|
Cytomel
Liothyronine is a manufactured form of the thyroid hormone triiodothyronine (T3). It is most commonly used to treat hypothyroidism and myxedema coma. It can be taken by mouth or by injection into a vein. Side effects may occur from excessive doses. This may include weight loss, fever, headache, anxiety, trouble sleeping, arrythmias, and heart failure. Use in pregnancy and breastfeeding is generally safe. Regular blood tests are recommended to verify the appropriateness of the dose being taken. Liothyronine was approved for medical use in 1956. It is available as a generic medication. In 2020, it was the 218th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 2million prescriptions. Medical uses Liothyronine may be used when there is an impaired conversion of T4 to T3 in peripheral tissues. The dose of liothyronine for hypothyroidism is a lower amount than levothyroxine due it being a higher concentrated synthetic medication. About 25 μg of liot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triiodothyronine
Triiodothyronine, also known as T3, is a thyroid hormone. It affects almost every physiological process in the body, including growth and development, metabolism, body temperature, and heart rate. Production of T3 and its prohormone thyroxine (T4) is activated by thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which is released from the anterior pituitary gland. This pathway is part of a closed-loop feedback process: Elevated concentrations of T3, and T4 in the blood plasma inhibit the production of TSH in the anterior pituitary gland. As concentrations of these hormones decrease, the anterior pituitary gland increases production of TSH, and by these processes, a feedback control system stabilizes the level of thyroid hormones in the bloodstream. T3 is the true hormone. Its effects on target tissues are roughly four times more potent than those of T4. Of the thyroid hormone that is produced, just about 20% is T3, whereas 80% is produced as T4. Roughly 85% of the circulating T3 is later ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triiodothyronine
Triiodothyronine, also known as T3, is a thyroid hormone. It affects almost every physiological process in the body, including growth and development, metabolism, body temperature, and heart rate. Production of T3 and its prohormone thyroxine (T4) is activated by thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which is released from the anterior pituitary gland. This pathway is part of a closed-loop feedback process: Elevated concentrations of T3, and T4 in the blood plasma inhibit the production of TSH in the anterior pituitary gland. As concentrations of these hormones decrease, the anterior pituitary gland increases production of TSH, and by these processes, a feedback control system stabilizes the level of thyroid hormones in the bloodstream. T3 is the true hormone. Its effects on target tissues are roughly four times more potent than those of T4. Of the thyroid hormone that is produced, just about 20% is T3, whereas 80% is produced as T4. Roughly 85% of the circulating T3 is later ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
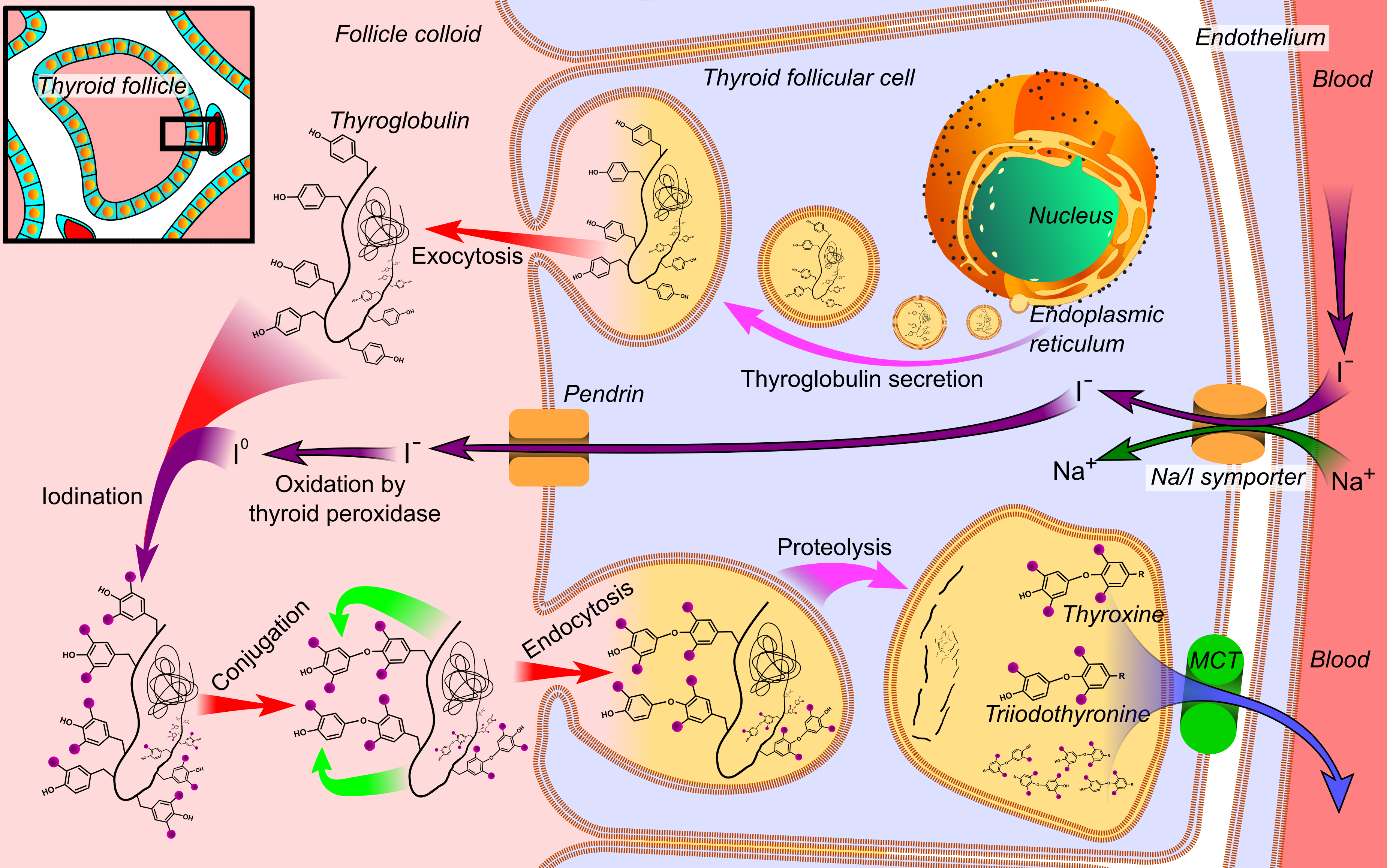
Thyroid Hormones
