome in four siblings observed with premature aging, which he explored as the subject of his dissertation of 1904. It has a global incidence rate of less than 1 in 100,000 live births (although incidence in Japan and Sardinia is higher, affecting 1 in 20,000–40,000 and 1 in 50,000, respectively). 1,300 cases had been reported as of 2006. Affected individuals typically grow and develop normally until puberty; the mean age of diagnosis is twenty-four, often realized when the adolescent growth spurt is not observed. The youngest person diagnosed was six years old. The median and mean ages of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skeletal Striated Muscle
Skeletal muscles (commonly referred to as muscles) are organs of the vertebrate muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The muscle cells of skeletal muscles are much longer than in the other types of muscle tissue, and are often known as muscle fibers. The muscle tissue of a skeletal muscle is striated – having a striped appearance due to the arrangement of the sarcomeres. Skeletal muscles are voluntary muscles under the control of the somatic nervous system. The other types of muscle are cardiac muscle which is also striated and smooth muscle which is non-striated; both of these types of muscle tissue are classified as involuntary, or, under the control of the autonomic nervous system. A skeletal muscle contains multiple fascicles – bundles of muscle fibers. Each individual fiber, and each muscle is surrounded by a type of connective tissue layer of fascia. Muscle fibers are formed from the fusion of developmental myoblasts in a proc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reactive Oxygen Species
In chemistry, reactive oxygen species (ROS) are highly reactive chemicals formed from diatomic oxygen (). Examples of ROS include peroxides, superoxide, hydroxyl radical, singlet oxygen, and alpha-oxygen. The reduction of molecular oxygen () produces superoxide (), which is the precursor to most other reactive oxygen species: :O2 + e^- -> \ ^\bullet O2- Dismutation of superoxide produces hydrogen peroxide (): :2 H+ + \ ^\bullet O2^- + \ ^\bullet O2^- -> H2O2 + O2 Hydrogen peroxide in turn may be partially reduced, thus forming hydroxide ions and hydroxyl radicals (), or fully reduced to water: :H2O2 + e^- -> HO^- + \ ^\bullet OH :2 H+ + 2 e- + H2O2 -> 2 H2O In a biological context, ROS are byproducts of the normal metabolism of oxygen. ROS have roles in cell signaling and homeostasis. ROS are intrinsic to cellular functioning, and are present at low and stationary levels in normal cells. In plants, ROS are involved in metabolic processes related to photoprotection and toleran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mouse Brain
The mouse brain refers to the brain of Mus musculus. Various brain atlases exist. For reasons of reproducibility, genetically characterized, stable strains like C57BL/6 were chosen to produce high-resolution images and databases. Well known online resources include: *Allen Brain Atlas * Mouse Brain LibraryHigh resolution mouse brain atlas*BrainMaps High-Resolution Brain Maps and Brain Atlases of ''Mus musculus'' Despite superficial differences, especially in size and weight, the mouse brain and its function can serve as a powerful animal model for study of human brain diseases or mental disorders (see e.g. Reeler, Chakragati mouse). This is because the genes responsible for building and operating both mouse and human brain are 90% identical. Transgenic mouse lines also allow neuroscientists to specifically target the labeling of certain cell types to probe the neural basis of fundamental processes. Anatomy The cerebral cortex of a mouse has around 8–14 million neurons while in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
8-oxo-2'-deoxyguanosine
8-Oxo-2'-deoxyguanosine (8-oxo-dG) is an oxidized derivative of deoxyguanosine. 8-Oxo-dG is one of the major products of DNA oxidation. Concentrations of 8-oxo-dG within a cell are a measurement of oxidative stress. In DNA Steady-state levels of DNA damages represent the balance between formation and repair. Swenberg et al. measured average frequencies of steady state endogenous DNA damages in mammalian cells. The most frequent oxidative DNA damage normally present in DNA is 8-oxo-dG, occurring at an average frequency of 2,400 per cell. When 8-oxo-dG is induced by a DNA damaging agent it is rapidly repaired. For example, 8-oxo-dG was increased 10-fold in the livers of mice subjected to ionizing radiation, but the excess 8-oxo-dG was rapidly removed with a half-life of 11 minutes. As reviewed by Valavanidis et al. increased levels of 8-oxo-dG in a tissue can serve as a biomarker of oxidative stress. They also noted that increased levels of 8-oxo-dG are frequently found d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nova Science Publishers, Inc
A nova (plural novae or novas) is a transient astronomical event that causes the sudden appearance of a bright, apparently "new" star (hence the name "nova", which is Latin for "new") that slowly fades over weeks or months. Causes of the dramatic appearance of a nova vary, depending on the circumstances of the two progenitor stars. All observed novae involve white dwarfs in close binary systems. The main sub-classes of novae are classical novae, recurrent novae (RNe), and dwarf novae. They are all considered to be cataclysmic variable stars. Classical nova eruptions are the most common type. They are likely created in a close binary star system consisting of a white dwarf and either a main sequence, subgiant, or red giant star. When the orbital period falls in the range of several days to one day, the white dwarf is close enough to its companion star to start drawing accreted matter onto the surface of the white dwarf, which creates a dense but shallow atmosphere. This atmosphe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)



_and_with_tumorigenesis_(B)._Brown_shows_8-oxo-dG.jpg)