File:Thyroid_system.svg, upright=1.5, The thyroid system of the thyroid hormones T3 and T4 rect 376 268 820 433 Thyroid-stimulating hormone rect 411 200 849 266 Thyrotropin-releasing hormone rect 297 168 502 200 Hypothalamus rect 66 216 386 256 Anterior pituitary gland rect 66 332 342 374 Negative feedback rect 308 436 510 475 Thyroid gland rect 256 539 563 635 Thyroid hormones rect 357 827 569 856 Catecholamine rect 399 716 591 750 Metabolism desc bottom-left Thyroid hormones are any hormones produced and released by the thyroid gland, namely triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4). They are tyrosine-based hormones that are primarily responsible for regulation of metabolism. T3 and T4 are partially composed of iodine. A deficiency of iodine leads to decreased production of T3 and T4, enlarges the thyroid tissue and will cause the disease known as simple goitre. The major form of thyroid hormone in the blood is thyroxine (T4), whose half-life of around one week is long ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasma Protein Binding
Plasma protein binding refers to the degree to which medications attach to proteins within the blood. A drug's efficiency may be affected by the degree to which it binds. The less bound a drug is, the more efficiently it can traverse or diffuse through cell membranes. Common blood proteins that drugs bind to are human serum albumin, lipoprotein, glycoprotein, and α, β‚ and γ globulins. Binding (drug distribution) A drug in blood exists in two forms: bound and unbound. Depending on a specific drug's affinity for plasma proteins, a proportion of the drug may become bound to the proteins, with the remainder being unbound. If the protein binding is reversible, then a chemical equilibrium will exist between the bound and unbound states, such that: :Protein + drug ⇌ Protein-drug complex Notably, it is the unbound fraction which exhibits pharmacologic effects. It is also the fraction that may be metabolized and/or excreted. For example, the "fraction bound" of the anticoagu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Nervous System
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all parts of the bodies of bilaterally symmetric and triploblastic animals—that is, all multicellular animals except sponges and diploblasts. It is a structure composed of nervous tissue positioned along the rostral (nose end) to caudal (tail end) axis of the body and may have an enlarged section at the rostral end which is a brain. Only arthropods, cephalopods and vertebrates have a true brain (precursor structures exist in onychophorans, gastropods and lancelets). The rest of this article exclusively discusses the vertebrate central nervous system, which is radically distinct from all other animals. Overview In vertebrates, the brain and spinal cord are both enclosed in the meninges. The meninges provide a barrier to chemicals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SSRI
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are a class of drugs that are typically used as antidepressants in the treatment of major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, and other psychological conditions. SSRIs increase the extracellular level of the neurotransmitter serotonin by limiting its reabsorption (reuptake) into the presynaptic cell. They have varying degrees of selectivity for the other monoamine transporters, with pure SSRIs having strong affinity for the serotonin transporter and only weak affinity for the norepinephrine and dopamine transporters. SSRIs are the most widely prescribed antidepressants in many countries. The efficacy of SSRIs in mild or moderate cases of depression has been disputed and may or may not be outweighed by side effects, especially in adolescent populations. Medical uses The main indication for SSRIs is major depressive disorder; however, they are frequently prescribed for anxiety disorders, such as social anxiety disorder, gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Permissiveness (biology)
In endocrinology, permissiveness is a biochemical phenomenon in which the presence of one hormone is required in order for another hormone to exert its full effects on a target cell. Hormones can interact in permissive, synergistic, or antagonistic ways. The chemical classes of hormones include amines, polypeptides, glycoproteins and steroids. Permissive hormones act as precursors to active hormones and may be classified as either prohormones or prehormones. It stimulate the formation of receptors of that hormone. Examples Thyroid hormone increases the number of beta adrenergic receptors available for epinephrine at the latter's target cell, thereby increasing epinephrine's effect on that cell. Specially in cardiac cell. Without the thyroid hormone, epinephrine would have only a weak effect. Cortisol exerts a permissive effect on growth hormone. The effects of a hormone in the body depend on its concentration. Permissive actions of glucocorticoids like cortisol generally occur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salt (chemistry)
In chemistry, a salt is a chemical compound consisting of an ionic assembly of positively charged cations and negatively charged anions, which results in a compound with no net electric charge. A common example is Salt, table salt, with positively charged sodium ions and negatively charged chloride ions. The component ions in a salt compound can be either inorganic compound, inorganic, such as chloride (Cl−), or organic chemistry, organic, such as acetate (). Each ion can be either monatomic ion, monatomic, such as fluoride (F−), or polyatomic ion, polyatomic, such as sulfate (). Types of salt Salts can be classified in a variety of ways. Salts that produce hydroxide ions when dissolved in water are called ''alkali salts'' and salts that produce hydrogen ions when dissolved in water are called ''acid salts''. ''Neutral salts'' are those salts that are neither acidic nor basic. Zwitterions contain an anionic and a cationic centre in the same molecule, but are not considered s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sympathomimetic Amine
Sympathomimetic drugs (also known as adrenergic drugs and adrenergic amines) are stimulant compounds which mimic the effects of endogenous agonists of the sympathetic nervous system. Examples of sympathomimetic effects include increases in heart rate, force of cardiac contraction, and blood pressure. The primary endogenous agonists of the sympathetic nervous system are the catecholamines (i.e., epinephrine drenaline norepinephrine oradrenaline and dopamine), which function as both neurotransmitters and hormones. Sympathomimetic drugs are used to treat cardiac arrest and low blood pressure, or even delay premature labor, among other things. These drugs can act through several mechanisms, such as directly activating postsynaptic receptors, blocking breakdown and reuptake of certain neurotransmitters, or stimulating production and release of catecholamines. Mechanisms of action The mechanisms of sympathomimetic drugs can be direct-acting (direct interaction between drug and rec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boxed Warning
In the United States, a boxed warning (sometimes "black box warning", colloquially) is a type of warning that appears on the package insert for certain prescription drugs, so called because the U.S. Food and Drug Administration specifies that it is formatted with a 'box' or border around the text. The FDA can require a pharmaceutical company to place a boxed warning on the labeling of a prescription drug, or in literature describing it. It is the strongest warning that the FDA requires, and signifies that medical studies indicate that the drug carries a significant risk of serious or even life-threatening adverse effects. Economists and physicians have thoroughly studied the effects of FDA boxed warnings on prescription patterns. It is not necessarily true that a physician and patient will have a conversation about a drug's boxed warning after it is issued. For instance, an FDA-mandated boxed warning decreased rosiglitazone use by 70%, but that still meant 3.8 million people ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyrotoxicosis
Hyperthyroidism is the condition that occurs due to excessive production of thyroid hormones by the thyroid gland. Thyrotoxicosis is the condition that occurs due to excessive thyroid hormone of any cause and therefore includes hyperthyroidism. Some, however, use the terms interchangeably. Signs and symptoms vary between people and may include irritability, muscle weakness, sleeping problems, a fast heartbeat, heat intolerance, diarrhea, enlargement of the thyroid, hand tremor, and weight loss. Symptoms are typically less severe in the elderly and during pregnancy. An uncommon complication is thyroid storm in which an event such as an infection results in worsening symptoms such as confusion and a high temperature and often results in death. The opposite is hypothyroidism, when the thyroid gland does not make enough thyroid hormone. Graves' disease is the cause of about 50% to 80% of the cases of hyperthyroidism in the United States. Other causes include multinodular goite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
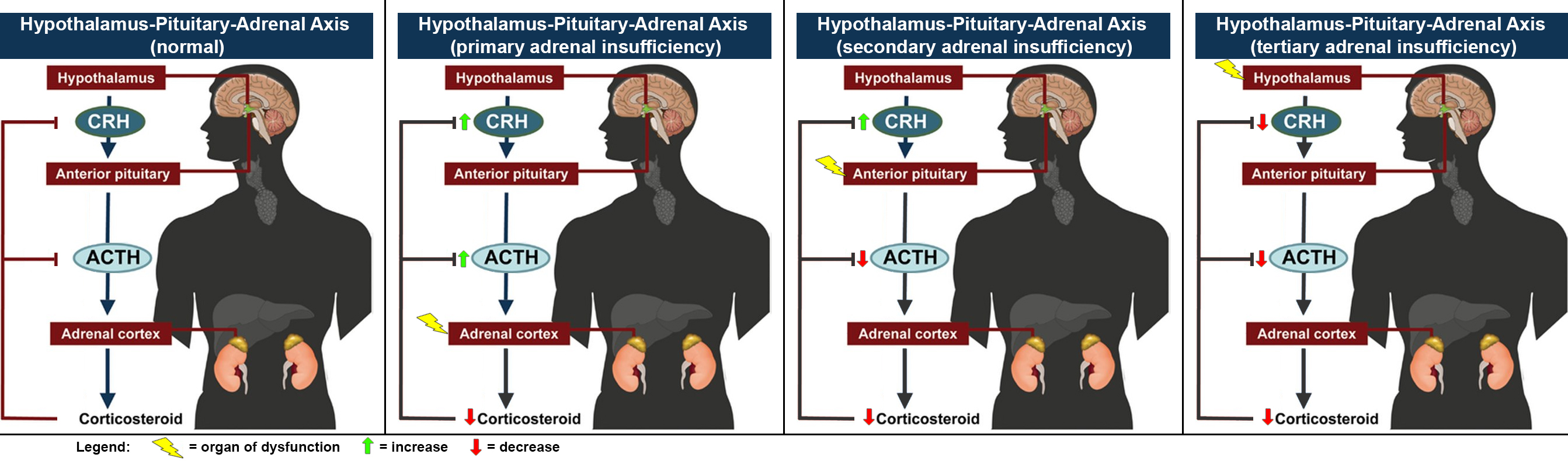
Adrenal Insufficiency
Adrenal insufficiency is a condition in which the adrenal glands do not produce adequate amounts of steroid hormones. The adrenal gland normally secretes glucocorticoids (primarily cortisol), mineralocorticoids (primarily aldosterone), and androgens. These hormones are important in regulating blood pressure, electrolytes, and metabolism as a whole. Deficiency of these hormones leads to symptoms ranging from abdominal pain, vomiting, muscle weakness and fatigue, low blood pressure, depression, mood and personality changes (in mild cases) to organ failure and shock (in severe cases). An adrenal crisis may occur if the body is subjected to stress, such as an accident, injury, surgery, or severe infection; this is a life-threatening medical condition resulting from severe deficiency of cortisol in the body. Death may quickly follow. Adrenal insufficiency can be caused by dysfunction of the adrenal gland itself, whether by destruction (e.g. Addison's disease), failure of development ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |